What is Discontinuous Innovation?
Discontinuous innovation is defined as a type of innovation that introduces significant changes and often creates new markets or displaces existing ones. It involves the development of new products, services, or business models that fundamentally alter the way things are done in an industry or sector.
Unlike continuous innovation, discontinuous innovation typically emerges from outside the established market players and can disrupt the existing market dynamics. It often starts by targeting a niche or overlooked segment of the market and gradually gains traction, eventually challenging and displacing established players.
Key Component of Discontinuous Innovation
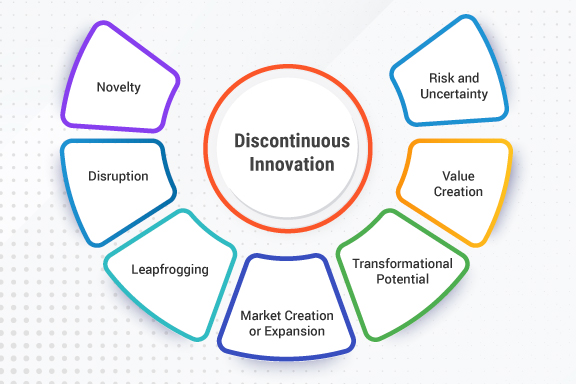
A key component of discontinuous innovation is the introduction of novel and disruptive ideas, technologies, or business models that challenge the status quo. This component comprises several key elements:
- Novelty: Discontinuous innovation involves introducing something new and different to the market. It goes beyond incremental innovation and pushes the boundaries of what is currently available. The innovation brings forth new ideas, concepts, or approaches that have the potential to create a significant impact.
- Disruption: Discontinuous innovation disrupts existing market dynamics, business models, or industry norms. It challenges established players, traditional ways of doing things, and the prevailing mindset. Disruptive innovations often start by targeting overlooked segments or underserved customers and gradually gain traction, displacing incumbents.
- Leapfrogging: Discontinuous innovation involves a leapfrog effect, where the innovation offers a significant advancement over existing solutions. It brings about a step-change in performance, functionality, or value proposition, providing a compelling reason for customers to adopt the new offering.
- Value Creation: Discontinuous innovation focuses on creating value for customers. It aims to deliver superior experiences, solve problems, or fulfill unmet needs in innovative ways. By providing unique value propositions, it attracts customers and drives adoption.
- Transformational Potential: Discontinuous innovation has the potential to transform industries, markets, and customer experiences. It can reshape business models, redefine customer expectations, and create new opportunities. By introducing disruptive ideas or technologies, it can lead to profound changes and shifts in the way things are done.
- Market Creation or Expansion: Discontinuous innovation can create new markets or open up untapped segments. It identifies unmet needs or addresses pain points that were previously overlooked, attracting customers who were not adequately served by existing offerings. It expands the boundaries of what is possible and unlocks new market opportunities.
- Risk and Uncertainty: Discontinuous innovation involves inherent risks and uncertainties. It ventures into unknown territories, faces technological challenges, market acceptance uncertainties, and potential resistance from incumbents. Organizations pursuing discontinuous innovation must be prepared to navigate these risks and uncertainties effectively.
