What is Primary Market Research?
Primary market research is defined as the process of collecting and analyzing data directly from original sources to gain insights and information about a specific market, target audience, product, or service. This type of research involves gathering information that is not readily available through existing sources, such as published reports, databases, or literature.
Primary market research characteristics
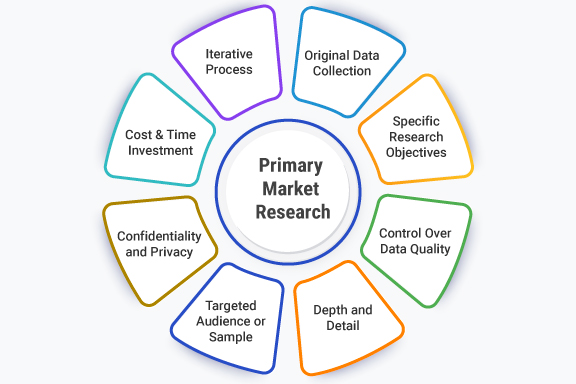
Primary market research is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from secondary research and make it a valuable tool for gaining insights into specific business-related questions or issues:
- Original Data Collection: Primary research involves the collection of original data directly from the source. Researchers gather information firsthand rather than relying on existing data sources.
- Specific Research Objectives: Primary research is conducted with clear and well-defined research objectives or questions in mind. It is designed to address specific business concerns or information gaps.
- Customization: Researchers have the flexibility to design research methodologies such as qualitative research methods and data collection instruments (such as surveys or interviews) that are tailored to the unique needs of the research project.
- Control Over Data Quality: Since data is collected directly, researchers have control over the quality and accuracy of the data. They can ensure that the data collected aligns with the research objectives.
- Depth and Detail: Primary research often provides in-depth insights into the subject of study. Researchers can explore topics comprehensively and may uncover nuances and details that may not be readily available through secondary sources.
- Fresh and Current Information: Primary research provides up-to-date information because it is conducted in real time or within a specific timeframe. This is particularly valuable for industries or markets that are rapidly evolving.
- Flexibility in Data Collection Methods: Researchers can choose from a variety of data collection methods, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, experiments, and more, depending on what is most suitable for their research objectives.
- Targeted Audience or Sample: Primary research allows researchers to select a specific target audience or sample group that closely aligns with the research objectives. This ensures that the data collected is relevant to the study.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: Researchers can ensure the confidentiality and privacy of participants, which may be crucial when sensitive or proprietary information is involved.
- Cost and Time Investment: Primary research can be more resource-intensive in terms of time and cost compared to secondary research because it involves designing, conducting, and analyzing research activities from scratch.
- Potential Bias: While primary research offers control, it can also be influenced by researcher bias or participant bias. Researchers need to take steps to minimize these biases.
- Sample Size: The sample size in primary research can vary widely based on research goals and resources. A larger sample size can enhance the reliability of the findings.
- Iterative Process: In some cases, primary research may involve an iterative process, where initial findings inform further research or adjustments to research methodologies.
Overall, primary market research is a valuable tool for organizations looking to gain a deep understanding of their target audience, industry, or specific business challenges. Its customization, control, and focus on collecting fresh and relevant data make it an essential component of strategic decision-making and market analysis.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
Primary and secondary market research are two distinct approaches to gathering information and data for business purposes. Here’s a comparison of the two:
1. Nature of Data
- Primary Research: Involves collecting original data directly from individuals, groups, or sources. This data is specific to the research objectives and is not previously available. Examples include surveys, interviews, and observations.
- Secondary Research: Involves using existing data and information that has already been collected by others for different purposes. This data is readily available and includes sources like reports, articles, industry studies, and public databases.
2. Cost and Time
- Primary Research: Typically more time-consuming and costly because it involves designing and conducting research activities from scratch, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Secondary Research: Generally faster and more cost-effective as it relies on already available data. However, accessing certain proprietary or specialized sources may incur costs.
3. Objectivity
- Primary Research: Allows for more control over the research process, ensuring that data is collected according to specific research objectives. However, it may be influenced by the biases of the researchers or participants.
- Secondary Research: Data is typically collected by third parties, so it may be more objective and less influenced by the biases of the organization conducting the research.
4. Customization
- Primary Research: Provides the opportunity to tailor research instruments and methodologies to address specific research questions or business needs.
- Secondary Research: Offers pre-existing data, which may not always align perfectly with the research objectives and may require adaptation or supplementation.
5. Depth of Insights
- Primary Research: Often provides deeper insights into specific issues or questions because it is designed to address particular concerns and allows for in-depth exploration.
- Secondary Research: Provides a broader overview of the market or topic, but it may not offer the same level of detail or granularity as primary research.
6. Timing
- Primary Research: Takes time to plan, execute, and analyze, so it may not be suitable for time-sensitive decisions.
- Secondary Research: This can be quickly accessed, making it more suitable for time-critical decisions.
7. Risk
- Primary Research: Carries the risk of investing resources in research activities that may not yield the desired results or insights.
