In today’s competitive landscape, businesses must rely on informed decision-making to thrive. One of the essential tools in this process is market research. But what exactly is market research, and why is it vital for success? In this article, we’ll delve into the definition of market research, its significance, and its various applications in the business world.
What is Market Research?
Market research is the systematic gathering, analysis, and interpretation of information about a market, including information about the target audience, competitors, and the overall industry landscape. The goal is to understand customer needs and market trends, enabling businesses to make informed decisions.
To define market research, it can be described as a critical component of marketing strategy that involves the collection and analysis of data to identify market opportunities, assess demand, and evaluate competition. This definition of market research underscores its role in guiding strategic planning.
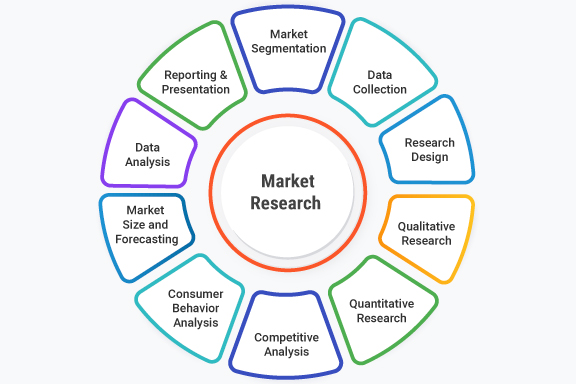
Key components of market research:
Market research typically involves several key components that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the market and its dynamics. These components include:
- Market Segmentation: Identifying and dividing the target market into distinct segments based on demographics, psychographics, behavior, or other relevant characteristics. This helps tailor marketing strategies to specific customer groups.
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from primary and secondary sources. Primary data refers to information collected directly from the target market through surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Secondary data involves leveraging existing research, reports, industry databases, or government sources.
- Research Design: Developing a research plan that outlines the objectives, methodology, and timeline for conducting the research. This includes selecting appropriate research methods, determining the sample size, and defining the sampling technique.
- Qualitative Research: Utilizing techniques like interviews, focus groups, or observations to gain in-depth insights into consumer attitudes, opinions, motivations, and behaviors. Qualitative research helps explore underlying reasons and provides a richer understanding of the market.
- Quantitative Research: Employing surveys, questionnaires, or structured data analysis to gather numerical data on a larger scale. Quantitative research enables statistical analysis, measurement of market trends, and generation of quantitative insights and metrics.
- Competitive Analysis: Assessing competitors’ strategies, strengths, weaknesses, market positioning, and offerings. This helps identify market opportunities, potential threats, and areas for differentiation.
- Consumer Behavior Analysis: Examining consumer decision-making processes, buying habits, preferences, and satisfaction levels. Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies and targeted campaigns.
- Market Size and Forecasting: Estimating the total market size, growth potential, and future trends. Market sizing helps assess the market’s attractiveness and potential demand for products or services.
- Data Analysis: Applying statistical techniques and tools to analyze collected data and derive meaningful insights. This includes data cleaning, segmentation analysis, correlation analysis, regression analysis, and other statistical methods.
- Reporting and Presentation: Summarizing research findings, insights, and recommendations in a clear and concise manner. Effective communication of research results ensures that stakeholders can make informed decisions based on the findings.
These components work together to provide a holistic view of the market, consumer behavior, and competitive landscape, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and develop effective marketing strategies.
Types of Market Research
Market research is a diverse field, and there are two primary categories that businesses typically engage with:
1. Primary Market Research: Primary research involves collecting new data directly from the source. This can be done through surveys, interviews, focus groups, or observations. The benefit of primary research is that it provides specific and relevant insights tailored to your business needs. However, it can be more time-consuming and costly compared to other methods.
2. Secondary Market Research: Secondary research uses existing data that has already been collected, such as reports, industry studies, government publications, and competitive analysis. This type of research is often faster and less expensive, but it may not be as specific to your unique questions or challenges.
Each type of market research offers distinct advantages and can be used depending on your company’s goals, timelines, and budget.
Learn more: What is Customer Experience (CX) Research?
Market Research Process
Step 1. Define Research Objectives
The first step in market research is to clearly define the research objectives. This involves identifying the specific information needed, the target audience, and the desired outcomes of the research.
Step 2. Design Research Plan
Once the objectives are defined, the next step is to design a research plan that outlines the methodology, data collection techniques, sample size, and timeline. The research plan should be tailored to address the research objectives and provide reliable and valid data.
Step 3 Data Collection
In this stage, data is collected using primary or secondary research methods. Primary research involves gathering data directly from respondents through surveys, interviews, focus groups, or observations. Secondary research involves gathering existing data from published sources, industry reports, or databases.
Step 4. Market research Analysis
Once the data is collected, it needs to be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and insights. This can involve quantitative research and analysis, such as statistical techniques, or qualitative research and analysis, such as thematic coding or content analysis. The goal is to derive meaningful insights from the data that can inform decision-making.
Step 5. Final Market Research Insights
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the findings and extract actionable insights. This involves drawing conclusions, identifying key trends, and relating them to the research objectives. The insights should provide valuable information that guides marketing strategies, product development, or business decisions.
Step 6. Reporting Research Findings
The final step is to present the research findings in a clear and concise manner. A market research report is typically prepared, which includes an executive summary, methodology, findings, insights, and recommendations. The report should effectively communicate the research results to stakeholders and provide actionable recommendations based on the insights.