Benefits and Challenges of Discontinuous Innovation
Discontinuous innovation offers several benefits and opportunities, but it also presents challenges. Let’s explore both aspects:
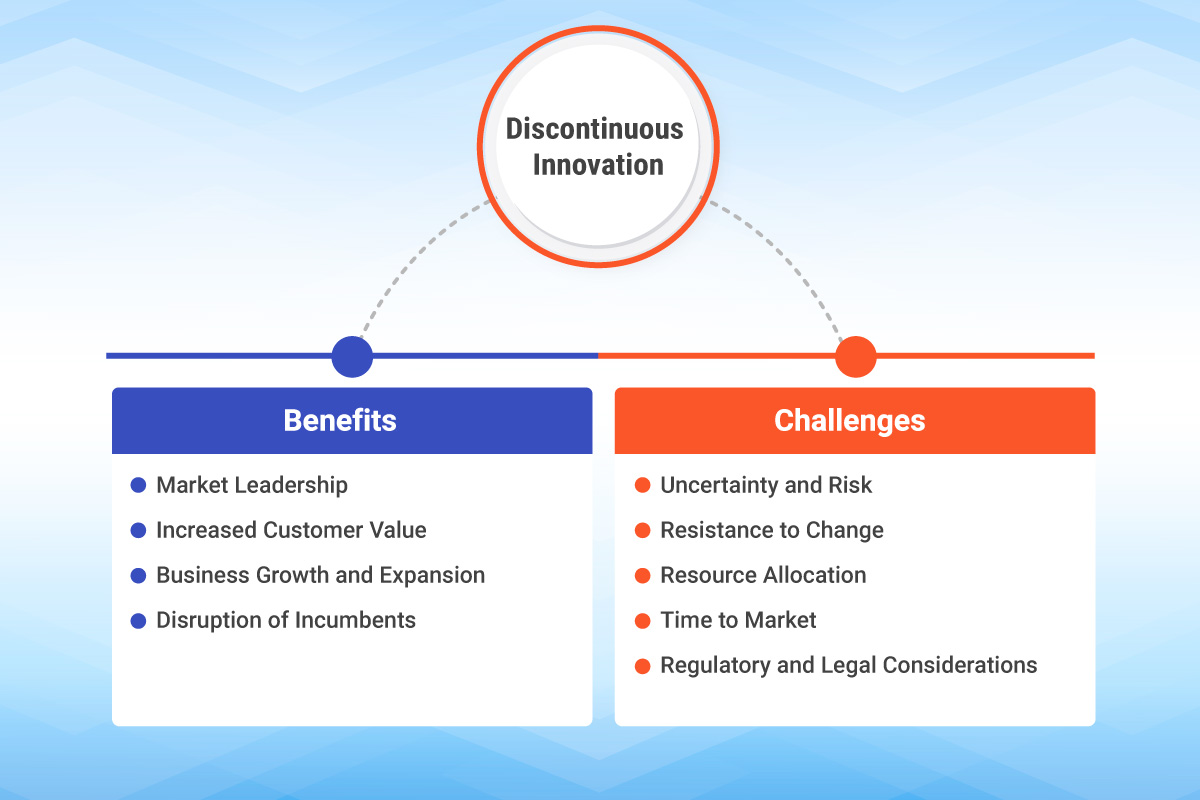
Benefits of Discontinuous Innovation:
- Market Leadership: Discontinuous innovation can enable organizations to become market leaders by creating new markets or capturing untapped segments. It allows companies to gain a competitive advantage and differentiate themselves from existing players.
- Increased Customer Value: Discontinuous innovation often results in significant improvements in product innovation and its performance, functionality, and cost-effectiveness. This leads to enhanced customer value, improved user experiences, and increased customer satisfaction.
- Business Growth and Expansion: Successful discontinuous innovation can fuel business growth and expansion by opening up new revenue streams, attracting new customers, and diversifying product offerings. It can help organizations penetrate new markets and increase market share.
- Disruption of Incumbents: Discontinuous innovation can disrupt established players in an industry, challenging their market dominance and forcing them to adapt or risk becoming obsolete. This creates opportunities for new entrants and promotes market competition.
Challenges of Discontinuous Innovation:
- Resistance to Change: Discontinuous innovation disrupts existing practices, business models, and sometimes even job roles. Resistance to change can come from within the organization, as employees may be reluctant to embrace technological innovation. Additionally, established market players may resist the disruption caused by discontinuous innovation.
- Uncertainty and Risk: Discontinuous innovation often involves venturing into uncharted territories, which brings inherent risks and uncertainties. The success of such innovation is not guaranteed, and organizations may face financial, technological, or market risks associated with developing and introducing novel products or services.
- Resource Allocation: Discontinuous innovation requires significant investments in market research, development, and market entry. Organizations must allocate resources strategically and make tough decisions regarding resource allocation between existing operations and new ventures.
- Time to Market: Developing and commercializing discontinuous innovations can take time, as they often involve complex technologies or significant market shifts. Time to market can be a challenge, especially when competitors are quick to respond or when the innovation’s window of opportunity is limited.
- Regulatory and Legal Considerations: Discontinuous innovation can encounter regulatory or legal hurdles. New technologies may require compliance with evolving regulations, intellectual property protection, or navigating legal frameworks that may not have anticipated the innovation.