- Secondary Research: Involves less risk because it relies on existing data, but there may be limitations in terms of data relevance or quality.
In practice, businesses often use a combination of both primary and secondary research to inform their decision-making processes. Secondary research can provide a foundational understanding of a market or industry, while primary research can offer specific, tailored insights to address unique business needs or challenges. The choice between primary and secondary research depends on factors like research objectives, budget, time constraints, and the depth of information required.
Learn more: What is Customer Research?
12 Primary Market Research Methods
Primary market research involves various methods for collecting original data directly from sources to answer specific research questions or address business needs. Here are some common primary market research methods:
1. Surveys: Surveys involve creating structured questionnaires or online forms and distributing them to a selected group of respondents. They can be conducted through phone, email, in-person interviews, or online platforms. Surveys are versatile and can gather quantitative data on customer preferences, opinions, and behaviors.
2. Interviews: Conducting one-on-one interviews with individuals or stakeholders can provide in-depth insights. Interviews can be structured (using a predetermined set of questions) or unstructured (allowing for open-ended discussions). They are particularly useful for exploring complex topics and gathering qualitative data.
3. Focus Groups: Focus groups consist of small groups of participants who engage in structured discussions led by a moderator. This method is valuable for exploring group dynamics, uncovering shared opinions, and understanding the nuances of participant perspectives. It’s often used in marketing research.
4. Observational Research: This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors, interactions, or events in real-world settings. Observational research such as qualitative observation can provide insights into consumer behavior, product usage patterns, and physical environments.
5. Experiments: Experiments allow researchers to manipulate variables and observe the effects on outcomes. They are often used to test hypotheses and determine causal relationships. For example, A/B testing in marketing involves experimenting with two different versions of a webpage or email to see which one performs better.
6. Online Research: Leveraging the internet for research purposes can be cost-effective and efficient. Online methods include online surveys, social media listening, website analytics, and data mining. These methods are suitable for gathering data from a large and diverse audience.
7. Field Research: Field research involves collecting data directly from the natural environment or location of interest. It can include activities like site visits, environmental studies, and on-site observations. Field research is common in geography, ecology, and social sciences.
8. Product Testing: Companies may conduct product testing with real users to assess product usability, functionality, and user satisfaction. Usability testing, in particular, helps identify user experience issues and refine product designs.
9. Mystery Shopping: Mystery shoppers are individuals hired to pose as regular customers and evaluate the quality of service and customer experience at retail stores, restaurants, or service providers. This method is often used in customer service assessments.
10. Ethnographic Research: Ethnography involves immersing researchers in the target audience’s culture and environment to gain a deep understanding of their behaviors, customs, and needs. It’s commonly used in anthropology and consumer research.
11. Content Analysis: Content analysis involves systematically analyzing written or visual content, such as documents, social media posts, or advertisements, to extract meaningful insights or patterns. It’s often used in media studies and social sciences.
12. Diaries and Journals: Participants keep diaries or journals to record their experiences, thoughts, or behaviors over a specified period. This method can provide valuable longitudinal data.
The choice of primary research method depends on the research objectives, the nature of the data needed, the target audience, available resources, and the depth of insights required. Researchers often use a combination of methods to triangulate findings and ensure the validity and reliability of the research results.
Learn more: What is Research Objective?
Top 10 Primary Market Research Examples
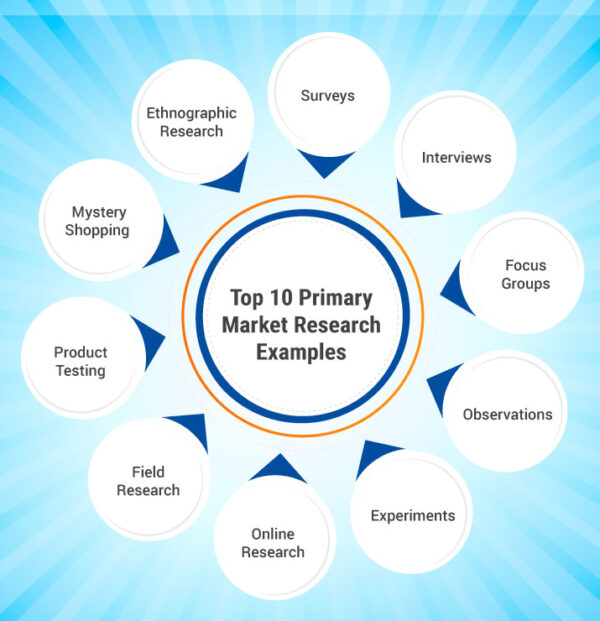
Primary market research involves collecting original data directly from individuals, groups, or sources to address specific research objectives or business questions. Here are some examples of primary market research methods and how they can be applied:
1. Surveys
Surveys are a common method of primary research. You can create questionnaires and distribute them to a targeted audience to collect data on various topics. For example:
A company launching a new product can conduct a survey to gather feedback on product features, pricing, and preferences from potential customers.
