What is Radical Innovation?
Radical innovation is defined as a significant and transformative breakthrough in technology, business models, processes, or products that creates a substantial shift in industry or society. It involves introducing revolutionary ideas, concepts, or approaches that challenge existing norms, disrupt markets, and often result in groundbreaking advancements.
It’s important to note that radical innovation is distinct from incremental innovation, which involves making gradual improvements and refinements to existing products, processes, or services. Radical innovation, on the other hand, represents a significant leap forward that reshapes industries and society.
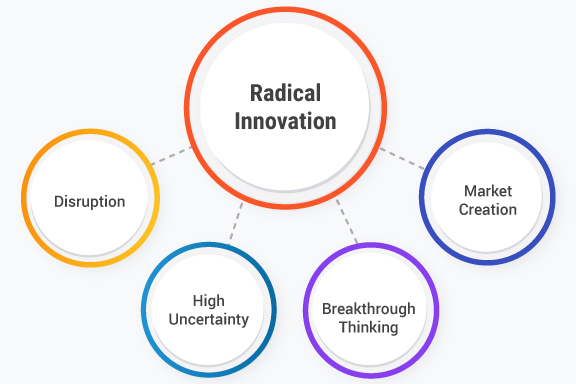
Characteristics of radical innovation include:
- Transformational Impact: Radical innovations have a profound and transformative impact on industries, markets, and society as a whole. They often redefine the rules and paradigms of the existing system.
- Disruption: Radical innovations disrupt established markets, technologies, and business model innovations, often rendering previous solutions obsolete or less relevant. They introduce new ways of doing things that fundamentally change the competitive landscape.
- High Uncertainty: Radical innovation is accompanied by high levels of uncertainty and risk. Since it involves venturing into uncharted territory, there is limited knowledge or prior experience to rely upon, making outcomes unpredictable.
- Breakthrough Thinking: Radical innovation requires a departure from incremental innovation and embraces a mindset of exploring unconventional ideas and possibilities. It involves thinking beyond existing boundaries and pushing the limits of what is considered possible.
- Market Creation: Radical innovations often create new markets or address unmet needs that were previously unrecognized. They bring forth novel solutions that capture the imagination of customers and open up new opportunities for growth.
Radical Innovation Process: 8 Key Steps
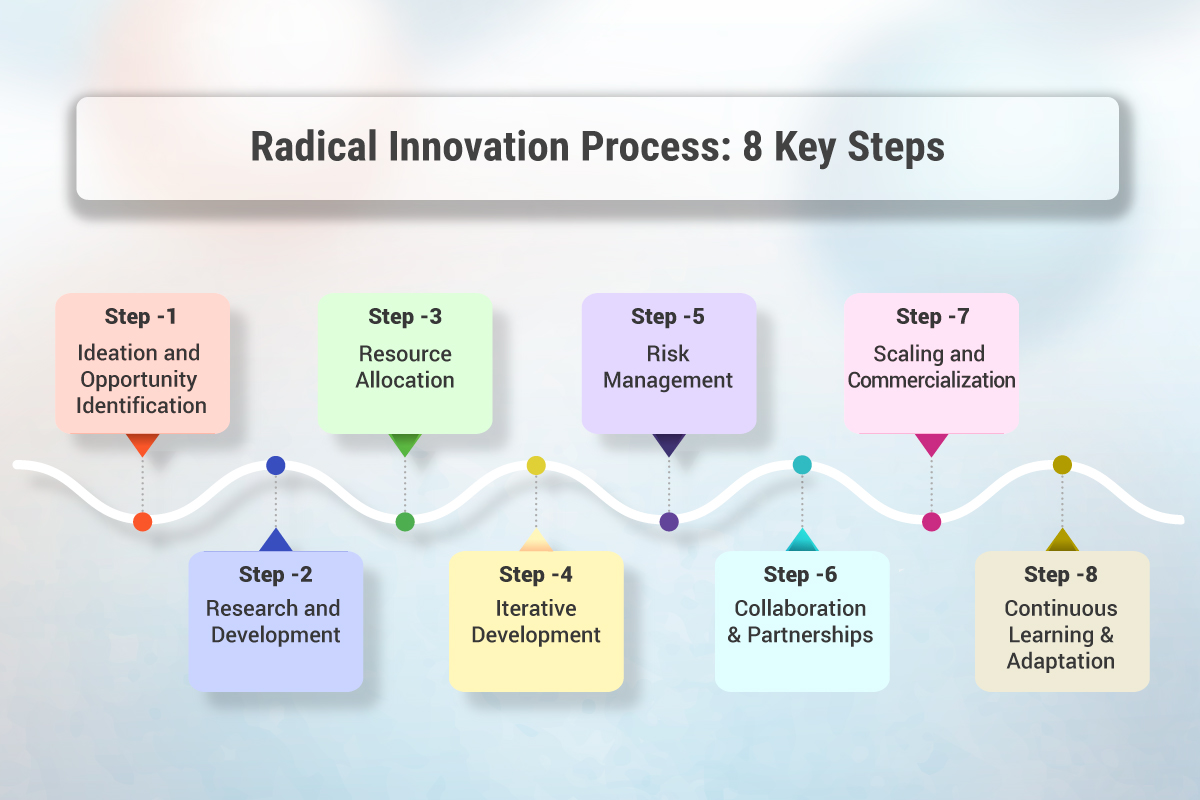
The process of achieving radical innovation can vary depending on the organization and industry, but here are some key steps commonly involved in the pursuit of radical innovation:
Step 1. Ideation and Opportunity Identification
The process begins with generating and identifying innovative ideas. This can be done through brainstorming sessions, market research, customer insights, technology scouting, or collaboration with external partners. The goal is to explore unconventional concepts and identify opportunities for radical breakthroughs.