To effectively leverage the benefits of discontinuous innovation while mitigating challenges, organizations need to foster a culture of innovation, embrace agility, and build adaptive strategies that allow them to navigate uncertainties and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Learn more: What is Continuous Innovation?
Discontinuous Innovation Process: 7 Key Steps
The process of discontinuous innovation involves several key steps to effectively develop and implement groundbreaking ideas. While the specific approach may vary depending on the organization and industry, here are the key steps typically involved in the discontinuous innovation process:
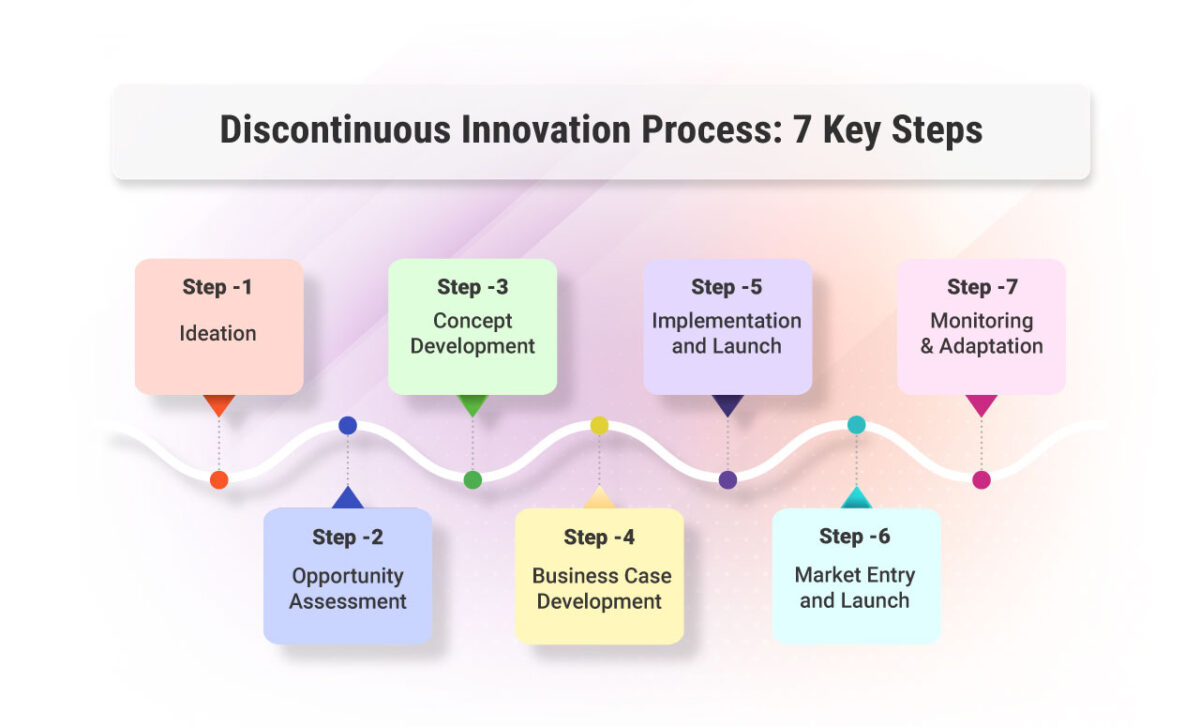
1. Ideation: The first step is ideation for potentially disruptive innovations. This can be done through brainstorming sessions, market research, customer feedback, or collaboration with external partners. The focus is on identifying unmet needs, emerging technologies, or overlooked market segments.
2. Opportunity Assessment: Once ideas are generated, they need to be evaluated to determine their viability and potential impact. This involves assessing the market potential, understanding customer needs, analyzing technological feasibility, and evaluating the competitive landscape. Ideas that show the most promise are selected for further development.
3. Concept Development: In this stage, the selected ideas are transformed into concrete concepts. Detailed research and development activities take place to refine the concepts, explore technical feasibility, create prototypes, and conduct feasibility studies. The aim is to validate the ideas and gather feedback for further iterations.
4. Business Case Development: A robust business case is built to evaluate the commercial viability of the concept. This includes conducting market analysis, estimating financial projections, assessing resource requirements, and identifying potential risks and mitigations. The business case helps in making informed decisions about pursuing or discarding the innovation.
