Table of Contents
What is Innovation Strategy?
Innovation strategy is defined as the cornerstone of forward-looking organizations, guiding them in harnessing creativity to navigate the evolving landscape of their industry. Crafted with precision, it serves as a dynamic roadmap, orchestrating the fusion of resources, capabilities, and external collaborations to birth groundbreaking ideas. This strategic compass is not merely a plan; it’s a catalyst for continuous evolution and competitive advantage.
At its core, an effective innovation strategy involves meticulous evaluation and selection of projects, striking a delicate balance between short-term gains and long-term vision. It allocates resources strategically, nurturing a portfolio of innovations ranging from incremental enhancements to disruptive breakthroughs. This portfolio approach ensures resilience and adaptability, propelling the organization ahead of competitors and fostering sustained growth.
By seamlessly integrating innovation into the fabric of operations, organizations unlock a perpetual wellspring of ingenuity, propelling them to the forefront of their industry. The strategic deployment of creativity fuels the development of products and services that resonate deeply with customers, setting new benchmarks and reshaping markets.
In summary, an innovation strategy isn’t just a roadmap—it’s a transformative force that propels organizations towards excellence, shaping the future of industries and redefining success.
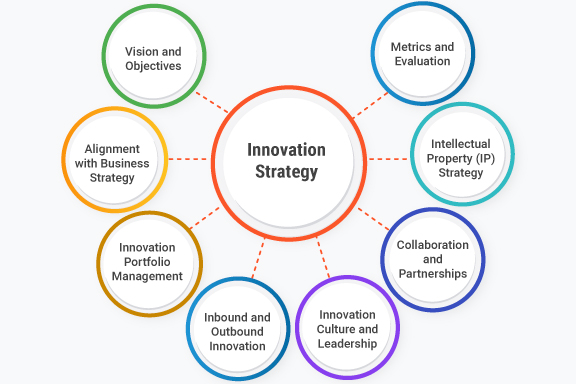
An effective innovation strategy typically includes the following key components:
- Vision and Objectives: The strategy starts with a clear vision that defines the desired future state of innovation within the organization. It establishes the objectives and goals for innovation, such as developing breakthrough products, entering new markets, improving operational efficiency, or enhancing customer experiences.
- Alignment with Business Strategy: The innovation strategy should be closely aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy. It should complement and support the broader strategic goals and priorities of the organization. The innovation strategy ensures that innovation efforts are directed towards areas that create strategic advantage and contribute to the organization’s long-term success.
- Innovation Portfolio Management: An innovation strategy involves managing a portfolio of innovation initiatives. It defines the criteria for selecting and prioritizing projects, balancing short-term and long-term goals, and allocating resources across different types of innovation (e.g., incremental, disruptive, sustaining). The strategy provides a framework for evaluating and managing the entire portfolio to maximize the organization’s innovation impact.
- Resource Allocation: An important component of an innovation strategy is resource allocation. It determines the allocation of financial, human, and technological resources to support innovation initiatives. The strategy ensures that sufficient resources are dedicated to innovation, including funding for research and development, technology infrastructure, talent acquisition, and training.
- Innovation Culture and Leadership: Building an innovation culture is crucial for successful innovation. The strategy outlines the values, behaviors, and practices necessary to foster a culture of innovation within the organization. It promotes a mindset of experimentation, risk-taking, and continuous learning. Leadership plays a critical role in driving and supporting the innovation agenda, modeling the desired behaviors, and creating an environment that encourages and rewards innovation.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration and partnerships can accelerate innovation by leveraging external expertise, resources, and networks. The innovation strategy includes approaches for collaboration with startups, research institutions, customers, and other stakeholders. It defines mechanisms for open innovation, joint ventures, strategic alliances, or acquisition of innovative companies.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Strategy: Protecting intellectual property is an important consideration in an innovation strategy. It establishes the organization’s approach to identifying, protecting, and managing intellectual property assets resulting from innovation activities. The strategy addresses the appropriate mechanisms for patenting, copyrighting, trademarking, or maintaining trade secrets to secure the organization’s competitive advantage.
- Metrics and Evaluation: The innovation strategy defines key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure and track the progress and impact of innovation initiatives. It establishes a system for evaluating the effectiveness of innovation efforts, monitoring the success of projects, and making data-driven decisions. Regular evaluation and feedback loops enable continuous improvement of the innovation strategy and its execution.
