Table of Contents
What is Innovation?
Innovation is defined as the process of bringing about new ideas, methods, products, services, or solutions that have a significant positive impact and value. It involves transforming creative concepts into tangible outcomes that improve efficiency, and effectiveness, or address unmet needs.
Innovation is not limited to technological advancements and encompasses novel approaches to problem-solving, processes, organizational practices, or business model innovations. At its core, innovation involves challenging the status quo, thinking outside the box, and taking calculated risks to drive progress and achieve breakthrough outcomes.
Innovation is driven by a combination of factors, including curiosity, creativity, and the desire for improvement. It requires a mindset that embraces change, welcomes ideation, and encourages experimentation. Innovation can occur in various contexts, such as business, science, technology, social sectors, or public services. It can lead to economic growth, social progress, improved quality of life, and sustainable development.
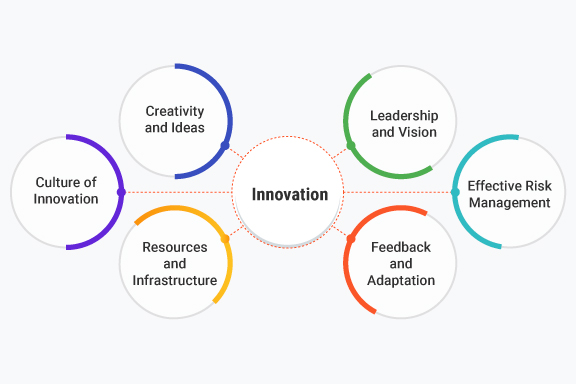
Key components that make innovation possible in an organization:
Several key components contribute to making innovation possible in an organization. These components provide the foundation and enable organizations and individuals to drive innovation effectively. Here are the key essential components:
- Creativity and Ideas: Creativity is the fuel for innovation. It involves generating new and original ideas, challenging assumptions, and thinking beyond conventional boundaries. It is the ability to connect disparate concepts and envision novel possibilities. The generation of diverse ideas, both incremental and disruptive, serves as the starting point for innovation.
- Culture of Innovation: An organizational culture that fosters and supports innovation is crucial. It includes values, attitudes, and behaviors that encourage curiosity, risk-taking, collaboration, and experimentation. A culture of innovation promotes an open and inclusive environment where individuals feel empowered to contribute their ideas and embrace change.
- Resources and Infrastructure: Adequate resources, both financial and non-financial, are essential for innovation. This includes dedicated funding, skilled human capital, technology infrastructure, research and development capabilities, and access to relevant information and data. Organizations need to allocate resources strategically to support innovation initiatives.
- Leadership and Vision: Effective leadership plays a vital role in driving and supporting innovation. Leaders set the vision, create a sense of purpose, and provide guidance and resources for innovation initiatives. They foster an environment that encourages risk-taking, empowers employees, and leads by example. Leadership commitment and support are crucial in nurturing a culture of innovation and driving innovation efforts.
- Feedback and Adaptation: Innovation requires a feedback loop that allows for continuous innovation. Feedback can come from customers, users, stakeholders, and market trends. Organizations need mechanisms to gather and analyze feedback, learn from successes and failures, and iterate on their innovation initiatives. The ability to adapt and pivot based on feedback is essential to refine and enhance innovative solutions.
- Effective Risk Management: Innovation involves inherent risks and uncertainties, which makes effective risk management crucial to mitigate potential challenges and ensure successful outcomes. Organizations need processes to identify, assess, and manage risks associated with innovation initiatives. This includes evaluating the feasibility, viability, and potential impact of innovative ideas and implementing risk mitigation strategies.
Learn more: What is Business Innovation?