Step 2. Research and Development
Once potential opportunities are identified, organizations invest in research and development to explore the feasibility and viability of the ideas. This involves conducting in-depth research, prototyping, testing, and experimenting to refine the concept and gather data on its potential impact.
Step 3. Resource Allocation
Radical innovation often requires significant resources, including funding, skilled personnel, and infrastructure. Allocating the necessary resources and securing executive support is crucial for advancing the innovation process. This may involve securing budgetary approvals, assembling multidisciplinary teams, and creating dedicated innovation units or departments.
Step 4. Iterative Development
Radical innovation is typically an iterative process that involves multiple cycles of testing, learning, and refining. As the concept evolves, feedback from customers, stakeholders, and experts is incorporated to improve the design, functionality, and market fit of the innovation.
Step 5. Risk Management
Radical innovation is inherently risky, and organizations need to actively manage and mitigate potential risks. This includes identifying and assessing risks associated with the innovation, implementing risk mitigation strategies, and monitoring and adjusting the innovation process as needed.
Step 6. Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration with external partners, such as research institutions, startups, suppliers, or industry experts, can accelerate the radical innovation process. Collaborative partnerships can provide access to specialized knowledge, technologies, or resources that complement the organization’s capabilities.
Step 7. Scaling and Commercialization
Once the innovation has been developed and tested successfully, the focus shifts to scaling and commercializing the solution. This involves creating a business model, developing a go-to-market strategy, securing intellectual property rights if applicable, and launching the innovation in the market.
Step 8. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Radical innovation requires an environment that fosters continuous learning, adaptability, and agility. Organizations should actively seek feedback, monitor market dynamics, and embrace a culture of innovation that encourages experimentation, learning from failures, and adapting strategies accordingly.
Learn more: What is Business Innovation?
5 Examples of Radical Innovation
The following 5 examples demonstrate how radical innovation has the power to disrupt established industries, introduce business model innovation, and bring about transformative changes that impact society at large.
- Tesla’s Electric Vehicles: Tesla Motors revolutionized the automotive industry by introducing high-performance electric vehicles with long-range capabilities. Their innovative electric car designs, advanced battery technology, and focus on sustainability disrupted the traditional gasoline-powered automobile market and paved the way for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
- Airbnb’s Sharing Economy Model: Airbnb transformed the hospitality industry by creating a platform that allows individuals to rent out their spare rooms or properties to travelers. By leveraging the sharing economy and embracing the power of technology innovation, Airbnb disrupted the traditional hotel industry and provided a new way for people to find affordable accommodations and generate income.
- SpaceX’s Reusable Rockets: SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, introduced the concept of reusable rockets in the aerospace industry. By developing rockets capable of returning to Earth and being reused, SpaceX dramatically reduced the cost of space launches, making space exploration and satellite deployment more accessible and economically feasible.
- 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized manufacturing processes. This technology innovation allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects by layering materials, enabling more efficient prototyping, customization, and on-demand production. It has the potential to disrupt traditional supply chains and manufacturing methods across industries.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology, originally introduced through the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, has the potential to revolutionize various industries. It is a decentralized and transparent ledger system that allows secure and immutable recording of transactions. Blockchain technology can transform industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more by enhancing transparency, reducing intermediaries, and enabling secure and efficient data management.
Learn more: What is Process Innovation?