5. Development and Testing: Once the business case is approved, the actual development of the disruptive innovation begins. This involves engineering, design, manufacturing, or software development processes, depending on the nature of the innovation. Iterative testing and refinement are crucial to ensure that the innovation meets the desired performance, quality, and user experience standards.
6. Market Entry and Launch: After successful development and testing, the disruptive innovation is ready for market entry. This stage involves developing a go-to-market strategy, including pricing, distribution, marketing, and sales plans. Launching the innovation requires careful execution, effective communication, and building awareness among target customers.
7. Monitoring and Adaptation: Once the innovation is introduced to the market, it is essential to monitor its performance, gather customer feedback, and track key metrics. This helps in identifying any necessary adjustments, improvements, or adaptations based on real-world usage and customer responses. Continuous monitoring and adaptation ensure the innovation remains relevant and competitive.
7 Key Examples of Discontinuous Innovation
These examples highlight how discontinuous innovations have transformed industries, created new markets, and changed the way people live, work, and interact with technology. Discontinuous innovation has the power to reshape industries and drive societal progress.
- Personal Computers: The introduction of personal computers revolutionized the computing industry. Companies like Apple and Microsoft brought user-friendly desktop computers to the market, enabling individuals and small businesses to have access to computing power and ushering in the era of personal computing.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, is a technological innovation that allows for the production of three-dimensional objects by gradually building them layer by layer.
- Digital Photography: The shift from film-based photography to digital cameras disrupted the traditional camera and film industry. Companies like Kodak, which had been dominant in the film industry, faced significant challenges as digital cameras offered convenient image capture, instant previews, and the ability to store and share photos digitally.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Electric vehicles are disrupting the automotive industry, challenging the dominance of internal combustion engine vehicles. Companies like Tesla have been at the forefront of this innovation, introducing high-performance electric cars with extended range capabilities and a focus on sustainability.
- Online Streaming Services: Streaming services such as Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video disrupted the traditional video rental market dominated by physical DVDs and video rental stores. These platforms allowed users to stream movies and TV shows directly to their devices, offering convenience, a vast library of content, and personalized recommendations.
- Mobile Phones: The advent of mobile phones brought about a discontinuous innovation that transformed the telecommunications industry. Companies like Nokia, Motorola, and later Apple and Samsung introduced compact, portable phones that went beyond basic voice communication, offering features such as text messaging, internet access, and mobile apps.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Sharing Platforms: Platforms like Airbnb and Uber disrupted the traditional hospitality and transportation industries, respectively. These platforms connect individuals who have spare rooms or vehicles with people in need of accommodation or transportation, challenging established business model innovation and providing new ways of accessing these services.
