What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research stands as a powerful research methodology dedicated to the systematic collection and analysis of measurable data. Through rigorous statistical and mathematical techniques, this method extracts insights from structured surveys, controlled experiments, or other defined data-gathering methods.
The primary objective of quantitative research is to measure and quantify variables, relationships, and patterns within the dataset. By testing hypotheses, making predictions, and drawing generalizable conclusions, it plays a crucial role in fields such as psychology, sociology, economics, and education. This approach often involves significant sample sizes, ensuring robust results.
Explore the depth of quantitative research with this comprehensive guide, offering practical examples and applications to demonstrate its real-world impact. Stay updated with the latest trends and developments in quantitative research as we continually refine our insights to provide you with the most relevant and cutting-edge information.
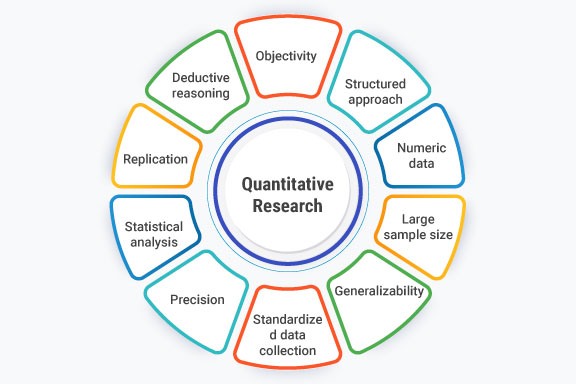
Quantitative Research: Key Characteristics
Below are the key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Objectivity: Quantitative research is grounded in the principles of objectivity and empiricism, which means that the research is focused on observable and measurable phenomena, rather than personal opinions or experiences.
- Structured approach: Quantitative research follows a structured and systematic approach to data collection and analysis, using clearly defined variables, hypotheses, and research questions.
- Numeric data: Quantitative research uses numerical data to describe and analyze the phenomena under study, such as statistical analysis, surveys, and experiments.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves large sample sizes to ensure statistical significance and to generalize findings to a larger population.
- Standardized data collection: Quantitative research typically involves standardized data collection methods, such as surveys or experiments, to minimize potential sources of bias and increase reliability.
- Deductive reasoning: Quantitative research uses deductive reasoning, where the researcher tests a specific hypothesis based on prior knowledge and theory.
- Replication: Quantitative research emphasizes the importance of replication, where other researchers can reproduce the study’s methods and obtain similar results.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves statistical analysis to analyze the data and test the research hypotheses, often using software programs to assist with data analysis.
- Precision: Quantitative research aims to be precise in its measurement and analysis of data. It seeks to quantify and measure the specific aspects of a phenomenon being studied.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to generalize findings from a sample to a larger population. It seeks to draw conclusions that apply to a broader group beyond the specific sample being studied.
Quantitative Research Examples
Below are 3 examples of quantitative research:
Example 1: Boosting Employee Performance with Innovative Training Programs
In this quantitative study, we delve into the transformative impact of a cutting-edge training program on employee productivity within corporate environments. Employing a quasi-experimental framework, we meticulously analyze the outcomes of a cohort undergoing innovative training against a control group.
Through advanced statistical methodologies, we unveil actionable insights into performance enhancements, arming organizations with data-driven strategies for workforce development and competitive advantage.
Example 2: Unveiling the Power of Physical Exercise on Mental Well-being
Unlocking the correlation between physical exercise and mental health, this quantitative inquiry stands at the forefront of holistic wellness research.
Through meticulous data collection and rigorous statistical analyses, we dissect the nuanced relationship between exercise regimens and mental well-being indicators.
Our findings not only underscore the profound impact of exercise on psychological resilience but also provide actionable insights for healthcare professionals and individuals striving for optimal mental health.
Example 3: Revolutionizing Education with Innovative Teaching Methodologies
In this groundbreaking study, we embark on a quantitative exploration of the transformative potential of innovative teaching methods on student learning outcomes. Utilizing a quasi-experimental design, we meticulously evaluate the efficacy of novel pedagogical approaches against conventional teaching methodologies.
