What is Social Innovation?
Social innovation is defined as a dynamic process of strategically developing and implementing inventive ideas, strategies, or interventions aimed at proactively addressing prevalent social issues and instigating positive, transformative change. At IdeaScale, our commitment to pioneering innovation sets us apart in this evolving landscape.
We actively engage in the creation and application of innovative methods, models, and approaches, targeting complex societal challenges including poverty, inequality, environmental sustainability, healthcare access, education, and more. Collaborating with a diverse array of stakeholders, including individuals, organizations, communities, and governments, we drive collaborative solutions that redefine the boundaries of social progress.
Social innovation manifests in various forms — from cutting-edge technologies to innovative business models, policies, programs, and services — all designed to make a tangible impact on individual lives and community well-being. What distinguishes us is our relentless pursuit of idea and innovation management software, ensuring our initiatives go beyond short-term fixes and catalyze enduring systemic change.
Our commitment extends beyond innovation alone; it’s rooted in recognizing the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental factors. We champion integrated and holistic approaches to complex societal challenges, concentrating on enhancing social outcomes, fostering inclusion, and advancing sustainable innovation.
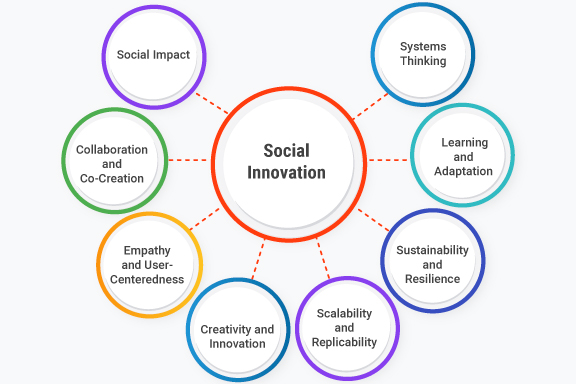
Characteristics of Social Innovation
Social innovation exhibits several key characteristics that distinguish it from other forms of innovation. Here are some prominent characteristics of social innovation:
- Social Impact: Social innovation aims to generate positive social impact and address pressing social challenges. It focuses on improving the well-being and quality of life for individuals and communities, particularly those who are marginalized or underserved.
- Collaboration and Co-Creation: Social innovation often involves collaboration and co-creation among diverse stakeholders, including individuals, organizations, communities, governments, and academia. Co-creation involves actively involving beneficiaries, end-users, and other stakeholders in the innovation process, ensuring their voices are heard and their needs are addressed. It recognizes the value of collective wisdom, expertise, and resources in finding innovative solutions.
- Systems Thinking: Social innovation takes a systemic approach to problem-solving, considering the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental factors. It aims to identify and address the root causes of social issues, rather than merely treating their symptoms.
- Innovative Strategies: Social innovation encourages unconventional thinking and the exploration of new ways to address problems. It may involve repurposing existing resources, leveraging technology innovation, redesigning processes, or adapting successful solutions from one context to another.
- Empathy and User-Centeredness: Social innovation places a strong emphasis on understanding the needs, aspirations, and perspectives of the people affected by social problems. It involves a deep sense of empathy and incorporates user-centered design principles to develop solutions that are relevant, inclusive, and meaningful to the intended beneficiaries.
- Creativity and Innovation: Social innovation encourages creative and innovative thinking to challenge conventional wisdom and develop novel approaches to social issues. It explores ideation, methods, technologies, business models, or policy frameworks that have the potential to disrupt existing systems and create positive change.
- Scalability and Replicability: Social innovation seeks solutions that can be scaled up or replicated to reach a broader population or address similar challenges in different contexts. It aims to create sustainable models that can be adopted and adapted by others to maximize impact.
- Measurable Outcomes: Effective social innovations have measurable outcomes and impact metrics. These metrics help assess the success of the innovation in achieving its intended goals.
- Empowerment and Inclusion: Social innovation aims to empower marginalized and vulnerable populations, ensuring their active participation in the innovation process and the benefits of its outcomes.
These characteristics collectively define the essence of social innovation, guiding its approach and mindset toward creating meaningful and lasting social change.