Types of Innovation: The Engines Behind Modern Business Success
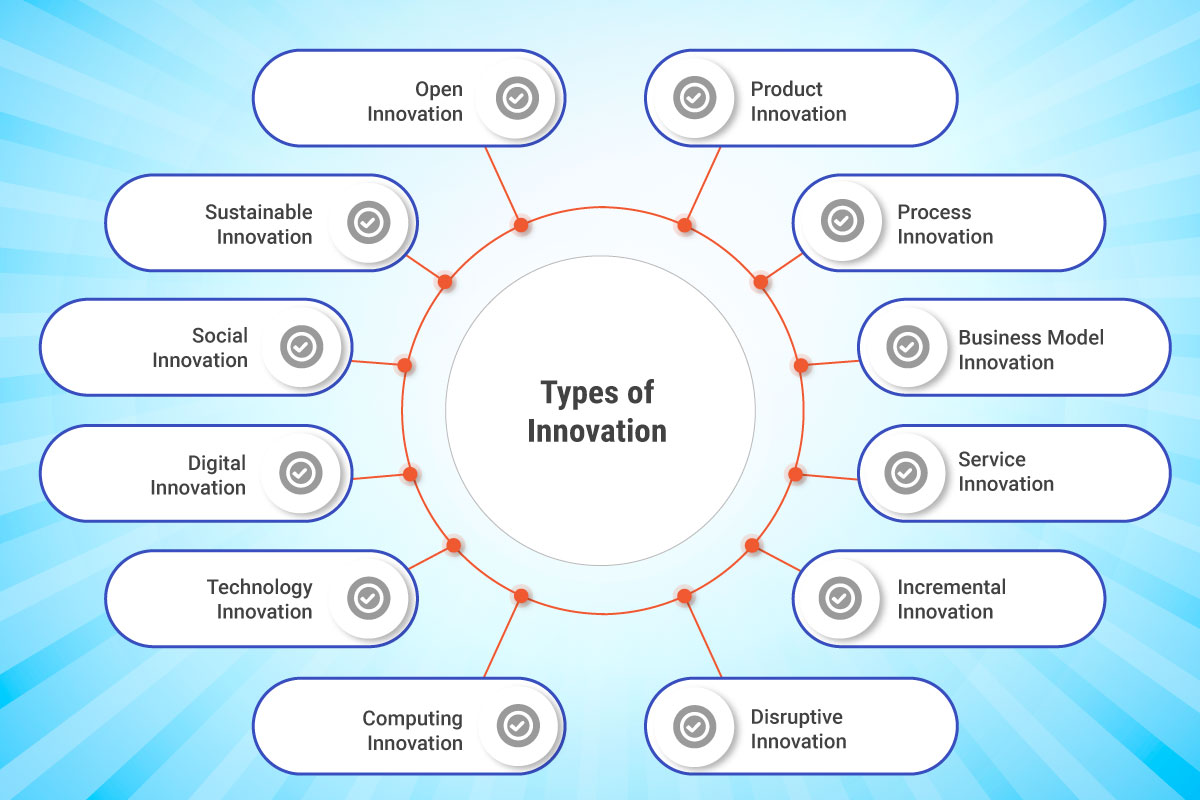
Innovation manifests in diverse forms, each serving unique purposes and delivering distinct benefits. Explore the key types of innovation crucial for modern businesses:
- Product Innovation: Product innovation involves developing novel products or enhancing existing ones to meet evolving market demands and customer expectations. It encompasses advancements in functionality, design, performance, and user experience.
- Process Innovation: Process innovation revolves around optimizing internal workflows, systems, and technologies to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and reduce costs. It enhances organizational agility and competitiveness.
- Business Model Innovation: Business model innovation redefines how businesses create, deliver, and capture value. It explores new revenue streams, cost structures, partnerships, and customer engagement strategies to drive market disruption and differentiation.
- Service Innovation: Service innovation focuses on transforming customer experiences through new service delivery methods, customization options, and enhanced accessibility. It aims to exceed customer expectations and strengthen brand loyalty.