Examples of Market Research
Here are some examples of market research. These examples illustrate the diverse applications of market research across various industries and scenarios:
Example 1: Customer Surveys for Product Improvement
One of the simplest yet effective market research examples is conducting customer surveys. This technique helps businesses gather direct feedback from their existing customers about the products they use. For instance, companies like Nike often use post-purchase surveys to understand what customers liked or disliked about a product. This feedback loop is crucial for tweaking products or launching new ones.
Example 2: Focus Groups for New Product Launches
Focus groups are another popular market research method. They involve a small group of people discussing a product or service. This is especially useful before launching new products. For example, Procter & Gamble (P&G) has used focus groups to test out its new beauty and skincare lines before making them widely available. This research method allows businesses to assess real-time reactions and opinions.
Example 3: Competitor Analysis for Market Positioning
Companies often conduct competitor analysis as part of their market research efforts to understand the market landscape. For example, Coca-Cola has long kept a close eye on PepsiCo’s strategies. By analyzing competitors’ marketing, pricing, and product strategies, businesses can optimize their own positioning. This kind of data analysis is critical in adjusting marketing strategies and staying ahead of the competition.
Example 4: Social Media Monitoring for Brand Sentiment
Social media platforms offer a wealth of data on consumer preferences. By analyzing online conversations about their brand or products, businesses can understand consumer sentiment and react accordingly. For example, Netflix uses social media monitoring to gauge audience reactions to new shows, helping to guide content creation and marketing strategies.
Example 5: A/B Testing for Marketing Campaigns
A/B testing is an essential form of market research, particularly for digital marketing. Companies run two versions of an ad, email, or landing page to determine which performs better. HubSpot uses A/B testing to refine its email marketing campaigns, ensuring higher click-through rates and conversions. This helps businesses optimize their marketing efforts with data-driven insights.
Learn more: What is Customer Feedback?
Market Research Methods
- Qualitative Market Research Methods
Qualitative market research methods focus on non-data intensive methods of information gathering and analysis. These methods focus on a small sample of respondents who are probed for an in-depth understanding of a subject. The goal of such a method is to gain an in-depth understanding of the market and consumer behavior based on open-ended questions and discussions.
For example, focus groups, one-on-one interviews, case studies, etc are popular qualitative methods of market research.
- Quantitative Market Research Methods
Quantitative market research focuses on data-intensive methods that return solid data that can be quantitatively analyzed in bulk. These methods often rely on a large sample of respondents who answer a common questionnaire, which may further have an internal logic to branch out to new questions based on answers to previous questions.
Examples of quantitative market research methods are physical survey questionnaires, online feedback surveys, Twitter polls, Net Promoter Score (NPS) questions after a product purchase, customer satisfaction (CSAT) feedback forms, etc.
Best Practices for Market Research in 2023

Market research is a crucial process that helps businesses understand their target market, consumer preferences, industry trends, and competitive landscape. By gathering and analyzing relevant data, companies can make informed decisions and develop effective marketing strategies. Here are some best practices for market research:
1. Define your research objectives: Clearly articulate the goals and purpose of your research. Identify the specific information you need to gather, such as customer insights, market size, competitor analysis, or product feedback.
2. Identify your target audience: Determine the specific demographic or customer segment you want to study. This will help you tailor your research methods and questions to gather the most relevant data.
3. Choose the right research methods: Select the most appropriate research methods based on your objectives and target audience. Common methods include surveys, interviews, focus groups, observation, secondary research, and data analysis.
4. Develop a research plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the research methodology, timeline, and resource allocation. This will ensure that the research is conducted efficiently and effectively.
5. Use a combination of qualitative and quantitative research: Qualitative research methods, such as interviews and focus groups, provide in-depth insights and opinions, while quantitative methods, like surveys and data analysis, offer statistical data and measurable metrics. Combining both approaches provides a comprehensive understanding of the market.
6. Collect data from multiple sources: Gather information from diverse sources, including primary data (collected directly from customers or target audiences) and secondary data (existing research, industry reports, and government data). This multi-source approach enhances the reliability and accuracy of your findings.
7. Maintain data quality and integrity: Ensure the data collected is accurate, reliable, and relevant to your research objectives. Use standardized measurement scales and survey techniques to maintain consistency.
8. Analyze and interpret the data: Use appropriate statistical analysis tools and techniques to analyze the collected data. Look for patterns, trends, and correlations that can provide valuable insights for decision-making.
9. Keep an eye on competitors: Conduct a competitive analysis to understand your competitors’ strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. This information can help you identify opportunities and develop effective marketing plans.
10. Stay ethical and maintain privacy: Adhere to ethical guidelines and protect the privacy of participants and their data. Obtain informed consent and ensure confidentiality throughout the research process.
11. Communicate and act on findings: Present your research findings in a clear and concise manner. Translate the insights into actionable strategies and recommendations that can drive business growth.
12. Continuously monitor the market: Market research is an ongoing process. Keep a pulse on industry trends, consumer preferences, and market dynamics to stay ahead of the competition and identify new opportunities.
By following these best practices, businesses can conduct effective market research that informs decision-making, helps identify growth opportunities, and supports the development of successful marketing strategies.
Learn more: What is Online Focus Group?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.