Learn more: What is Strategic Innovation?
Examples of Social Innovation
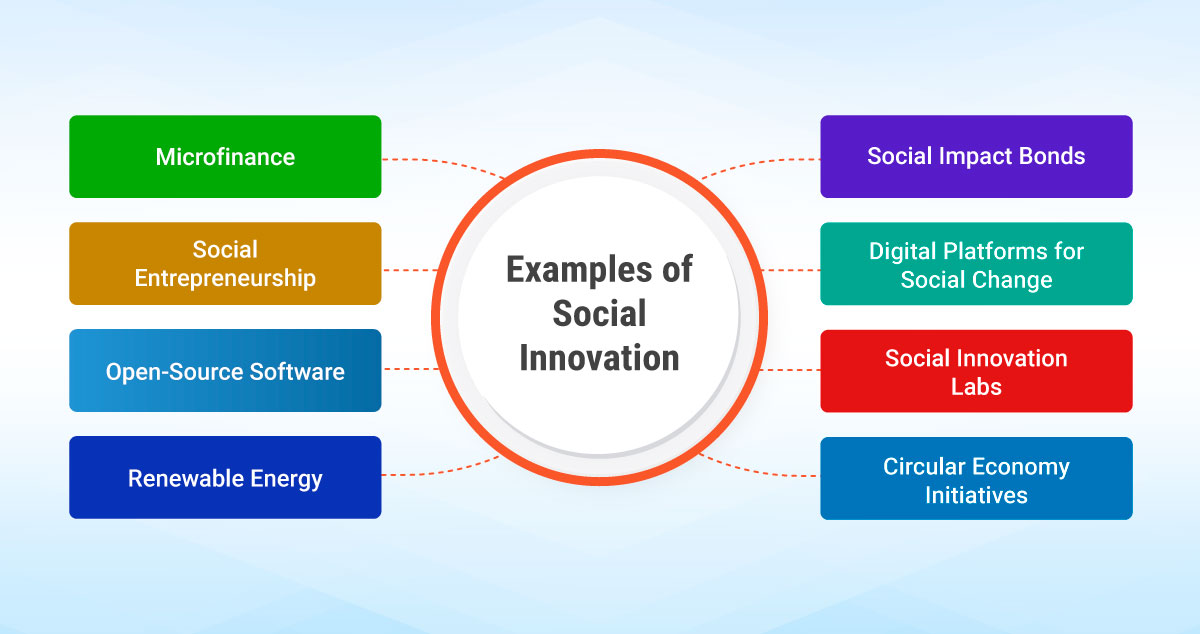
There are numerous examples of social innovation across various domains and sectors. Here are a few notable examples:
- Microfinance
Microfinance institutions, such as Grameen Bank, have pioneered a financial business model innovation to provide small loans and financial services to individuals who are traditionally excluded from the formal banking system. This approach has helped empower low-income entrepreneurs and promote economic development in many communities.
- Renewable Energy
Initiatives promoting renewable energy, such as solar and wind power projects, are significant examples of social innovation. These solutions address environmental concerns and provide sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, offering clean energy options and reducing carbon emissions.
- Social Entrepreneurship
Organizations like TOMS Shoes and Warby Parker have adopted a “buy-one-give-one” model, where for every product sold, they donate a similar product to individuals in need. This incremental innovation approach combines profitability with social impact, addressing issues such as access to shoes and eyewear for disadvantaged populations.
- Social Innovation Labs
Social innovation labs, such as the MaRS Solutions Lab and Nesta’s Innovation Lab, provide spaces for experimentation, collaboration, and co-creation to address complex social challenges. These labs bring together diverse stakeholders, including policymakers, researchers, entrepreneurs, and citizens, to develop and test innovative solutions through a participatory and iterative process.
- Open-Source Software
The open-source software movement, exemplified by projects like Linux and Wikipedia, has revolutionized knowledge sharing and collaboration. It allows people to freely access, use, and contribute to software and information resources, fostering global cooperation and democratizing access to knowledge and technology innovation.