Importance of Organization-wide Innovation Strategy
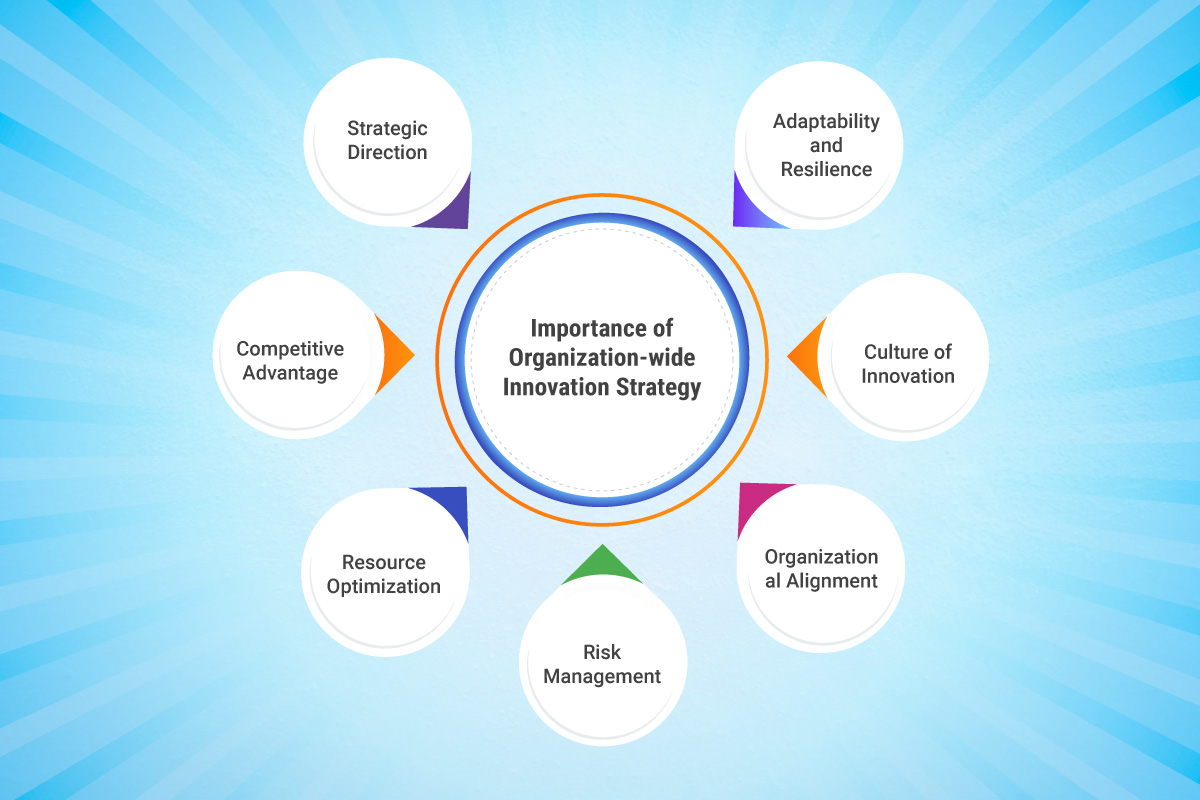
Having an organizational innovation strategy is important for several reasons:
1. Strategic Direction: An innovation strategy provides a clear strategic direction for innovation efforts within an organization. It ensures that innovation activities are aligned with the overall goals and objectives of the organization. By defining the desired outcomes and areas of focus, the strategy helps prioritize innovation initiatives and guides resource allocation toward the most impactful opportunities.
2. Competitive Advantage: Innovation strategy enables organizations to gain a competitive advantage in the market. It helps identify and seize opportunities for differentiation, whether through breakthrough products, unique customer experiences, process efficiencies, or disruptive business models. By proactively driving innovation, organizations can stay ahead of competitors, attract customers, and capture market share.
3. Resource Optimization: An innovation strategy helps optimize the allocation of resources, including financial, human, and technological resources. It ensures that resources are directed towards initiatives that have the greatest potential for success and impact. By aligning resource allocation with strategic innovation objectives, organizations can avoid waste and make the most efficient use of available resources.
4. Risk Management: Innovation involves uncertainty and risk. An innovation strategy provides a framework for managing risks associated with innovation initiatives. It enables organizations to assess and mitigate potential risks, both internal and external, that could impact the success of innovation projects. By taking a strategic approach to risk management, organizations can make informed decisions, minimize potential pitfalls, and increase the likelihood of successful innovation outcomes.
5. Organizational Alignment: An innovation strategy fosters alignment and coordination across different departments and stakeholders within the organization. It ensures that everyone is working towards common innovation goals and objectives. By aligning efforts, breaking down silos, and promoting cross-functional collaboration, organizations can leverage diverse perspectives, expertise, and resources to drive innovation more effectively.
