Table of Contents
What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative market research is defined as a type of research that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to understand market trends, consumer behavior, and other business-related variables. It typically involves surveying a large sample of people or a target audience to gather data using surveys, polls, or questionnaires, which is then analyzed using statistical techniques to identify patterns, correlations, and other insights.
Quantitative market research can be used to answer a wide range of questions, such as:
- What are the most popular products or services in a particular market?
- How much are people willing to pay for a particular product or service?
- What factors influence consumer purchasing decisions?
- How satisfied are customers with a particular product or service?
- What is the market share of different companies in a particular industry?
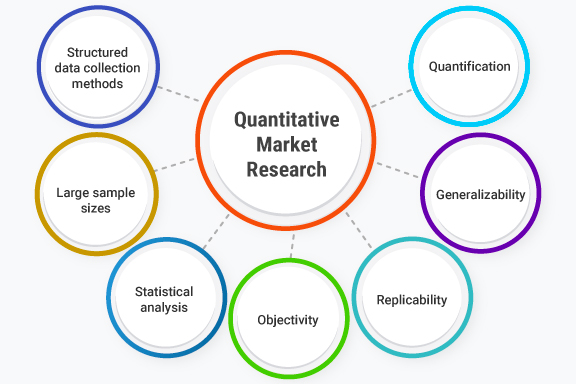
Characteristics of Quantitative Market Research
This type of research involves collecting numerical data and analyzing it using statistical methods to identify patterns, correlations, and other insights that can inform business decisions. Here are some of the key characteristics of quantitative market research:
- Structured data collection methods: Quantitative market research typically involves collecting data through structured qualitative research methods like surveys, experiments, or other techniques that allow for the collection of objective and measurable data. This structured approach helps ensure that the data collected is consistent and reliable.
- Large sample sizes: To ensure statistical significance, quantitative market research typically requires large sample sizes. This means that a large number of individuals need to be surveyed or studied to ensure that the data collected is representative of the broader population.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative market research relies heavily on statistical analysis to identify patterns and correlations in the data. This involves using techniques like regression analysis, correlation analysis, and hypothesis testing to draw conclusions from the data collected.
- Objectivity: The goal of quantitative market research is to gather objective and unbiased data that can be used to make informed decisions. To achieve this, researchers need to ensure that their methods are objective and that the data collected is free from bias.
- Replicability: One of the strengths of quantitative market research is that it is replicable. This means that other researchers can use the same methods to collect and analyze data, which allows for the results to be verified and validated over time.
- Generalizability: Quantitative market research aims to gather data that is representative of the broader population. This means that the insights and conclusions drawn from the data can be generalized to the broader population with a certain level of confidence.
- Quantification: Quantitative market research involves quantifying data using numerical measurements. This allows for the data to be easily analyzed and compared, and for statistical techniques to be used to draw insights from the data.
Steps for Quantitative Market Research

Here is a general overview of the methodology involved in conducting quantitative market research:
Step 1. Define the research question: The first step in conducting quantitative market research is to define the research question or problem. This involves identifying the specific information that needs to be gathered and the objectives of the research.
Step 2. Design the study: The next step is to design the study, which involves identifying the target population, selecting a sampling method, and developing a survey instrument or other data collection method. The study design should be tailored to the quantitative research question and the specific objectives of the research.
Step 3. Collect the data: Once the study design is in place, the data collection process can begin. This involves administering surveys or other data collection instruments to the sample population. The data collection process should be structured and standardized to ensure consistency and reliability in the data collected.
Step 4. Analyze the data: After the data has been collected, it is analyzed using statistical techniques such as regression analysis, correlation analysis, and hypothesis testing. This involves identifying patterns and correlations in the data and drawing insights from the data to answer the research question.
Step 5. Draw conclusions: The final step in the quantitative research methodology is to draw conclusions. The method is conducted based on the data analysis.This involves interpreting the data and drawing conclusions that are supported by the data collected. The conclusions should be relevant to the research question and the objectives of the research.
Learn more: What is qualitative market research?