- Circular Economy Initiatives
Circular economy models, such as recycling and upcycling programs, aim to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. These initiatives promote sustainable production and consumption patterns by reimagining the entire lifecycle of products, reducing environmental impact, and creating economic opportunities.
- Digital Platforms for Social Change
Digital platforms and technologies, such as crowdfunding platforms (e.g., Kickstarter, GoFundMe) and online advocacy platforms (e.g., Change.org), have enabled individuals and organizations to mobilize resources and raise awareness for social causes. By embracing digital innovation, these platforms facilitate grassroots participation and empower individuals to drive social change.
- Social Impact Bonds
Social impact bonds, also known as pay-for-success contracts, are innovative financing mechanisms that bring together private investors, nonprofits, and governments to address social issues. Investors provide upfront capital to fund social programs, and the government repays them with a financial return only if predetermined social outcomes are achieved.
These examples illustrate the diverse range of social innovation initiatives that have emerged worldwide, demonstrating the transformative power of innovative ideas, approaches, and collaborations in addressing social issues and creating positive social change.
Learn more: What is Open Innovation?
Top 10 Best Practices of Social Innovation
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to social innovation, certain best practices have emerged that can enhance the effectiveness and impact of social innovation initiatives. Here are some key best practices:
1. Deeply Understand the Problem
Take the time to thoroughly understand the social issue you are addressing. Engage with the affected communities, conduct market research, and listen to the perspectives of stakeholders. A deep understanding of the problem will help you identify its root causes, uncover insights, and develop targeted solutions.
2. Embrace Co-Creation and Collaboration
Foster collaboration among diverse stakeholders, including individuals, organizations, communities, and government entities. Encourage co-creation processes that involve beneficiaries and end-users in designing and implementing solutions. Collaboration can bring together a range of expertise, resources, and perspectives, leading to more holistic and sustainable outcomes.
3. Empower and Include Beneficiaries
Ensure that the voices and needs of the beneficiaries are central to the innovation process. Involve them in decision-making, co-design, and evaluation stages. Empower individuals and communities by building their capacity to actively participate in shaping and implementing solutions that directly affect them.
4. Adopt a Systems Thinking Approach
Consider the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental factors when addressing complex social challenges. Take a holistic view of the problem and analyze the broader system in which it exists. This approach helps identify leverage points for intervention and avoids unintended consequences.
5. Build Partnerships and Networks
Forge strategic partnerships with organizations, institutions, and individuals who share your goals. Collaborate with complementary entities to leverage their expertise, resources, and networks. Engage with academia, government agencies, NGOs, and private sector entities to tap into their knowledge and networks.
6. Iterate and Learn from Failure
Embrace a culture of innovation, experimentation, iteration, and learning. Be open to failure and view it as an opportunity for growth and improvement. Regularly evaluate and measure the impact of your initiatives, collecting feedback and adjusting your approach based on lessons learned.
7. Seek Sustainable Funding Models
Explore innovative financing mechanisms to support your social innovation initiatives. This could include partnerships with impact investors, government grants, social impact bonds, or revenue-generating models. Diversify your funding sources to ensure the long-term sustainability and scalability of your efforts.
8. Advocate for Policy Change
Social innovation can be further amplified by advocating for supportive policy environments. Engage with policymakers, civil society organizations, and communities to advocate for policy changes that enable and promote social innovation. Share evidence and insights from successful initiatives to inform policy discussions.
9. Foster a Culture of Innovation
Nurture a culture of innovation within your organization or community. Promote an environment that fosters creativity, encourages taking calculated risks, and embraces the exploration of novel concepts. Embrace diversity of thought and encourage individuals to challenge the status quo. Create spaces and processes that facilitate ideation and experimentation.
10. Share Knowledge and Scale Impact
Document and share knowledge gained from your social innovation efforts. Publish findings, best practices, and lessons learned to contribute to the broader social innovation field. Collaborate with other practitioners and stakeholders to scale up successful models and replicate impactful solutions in different contexts.
By embracing these best practices, social innovators can maximize their potential to create positive and sustainable social change.
Learn more: What is Computing Innovation?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.