Learn more: What is Business Model Innovation?
Top 10 Best Practices of Discontinuous Innovation Management
Managing discontinuous innovation effectively requires a strategic and adaptive approach. Here are some best practices for managing discontinuous innovation:
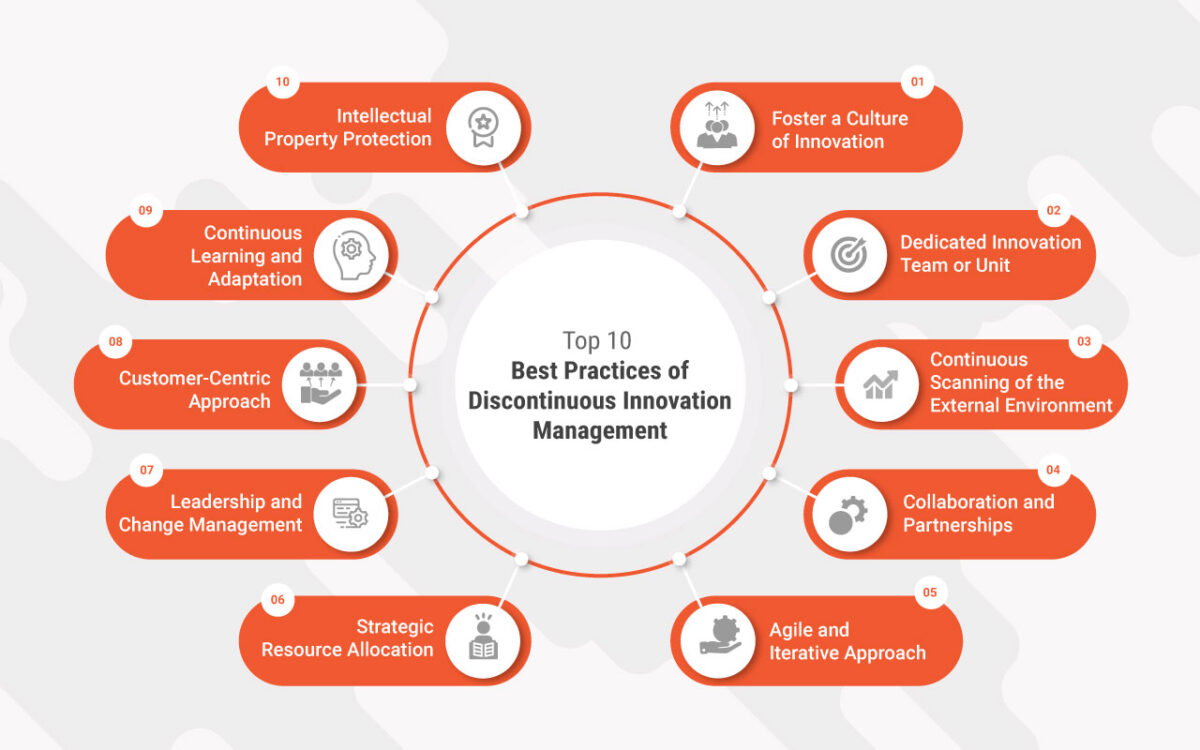
1. Foster a Culture of Innovation
Foster an organizational culture of innovation that deeply appreciates and actively encourages innovation. Encourage employees to generate and share ideas, reward creativity, and provide resources and support for experimentation and risk-taking.
2. Dedicated Innovation Team or Unit
Establish a dedicated team or unit responsible for managing discontinuous innovation initiatives. This team can focus solely on exploring disruptive opportunities, conducting research, developing prototypes, and driving innovation projects forward.
3. Continuous Scanning of the External Environment
Stay abreast of emerging technologies, market trends, customer needs, and regulatory changes. Regularly scan the external environment to identify potential disruptive opportunities and threats. Engage in industry networks, collaborate with research institutions, and monitor startup ecosystems to tap into external sources of innovation.
4. Collaboration and Partnerships
Foster collaborations and partnerships with external entities such as startups, research institutions, and industry experts. Partnering with external stakeholders can provide access to new ideas, expertise, and resources, accelerating the development and implementation of discontinuous innovations.
5. Agile and Iterative Approach
Embrace an agile and iterative approach to innovation. Break down the innovation process into smaller, manageable phases, allowing for frequent testing, learning, and adaptation. Emphasize quick prototyping, rapid feedback loops, and continuous improvement to validate and refine ideas.
6. Strategic Resource Allocation
Allocate resources strategically to support discontinuous innovation initiatives. Strike a balance between investing in core operations and exploring new disruptive opportunities. Provide dedicated funding, infrastructure, and talent to support innovation projects, recognizing that they may require different timelines, risk profiles, and resource needs than incremental innovations.
7. Leadership and Change Management
Strong leadership and change management are critical for managing discontinuous innovation. Leaders should champion innovation, communicate the importance of disruptive thinking, and create a supportive environment for experimentation and learning. Effectively manage the cultural and organizational changes that come with discontinuous innovation.
8. Customer-Centric Approach
Place a strong emphasis on understanding customer needs, pain points, and aspirations. Involve customers throughout the innovation process, from ideation to testing and feedback. Incorporate customer insights into the development and refinement of discontinuous innovations to ensure market relevance.
9. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Encourage a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. Embrace failures as valuable learning opportunities and promote a culture of experimentation. Use data, analytics, and customer feedback to iterate and refine discontinuous innovations based on real-world usage and market dynamics.
10. Intellectual Property Protection
Develop strategies to protect intellectual property associated with discontinuous innovations. This may involve securing patents, copyrights, trademarks, or trade secrets to safeguard unique technologies, designs, or business models.
Learn more: What is Process Innovation?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.