Top 10 Best Practices for Implementing Radical Innovation
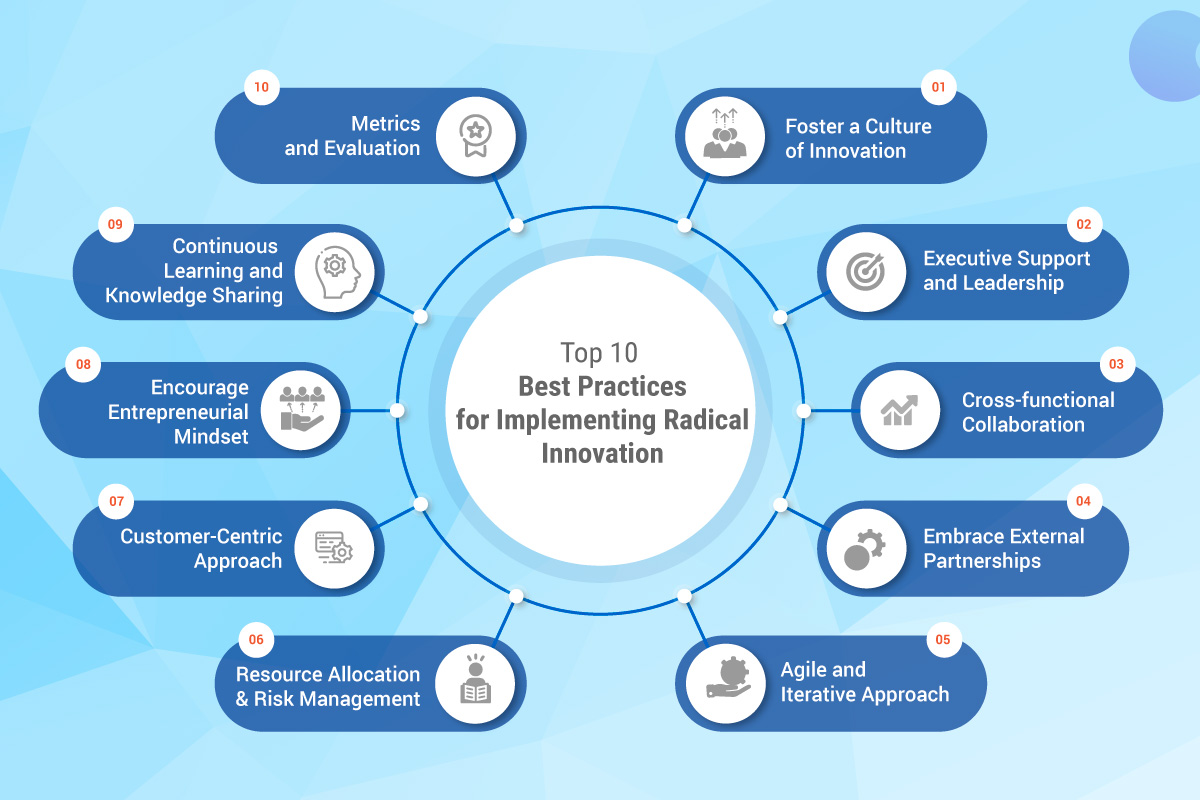
Implementing radical innovation can be a complex and challenging process. Here are ten best practices to consider when embarking on a journey of implementing radical innovation within an organization:
1. Foster a Culture of Innovation: Create a supportive and inclusive organizational culture that encourages and rewards innovation. Foster an environment where employees are empowered to ideation, take risks, and challenge the status quo.
2. Executive Support and Leadership: Obtain strong support from top-level executives who champion and drive radical innovation initiatives. Leadership commitment is crucial for securing resources, aligning organizational goals, and overcoming resistance to change.
3. Embrace External Partnerships: Collaborate with external partners, such as startups, research institutions, or industry experts, to tap into external knowledge, technologies, and resources. External partnerships can bring fresh perspectives, accelerate the innovation process, and expand the organization’s capabilities.
4. Cross-functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration and interdisciplinary teams to harness diverse perspectives and expertise. Facilitate communication and collaboration among different departments, encouraging the exchange of ideas and knowledge.
5. Agile and Iterative Approach: Adopt an agile and iterative approach to the innovation process. Break down large initiatives into smaller, manageable projects, allowing for quick experimentation, learning, and adaptation. Embrace feedback loops to refine and improve the innovation over time.
6. Resource Allocation and Risk Management: Allocate appropriate resources, including funding, talent, and infrastructure, to support radical innovation initiatives. Assess and manage risks associated with the innovation process through careful planning, risk mitigation strategies, and regular monitoring.
7. Encourage Entrepreneurial Mindset: Cultivate an entrepreneurial mindset within the organization, encouraging employees to think like entrepreneurs and take ownership of their ideas. Provide opportunities for intrapreneurship, where employees can pursue innovative projects within the organizational framework.
8. Customer-Centric Approach: Place the customer at the center of the innovation process. Continuously engage to gather customer feedback, and involve them in the co-creation of solutions. Understand their needs, pain points, and aspirations to develop innovations that truly address their requirements.
9. Continuous Learning and Knowledge Sharing: Foster a learning organization by encouraging continuous learning, knowledge sharing, and open communication. Establish platforms and processes for employees to share insights, best practices, and lessons learned from the innovation initiatives.
10 Metrics and Evaluation: Define relevant metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success and impact of radical innovation initiatives. Regularly evaluate and assess the outcomes against the set goals to refine strategies, learn from failures, and continuously improve the innovation process.
Learn more: What is Product Innovation?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.