Through rigorous statistical analyses of pre-test and post-test data, we unearth compelling evidence of enhanced academic performance, paving the way for educational institutions to embrace innovation and elevate learning experiences.
Example 4: Assessing the Impact of Social Media Usage on Academic Performance
In this quantitative research endeavor, we delve into the relationship between social media usage patterns and academic achievement among college students. Employing a correlational research design, we collect data on students’ social media habits and their corresponding GPA scores.
Through regression analysis and other statistical techniques, we uncover insights into how factors such as frequency of social media use, types of platforms utilized, and time spent online correlate with academic performance. These findings provide valuable insights for educators, policymakers, and students themselves to optimize study habits and achieve academic success in the digital age.
Example 5: Analyzing the Effects of Financial Literacy Programs on Saving Behavior
This quantitative study investigates the efficacy of financial literacy programs in promoting responsible saving behavior among young adults. Using a randomized controlled trial methodology, we administer financial education interventions to a sample population and compare their saving habits to a control group over a specified period.
Through statistical analysis of savings rates, expenditure patterns, and financial decision-making, we discern the impact of financial literacy interventions on participants’ saving behaviors. These findings offer valuable implications for financial institutions, policymakers, and educators seeking to empower individuals with the knowledge and skills to make sound financial decisions and achieve long-term financial well-being.
Learn more: What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative Research: Key Advantages
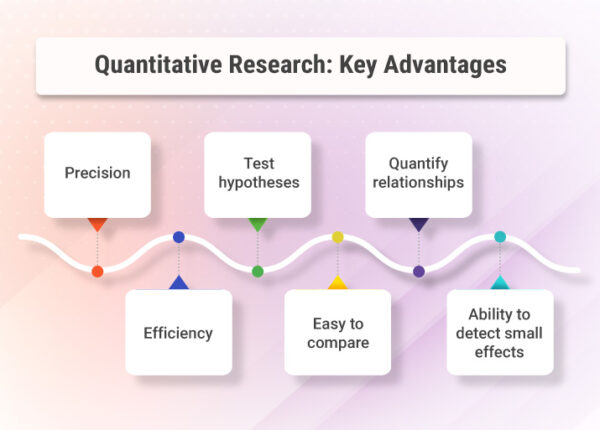
The advantages of quantitative research make it a valuable research method in a variety of fields, particularly in fields that require precise measurement and testing of hypotheses.
- Precision: Quantitative research aims to be precise in its measurement and analysis of data. This can increase the accuracy of the results and enable researchers to make more precise predictions.
- Test hypotheses: Quantitative research is well-suited for testing specific hypotheses or research questions, allowing researchers to draw clear conclusions and make predictions based on the data.
- Quantify relationships: Quantitative research enables researchers to quantify and measure relationships between variables, allowing for more precise and quantitative comparisons.
- Efficiency: Quantitative research often involves the use of standardized procedures and data collection methods, which can make the research process more efficient and reduce the amount of time and resources required.
- Easy to compare: Quantitative research often involves the use of standardized measures and scales, which makes it easier to compare results across different studies or populations.
- Ability to detect small effects: Quantitative research is often able to detect small effects that may not be observable through qualitative research methods, due to the use of statistical analysis and large sample sizes.
Quantitative Research Methodology
Quantitative research is a type of research that focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to answer research questions. There are two main methods used to conduct quantitative research:
1. Primary Method
There are several methods of primary quantitative research, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Surveys: Surveys are a common method of quantitative research and involve collecting data from a sample of individuals using standardized questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can be conducted in various ways, such as online, by mail, by phone, or in person. Surveys can be used to study attitudes, behaviors, opinions, and demographics.
One of the main advantages of surveys is that they can be conducted on a large scale, making it possible to obtain representative data from a population. However, surveys can suffer from issues such as response bias, where participants may not provide accurate or truthful answers, and nonresponse bias, where certain groups may be less likely to participate in the survey.