Quantitative Market Research Methods
There are several common techniques used in quantitative market research, each with its own advantages and limitations. Here, we will explore some of the most commonly used techniques in quantitative market research.
-
Surveys
Surveys are one of the most widely used techniques in quantitative market research. Surveys involve collecting data from a large number of individuals through a structured questionnaire or interview. Surveys can be conducted online, by mail, or over the phone. Surveys are a popular choice because they allow businesses to collect large amounts of data quickly and at a relatively low cost. They are also highly customizable, making it possible to tailor questions to specific research questions and objectives.
-
Experiments
Experiments are a quantitative market research technique used to test the impact of specific variables on consumer behavior or attitudes. There are two types of experiments. One is the laboratory experiments and the other one is the field experiments. Laboratory experiments are conducted in a controlled environment, while field experiments are conducted in a natural setting. Both types of experiments provide valuable insights into consumer behavior and can help businesses make data-driven decisions.
-
Observational Studies
Observational studies involve observing individuals in their natural environment and collecting data on their behavior. This can be done through direct observation or through the use of technology like cameras or tracking devices. Observational studies can provide valuable insights into consumer behavior, but they can also be time-consuming and may require a large sample size to be effective.
-
Secondary Data Analysis
With secondary data analysis, researchers can analyze data that has already been collected by others instead of collecting new data themselves. This can include data from government agencies, industry associations, or other sources. Secondary data analysis can be a cost-effective way to conduct market research, but it may be less customizable than other techniques.
-
Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies involve collecting data from the same individuals over a period of time. This allows researchers to observe changes in behavior or trends over time. Longitudinal studies can provide valuable insights into consumer behavior, but they can be costly and time-consuming to conduct.
-
Cross-sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies involve collecting data from individuals at a single point in time. This allows researchers to compare data from different groups or populations. Cross-sectional studies can provide valuable insights into differences between groups, but they may not provide as much insight into changes over time.
Examples of Quantitative Market Research Questions
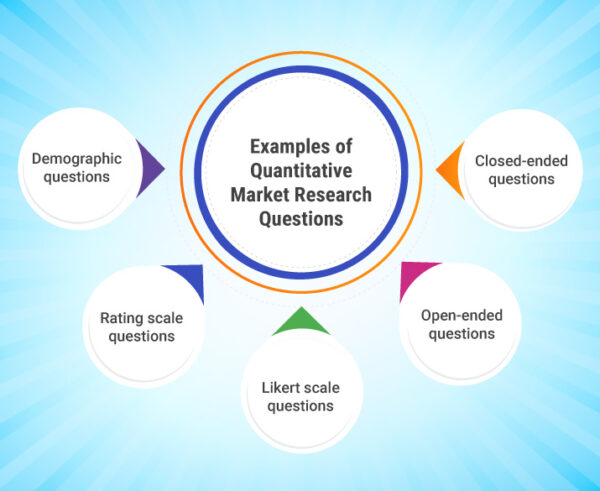
There are several types of quantitative market research questions that can be used in the research process. Here are several of the most frequently used types:
1. Closed-ended questions
Closed-ended questions are questions that have a limited set of response options. Respondents are asked to select one or more options from a list of predefined responses. Closed-ended questions are useful for collecting objective and measurable data that can be analyzed statistically.
Example: How often do you purchase coffee?
- a) Daily
- b) Weekly
- c) Monthly
- d) Rarely
- e) Never
2. Open-ended questions
Open-ended questions are questions that allow respondents to provide their own answers, without any predefined response options. Open-ended questions are useful for gathering detailed and nuanced information, but they can be more difficult to analyze statistically.
Example: What factors influence your decision to purchase coffee?
3. Likert scale questions
Likert scale questions are questions that ask respondents to indicate their level of agreement or disagreement with a statement on a scale. The scale typically ranges from strongly agree to strongly disagree, with several points in between. Likert scale questions are useful for gathering data on attitudes and opinions.
Example: The quality of the coffee meets your expectation. What is your thought?