- Incremental Innovation: Incremental innovation entails continuous enhancements and refinements to existing products, services, or processes. It fosters gradual improvements in efficiency, quality, and user satisfaction, ensuring sustained market relevance.
- Disruptive Innovation: Disruptive innovation introduces groundbreaking solutions that challenge existing market norms and create new value propositions. It starts in niche markets and progressively displaces incumbents by addressing unmet customer needs.
- Open Innovation: Open innovation involves collaborating with external stakeholders—such as customers, suppliers, and research institutions—to co-create innovative solutions. It leverages external expertise and resources to accelerate innovation cycles and foster industry leadership.
- Sustainable Innovation: Sustainable innovation focuses on developing environmentally friendly products, services, and business models that minimize ecological footprints and promote social responsibility. It addresses global challenges like climate change and resource conservation.
- Social Innovation: Social innovation tackles societal challenges through novel products, services, or approaches that enhance community well-being, promote inclusivity, and drive positive social change. It fosters sustainable development and ethical business practices.
- Digital Innovation: Digital innovation harnesses digital technologies—such as AI, IoT, and blockchain—to revolutionize products, services, and operational processes. It optimizes efficiency, enhances data-driven decision-making, and drives digital transformation.
- Technology Innovation: Technology innovation drives advancements in scientific and technological fields—ranging from biotechnology to renewable energy—to address complex global issues and improve quality of life.
- Computing Innovation: Computing innovation pioneers breakthroughs in computing technologies and IT systems—enabling new capabilities, enhancing cybersecurity, and driving digital evolution across industries.
Furthermore, any of the above types of innovation can be approached through continuous innovation or discontinuous innovation:
- Continuous Innovation: Continuous innovation is the iterative improvements that refine existing offerings and sustain competitive advantage through ongoing adaptation.
- Discontinuous Innovation: Discontinuous innovation is radical transformations that disrupt markets, redefine industry standards, and create new growth opportunities through visionary leaps.
Each type of innovation offers distinct advantages and strategic opportunities for organizations aiming to innovate effectively in today’s dynamic market landscape. Implementing a tailored innovation strategy that integrates these types can propel your business towards sustained growth and market leadership.
Innovation Examples: 10 Breakthroughs That Disrupted Entire Industries
Innovation drives progress, solving old problems in new ways. Across every sector—technology, healthcare, energy, and beyond—innovative thinking has redefined how we live, work, and connect. Below are 10 of the best innovation examples that disrupted their industries, showcasing the power of forward-thinking solutions.
1. Airbnb – Reinventing Hospitality
Airbnb transformed travel with its peer-to-peer model, allowing homeowners to rent out rooms or entire properties. By bypassing traditional hotel systems, it created a scalable, trust-based sharing economy—one that reshaped how we book stays and explore new places.
2. Tesla’s Electric Vehicles – Driving Sustainable Mobility
Tesla didn’t invent electric vehicles, but it made them desirable and scalable. Through cutting-edge battery tech, autonomous features, and sleek design, Tesla has accelerated EV adoption globally—making clean transportation a practical reality.
3. SpaceX Reusable Rockets – Lowering the Cost of Space
SpaceX’s reusable launch technology broke the decades-old mold of single-use rockets. By landing and reusing boosters, they dramatically cut the cost of space missions and opened doors for commercial space travel.
4. 3D Printing – On-Demand, Custom Manufacturing
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and small-batch production. It’s revolutionized sectors like healthcare (prosthetics), aerospace (lightweight parts), and consumer goods by eliminating traditional supply chain constraints.
5. CRISPR Gene Editing – Precision Healthcare Innovation
CRISPR-Cas9 allows scientists to edit genes with unprecedented accuracy. From treating genetic diseases to engineering crops, this biotechnology is reshaping medicine and agriculture with precision previously unimaginable.