6. Culture of Innovation: An innovation strategy helps nurture a culture of innovation within the organization. It sends a strong message that innovation is valued, encouraged, and supported at all levels. By promoting a culture of innovation, creativity, risk-taking, and continuous learning, organizations can unleash the full potential of their employees and foster an environment conducive to generating and implementing innovative ideas.
7. Adaptability and Resilience: In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, organizations need to be adaptable and resilient. An innovation strategy helps build these capabilities by encouraging agility, flexibility, and the ability to respond to evolving market conditions and customer needs. It promotes a mindset of continuous improvement and the willingness to embrace change, enabling organizations to navigate disruptions and stay relevant in the long term.
Learn more: What is Innovation Framework?
Examples of Innovation Strategy
Innovation strategy examples abound among industry giants, each showcasing unique approaches to driving forward-thinking solutions and redefining their respective markets. Let’s delve into some standout strategies:
1. Microsoft’s Innovation Strategy: Microsoft’s recent pivot towards radical innovation, particularly in healthcare, underscores its commitment to R&D as a catalyst for market advancement.
2. Google’s Innovation Strategy: Google’s multifaceted innovation initiatives, spanning disruptive, radical, and architectural innovation, exemplify its dedication to pushing boundaries and exploring new frontiers.
3. Apple’s Innovation Strategy: Apple’s mastery of seamless integration between hardware, software, and services epitomizes innovation excellence, setting benchmarks for user experience and design in the technology realm.
4. Samsung’s Innovation Strategy: Samsung’s journey from incremental to diversified innovation, encompassing AI, IoT, and more, highlights its proactive approach to staying ahead in a rapidly evolving landscape.
5. Amazon’s Innovation Strategy: Amazon’s relentless pursuit of customer obsession permeates every facet of its operations, driving innovation in areas such as e-commerce, supply chain, and digital services.
6. Tesla’s Innovation Strategy: Tesla’s groundbreaking innovations in electric vehicles, renewable energy, and autonomous driving epitomize value innovation, reshaping the automotive industry and paving the way for sustainable transportation solutions.
These examples showcase how innovation strategies are tailored to the unique strengths and objectives of each organization, ultimately propelling them toward sustained growth and market leadership.
Here are a few examples of innovation strategies that organizations have implemented:
- Disruptive Innovation Strategy
Some organizations adopt a disruptive innovation strategy, aiming to create new markets and challenge existing industry norms. For example, Tesla’s innovation strategy focuses on developing electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions to disrupt the automotive and energy sectors. This strategy involves investing in advanced battery technology, building a network of charging stations, and creating business model innovation to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles.
- Open Innovation Strategy
Open innovation strategies involve collaborating with external partners, such as startups, research institutions, and customers, to co-create and leverage innovative solutions. For instance, Procter & Gamble (P&G) implemented an open innovation strategy by establishing its Connect+Develop program. P&G sought external partnerships to source new ideas and technologies, resulting in successful collaborations for product development and market expansion.
- Incremental Innovation Strategy
Organizations can focus on continuous improvement and incremental innovation to enhance existing products, processes, or services. For example, Apple’s innovation strategy has been centered around incremental innovation, releasing regular updates and improvements to its product line. By consistently refining its products and incorporating user feedback, Apple maintains its competitive edge and customer loyalty.
- Blue Ocean Strategy
The blue ocean strategy aims to create new market spaces by offering innovative products or services that are distinct from existing competitors. Cirque du Soleil adopted a blue ocean strategy in the entertainment industry by combining elements of circus and theater to create a unique, high-quality, and artistic performance experience. This strategy allowed Cirque du Soleil to attract new audiences and differentiate itself from traditional circuses.
- Platform Innovation Strategy
Some organizations focus on building platforms that enable third-party developers and businesses to create and deliver value-added services. A notable example is the Android operating system developed by Google. By creating an open platform, Google facilitated innovation from a wide range of developers, leading to a vibrant app ecosystem and widespread adoption of Android devices.
- Customer-Centric Innovation Strategy
Organizations can adopt a customer-centric innovation strategy that emphasizes understanding and addressing customer needs. Amazon is known for its customer-centric approach, continuously improving its e-commerce platform and expanding its services based on customer feedback. This strategy includes innovations such as personalized recommendations, fast shipping options, and Amazon Prime membership benefits.
These examples demonstrate how organizations can implement various innovation strategies to drive growth, differentiate themselves from competitors, and create value for customers. Innovation strategies should be tailored to an organization’s unique context, goals, and market dynamics to effectively leverage innovation as a strategic driver.
Learn more: What is Product Innovation?