- a) Strongly agree
- b) Agree
- c) Neutral
- d) Disagree
- e) Strongly disagree
4. Rating scale questions
Rating scale questions are questions that ask respondents to rate a particular product or service on a numerical scale. Rating scale questions are useful for gathering data on customer satisfaction and product performance.
Example: On a scale of 1-10, how likely are you to recommend our coffee to a friend?
5. Demographic questions
Demographic questions are questions that ask respondents to provide information about their age, gender, income, education level, and other demographic characteristics. Demographic questions are useful for segmenting the market and understanding differences in consumer behavior across demographic groups.
Example: What is your age?
- a) Under 18
- b) 18-24
- c) 25-34
- d) 35-44
- e) 45-54
- f) 55 or older
Learn more: What is quantitative research?
9 Best Practices for Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research questions are an essential component of the research process. By crafting effective research questions, businesses can gather objective and measurable data that can inform their decision-making processes. By using a combination of closed-ended, open-ended, Likert scale, rating scale, and demographic questions, businesses can gather a comprehensive range of data on consumer behavior, attitudes, preferences, and demographics.
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of quantitative market research, it is essential to follow best practices throughout the research process. Here, we will explore the key best practices for conducting successful quantitative market research.
- Define Clear Research Objectives: Before initiating any quantitative market research project, it is crucial to define clear research objectives. What specific information or insights are you seeking to obtain? Are you interested in understanding market size, identifying customer segments, or evaluating the effectiveness of a marketing campaign? Defining research objectives will guide the entire research process, from questionnaire design to data analysis.
- Use Valid and Reliable Measurement Tools: Selecting valid and reliable measurement tools is essential for accurate data collection. Whether it is designing surveys, questionnaires, or experiments, the measurement instruments should be well-constructed, properly validated, and free from bias. Pre-testing the measurement tools with a small sample can help identify and address any issues before conducting the full study.
- Ensure a Representative Sample: The sample used in quantitative research should be representative of the target population to generalize findings effectively. Random sampling techniques, such as simple random sampling or stratified sampling, can help ensure that each member of the population has an equal chance of being included in the study. Adequate sample size calculation based on statistical principles should be performed to ensure the study’s power and reliability.
- Design Clear and Unambiguous Questionnaires: The questionnaire design plays a critical role in quantitative market research. Questions should be clear, concise, and unambiguous to minimize response errors and ensure data accuracy. Avoid leading questions or biased language that may influence respondents’ answers. Properly sequencing questions and using appropriate response scales (e.g., Likert scales, multiple-choice options) can also enhance the quality of data collected.
- Pilot Test the Questionnaire: Before conducting the full-scale study, it is advisable to conduct a pilot test with a small sample to identify any potential issues with the questionnaire. Pilot testing helps validate the measurement tools, identify ambiguities, and gauge the time required to complete the survey. Feedback from pilot participants can provide valuable insights for refining and improving the questionnaire.
- Use Robust Data Analysis Techniques: Applying appropriate data analysis techniques is essential for deriving meaningful insights from quantitative research. Statistical methods such as descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, regression analysis, and significance testing can help uncover relationships, trends, and patterns in the data. Employing advanced analytics tools and software can facilitate complex data analysis and visualization.
- Ensure Data Quality and Accuracy: Maintaining data quality and accuracy is crucial in quantitative market research. Data cleaning and validation processes should be employed to identify and rectify errors or inconsistencies in the data. Outliers, missing data, and other anomalies should be addressed appropriately to ensure the reliability and integrity of the data set.
- Interpret Findings with Context: When interpreting quantitative research findings, it is essential to consider the broader context and implications. Avoid overgeneralizing or drawing unwarranted conclusions based on statistical significance alone. Qualitative research methods, such as follow-up interviews or focus groups, can provide additional context and help explain the underlying reasons behind quantitative findings.
- Communicate Results Effectively: Effectively communicating research findings is crucial for driving data-driven decision-making within an organization. Presenting results in a clear, concise, and visually engaging manner helps stakeholders understand the key insights and implications. Visual aids such as charts, graphs, and infographics can effectively convey complex information. Tailor the presentation of findings to the audience, highlighting actionable recommendations.
Learn more: What is Quantitative Observation?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.