6. Netflix Streaming – Disrupting Traditional Media
Netflix disrupted cable and video rentals by introducing on-demand streaming. What started as DVD delivery became a global content platform that personalized entertainment and set the gold standard for digital media consumption.
7. Mobile Payment Platforms – Cashless Convenience
Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal revolutionized transactions by making them fast, secure, and mobile. These fintech innovations enabled digital wallets, transforming the way we shop, bank, and send money.
8. Amazon Alexa – Voice as the New User Interface
Alexa brought voice-controlled AI to the masses. By combining smart speakers with natural language processing, Amazon changed how we interact with devices—from controlling smart homes to shopping with our voice.
9. Urban Micromobility – Smart, Sustainable Transport
Startups like Lime and Bird popularized e-scooters and bike-sharing, offering a greener solution for last-mile travel. These urban mobility innovations reduce congestion and carbon emissions in growing cities.
10. Solar Energy Advancements – Powering a Clean Future
Modern solar technologies, including high-efficiency panels and affordable storage, have made renewable energy more accessible. From rooftops to solar farms, solar power is accelerating the global shift to sustainability.
What These Innovation Examples Teach Us
Each example above reveals a clear pattern: successful innovation solves a real pain point, leverages new technology, and scales effectively. Whether it’s democratizing access (Airbnb), lowering costs (SpaceX), or increasing convenience (mobile payments), the best innovations challenge the status quo and create lasting change.
Learn more: What is Innovation Management?
Innovation Process: 7 Key Steps to Turn Ideas into Impact
The innovation process typically involves a series of key steps that organizations follow to foster and implement innovation. While specific approaches may vary, here are the common steps involved in the innovation process:
Step 1. Identify Opportunities
The first step is to identify opportunities for innovation. This can be done through market research, customer insights, trend analysis, or internal assessments. The goal is to uncover unmet needs, emerging trends, or areas for improvement that can be addressed through innovation.
Step 2. Generate Ideas
Once opportunities are identified, the next step is to generate ideas. This can be done through brainstorming sessions, idea competitions, customer feedback, or cross-functional collaboration. The aim is to generate a wide range of creative and innovative ideas that have the potential to address the identified opportunities.
Step 3. Evaluate and Select Ideas
After ideation, the next step is to evaluate and select the most promising ones. This involves assessing the feasibility, viability, and desirability of each idea. Consider factors such as market potential, technical feasibility, resource requirements, alignment with strategic goals, and potential impact. The goal is to identify the ideas that are worth pursuing further.
Step 4. Develop and Prototype
Once ideas are selected, they can be further developed and prototyped. This involves translating the selected ideas into tangible prototypes, mock-ups, or minimum viable products (MVPs). The aim is to test and validate the concepts, gather feedback, and refine the ideas based on customer insights and technical feasibility.
Step 5. Test and Iterate
In this step, the prototypes or MVPs are tested with users or in real-world scenarios. Customer feedback is collected, and the concepts are iterated and refined based on the insights gained. This iterative process helps to validate assumptions, uncover potential issues, and improve the innovation before moving to the next stage.
Step 6. Implement and Scale
Once the innovation has been tested and refined, it can be implemented and scaled up. This involves developing a detailed implementation plan, allocating resources, and executing the necessary actions to bring the innovation to market or implement it within the organization. The goal is to ensure a smooth transition from the development phase to full-scale implementation.
Step 7. Monitor and Evaluate
After implementation, it is important to monitor and evaluate the performance and impact of the innovation. This involves tracking key metrics and performance indicators to assess the success of the innovation. Regular evaluation helps identify areas for improvement, make necessary adjustments, and capture learnings for future innovation initiatives.
Innovation is an ongoing process, and organizations should foster a culture of innovation. This involves capturing feedback, promoting learning from both successes and failures and continuously seeking new opportunities for innovation. Regularly revisiting and refining the innovation process itself is also essential to optimize the organization’s ability to innovate effectively.
Learn more: What is Innovation Strategy?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.