Innovation Strategy Framework: 4 Key Steps
An innovation strategy framework provides a structured approach for organizations to develop and implement their innovation strategy. While the framework may differ from company to company, here is the wireframe of the widely used four-step innovation strategy framework:
Step 1. Analysis and Assessment
The first step involves analyzing the internal and external factors that impact innovation. This includes assessing the organization’s current innovation capabilities, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and understanding market trends, customer needs, and competitive landscape. The goal is to gain insights into the organization’s innovation readiness and identify areas where innovation efforts can have the most significant impact.
Step 2. Setting Strategic Direction
Based on the analysis, the next step is to define the organization’s strategic direction for innovation. This involves setting clear objectives and goals aligned with the overall business strategy. The strategic direction should consider the desired outcomes, areas of focus (e.g., product innovation, process innovation), and the balance between incremental and disruptive innovation. It also includes establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and success.
Step 3. Action Planning and Execution
In this step, the organization develops an action plan to execute the innovation strategy. This includes identifying specific initiatives, projects, and activities to achieve the defined objectives. The plan should outline the required resources, timelines, responsibilities, and budget allocation for each initiative. It may also involve setting up innovation teams or dedicated innovation labs to drive and manage innovation efforts. Regular monitoring, feedback loops, and adjustments are crucial during the execution phase.
Step 4. Evaluation and Iteration
The final step involves evaluating the effectiveness of the innovation strategy and making necessary adjustments. It includes measuring the outcomes against the defined KPIs and conducting periodic reviews to assess the progress and impact of innovation initiatives. Feedback from customers, stakeholders, and employees is valuable for identifying areas of improvement. Based on the evaluation, the organization can refine the strategy, reallocate resources, and update the action plan for subsequent iterations.
It’s important to note that the innovation strategy framework can be customized and tailored to fit the specific needs and context of an organization. The framework provides a systematic approach to developing and implementing an innovation strategy, helping organizations effectively navigate the complexities of innovation and increase their chances of successful outcomes.
Learn more: What is Technology Innovation?
Top 10 Best Practices for Creating and Managing an Innovation Strategy
Creating and managing an innovation strategy requires a systematic approach and ongoing effort. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Set Clear Objectives
Define clear objectives for your innovation strategy that align with your organization’s overall goals. These objectives should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Clear objectives provide a clear direction and focus for your innovation efforts.
2. Conduct a Comprehensive Assessment
Conduct a thorough assessment of your organization’s internal capabilities, external market trends, customer needs, and competitive landscape. This assessment will help identify gaps, opportunities, and potential areas for innovation. Consider conducting surveys, market research, and competitive analysis to gather relevant data.
3. Foster an Innovation Culture
Create a culture of innovation where employees are encouraged to provide feedback, generate and share ideas, experiment with new approaches, and embrace a mindset of continuous learning. Provide training, resources, and incentives to foster creativity, collaboration, and risk-taking.
4. Establish Innovation Processes and Structures
Define clear processes and structures to support innovation within your organization. Establish cross-functional innovation teams or departments responsible for driving innovation initiatives. Implement a systematic ideation, evaluation, and implementation process. Foster open communication and collaboration between different teams and departments.
5. Collaborate Externally
Embrace external collaborations and partnerships to fuel innovation. Collaborate with startups, research institutions, customers, and industry experts to leverage their knowledge, resources, and expertise. Engage in open innovation practices, such as hackathons, joint ventures, or strategic alliances, to tap into external creativity and accelerate innovation.
6. Allocate Resources Wisely
Allocate appropriate resources, including financial, human, and technological, to support your innovation strategy. Ensure that resources are allocated based on strategic priorities and potential impact. Develop a clear budget and resource allocation plan that aligns with your innovation objectives
7. Encourage Experimentation and Risk-Taking
Foster a culture of experimentation and risk-taking. Encourage employees to test new ideas, prototypes, and approaches. Embrace a fail-fast mentality that views failures as learning opportunities. Provide a safe space for employees to take calculated risks and reward innovative efforts.
8. Measure and Track Progress
Establish metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure and track the progress of your innovation strategy. Regularly review and analyze these metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of your innovation initiatives. Use the insights gained to make informed decisions, adjust your strategy, and reallocate resources as needed.
9. Iterate and Learn
Embrace a continuous innovation mindset and regularly evaluate and reflect on your innovation strategy, processes, and outcomes. Seek feedback from customers, employees, and stakeholders to gather insights and identify areas for improvement. Iterate your strategy based on the lessons learned and emerging market trends.
10. Leadership Support and Communication
Obtain leadership support and commitment for your innovation strategy. Ensure that senior leaders communicate the importance of innovation, align goals and incentives with the strategy, and actively participate in driving innovation initiatives. Regularly communicate updates, progress, and successes to keep employees engaged and motivated.
Learn more: What is Business Innovation?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.