Experiments: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables to determine their effects on an outcome of interest. Experiments can be carried out in controlled laboratory settings or in real-world field environments. Experiments can be used to test causal relationships between variables and to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
One of the main advantages of experiments is that they provide a high level of control over the variables being studied, which can increase the internal validity of the study. However, experiments can suffer from issues such as artificiality, where the experimental setting may not accurately reflect real-world situations, and demand characteristics, where participants may change their behavior due to the experimental setting.
Observational studies: Observational studies involve observing and recording data without manipulating any variables. Observational studies can be conducted in various settings, such as naturalistic environments or controlled laboratory settings. Observational studies can be used to study behaviors, interactions, and phenomena that cannot be manipulated experimentally.
One of the main advantages of observational studies is that they can provide rich and detailed data about real-world phenomena. However, observational studies can suffer from issues such as observer bias, where the observer may interpret the data in a subjective manner, and reactivity, where the presence of the observer may change the behavior being observed.
Content analysis: Content analysis involves analyzing media or communication content, such as text, images, or videos, to identify patterns or trends. Content analysis can be used to study media representations of social issues or to identify patterns in social media data.
One of the main advantages of content analysis is that it can provide insights into the cultural and social values reflected in media content. However, content analysis can suffer from issues such as the subjectivity of the coding process and the potential for errors or bias in the data collection process.
Psychometrics: Psychometrics involves the development and validation of standardized tests or measures, such as personality tests or intelligence tests. Psychometrics can be used to study individual differences in psychological traits and to assess the validity and reliability of psychological measures.
One of the main advantages of psychometrics is that it can provide a standardized and objective way to measure psychological constructs. However, psychometrics can suffer from issues such as the cultural specificity of the measures and the potential for response bias in self-report measures.
2. Secondary Method
Secondary quantitative research methods involve analyzing existing data that was collected for other purposes. This can include data from government records, public opinion polls, or market research studies. Secondary research is often quicker and less expensive than primary research, but it may not provide data that is as specific to the research question.
One of the main advantages of secondary data analysis is that it can be a cost-effective way to obtain large amounts of data. However, secondary data analysis can suffer from issues such as the quality and relevance of the data, and the potential for missing or incomplete data.
Learn more: What is Quantitative Observation?
7 Best Practices to Conduct Quantitative Research
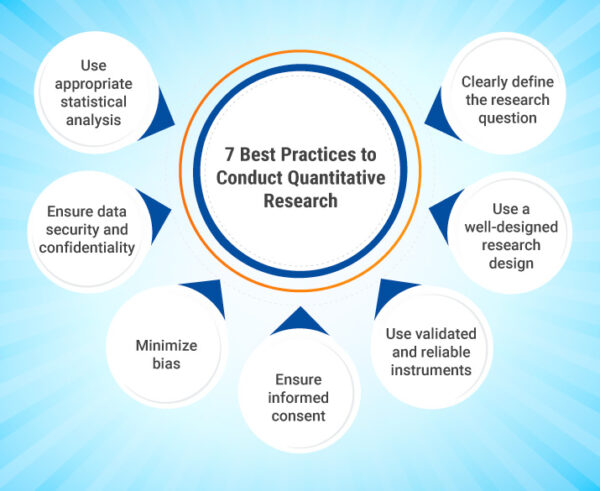
Here are the key best practices that should be followed when conducting quantitative research:
1. Clearly define the research question: The research question should be specific, measurable, and focused on a clear problem or issue.
2. Use a well-designed research design: The research design should be appropriate for the research question, and should include a clear sampling strategy, data collection methods, and statistical analysis plan.
3. Use validated and reliable instruments: The instruments used to collect data should be validated and reliable to ensure that the data collected is accurate and consistent.
4. Ensure informed consent: Participants should be fully informed about the purpose of the research, their rights, and how their data will be used. Informed consent should be obtained before data collection begins.
5. Minimize bias: Researchers should take steps to minimize bias in all stages of the research process, including study design, data collection, and data analysis.
6. Ensure data security and confidentiality: Data should be kept secure and confidential to protect the privacy of participants and prevent unauthorized access.
7. Use appropriate statistical analysis: Statistical analysis should be appropriate for the research question and the data collected. Accurate and clear reporting of results is imperative in quantitative research.
Learn more: What is Qualitative Research?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.