2. Interviews
Conducting one-on-one interviews with individuals can provide in-depth insights. Examples include:
- An educational institution interviewing recent graduates to understand their career goals and assess the effectiveness of its programs.
- A healthcare provider interviews patients to gauge satisfaction levels and identify areas for improvement in service quality.
3. Focus Groups
Focus groups involve small, structured discussions with a select group of participants who share certain characteristics or interests. They can be used for:
- A marketing agency organizes focus groups to evaluate the effectiveness of an advertising campaign and gather opinions on messaging and imagery.
4. Observations
Observational research involves directly watching and recording behaviors, interactions, or activities in real-world settings. For instance:
- A retail store owner observes customer traffic patterns and shopping behavior to optimize store layout and product placement.
4. Experiments
Controlled experiments allow you to manipulate variables to test hypotheses. Examples include:
- A food manufacturer conducts taste tests to determine the preferred flavor of a new snack product.
- An e-commerce website testing different website designs to measure their impact on user engagement and conversion rates.
6. Online Research
Leveraging online platforms and tools for primary research can be cost-effective. This might include:
- An e-commerce business analyzing website analytics data and user feedback to improve the online shopping experience.
- A social media company conducts surveys on its platform to understand user preferences and gather feedback on new features.
7. Field Research
Field research involves gathering data directly from the field, often in real-world environments. Examples include:
- An environmental organization conducting field research to assess the impact of pollution on a local ecosystem.
- A tourism agency studying tourist behavior and preferences by conducting on-site surveys at popular travel destinations.
8. Product Testing
Companies can use primary research to test new products or prototypes. For example:
- An electronics manufacturer may conduct usability testing with potential users to identify and address product design flaws.
9. Mystery Shopping
- Mystery shoppers pose as regular customers to evaluate the quality of service and customer experience at retail stores, restaurants, or service providers.
10. Ethnographic Research
- This involves immersing researchers in the target audience’s environment to gain a deep understanding of their culture, behaviors, and needs. It’s often used in anthropology and marketing to study consumer behavior.
These are just a few examples of primary market research methods. The choice of method depends on the research objectives, target audience, available resources, and the depth of insights required to make informed business decisions.
Learn more: What is Focus Group Research?
15 Best Practices of Primary Market Research
To conduct effective primary market research, it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure that your research is well-planned, executed, and provides valuable insights. Here are some primary market research best practices:
1. Clearly Define Objectives: Start by defining specific and well-defined research objectives. What questions do you want to answer? What information do you need to collect? Establishing clear objectives will direct your research endeavors.
2. Identify Your Target Audience: Determine the group or individuals you need to gather data from. Understand their demographics, preferences, and behaviors to create a sample that represents your target market accurately.
3. Choose the Right Research Method: Select the research method or methods that align with your objectives and the type of data you need. Consider factors like budget, timeline, and the depth of insights required.
4. Develop a Research Plan: Create a detailed research plan that outlines the research methodology, data collection process, timeline, and budget. Having a well-structured plan helps you stay organized and focused.
5. Design Effective Research Instruments: If you’re using surveys, questionnaires, or interview scripts, ensure they are well-crafted. Use clear, unbiased, and unambiguous language. Pilot-test your instruments to identify and address any issues before conducting the full research.
6. Recruit a Representative Sample: If your research involves a sample group, make sure it represents your target audience accurately. Random sampling or stratified sampling can help reduce bias.
7. Ensure Data Quality: Implement quality control measures to ensure accurate and reliable data collection. Train interviewers or survey administrators, monitor the data collection process, and validate responses when possible.
8. Maintain Ethical Practices: Respect participants’ privacy, obtain informed consent, and ensure that your research complies with ethical guidelines and regulations, especially when dealing with sensitive topics or personal data.
9. Minimize Bias: Be aware of potential sources of bias in your research, such as confirmation bias or leading questions in surveys. Take steps to minimize these biases in your data collection and analysis.
10. Use a Mix of Data Sources: Whenever possible, triangulate your findings by using multiple data sources or research methods. This can enhance the validity and reliability of your results.
11. Manage Data Effectively: Implement a data management plan to organize, store, and secure your research data. Use appropriate tools and software for data collection, storage, and analysis.
12. Analyze Data Thoroughly: Conduct a robust analysis of your data to draw meaningful insights. Use appropriate statistical techniques, visualization tools, or qualitative research methods, depending on your research type.
13. Report Findings Clearly: Present your research findings in a clear and concise manner. Use visuals like charts and graphs to illustrate key points. Provide recommendations based on your findings.
14. Iterate and Improve: After completing your research, evaluate the process and outcomes. Consider what worked well and what could be improved for future research projects.
15. Act on Insights: Use the insights gained from your research to make informed business decisions. Your research should have a practical impact on your organization’s strategy, product development, marketing, or other areas.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your primary market research is well-conducted, reliable, and valuable for making informed business decisions. Additionally, consider seeking guidance from experienced researchers or consulting experts in research methods if you are new to primary research.
Learn more: What is Research Design?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.