Table of Contents
What is Focus Group Research?
Focus group research is defined as a qualitative research method used to gather data from a small, diverse group of people in a facilitated group discussion. This method is commonly used in marketing and social science research to gain insight into the opinions, attitudes, and perceptions of a target audience.
In a typical focus group, a moderator leads a discussion among a group of 6-12 participants, who are chosen based on certain demographic or psychographic criteria, such as age, gender, income, or lifestyle. The participants are asked open-ended questions about a particular topic, product, or service, and are encouraged to share their opinions, experiences, and feelings with the group.
Focus group research Key characteristics
Focus group research has several key characteristics that distinguish it as a qualitative research method:
- Small Group Dynamics: Focus group research involve a small number of participants, typically ranging from 6 to 10 individuals. This small size allows for meaningful interactions and in-depth discussions.
- Moderator-Led Discussions: A trained moderator guides the focus group discussion. The moderator’s role is to facilitate the conversation, ask open-ended questions, and ensure that all participants have an opportunity to share their thoughts and opinions.
- Interactive and Group-Based: Participants engage in a group discussion rather than responding to surveys or questionnaires individually. The interactions among participants can lead to the generation of new ideas and perspectives.
- Qualitative Data Collection: Focus group research generates data through qualitative research, which is descriptive, non-numerical information. The aim is to capture the richness of participants’ experiences, attitudes, beliefs, and opinions.
- Open-Ended Questions: Participants are prompted with open-ended questions that encourage them to elaborate on their thoughts and provide detailed responses. This approach allows for the exploration of complex ideas and viewpoints.
- Exploration of Perceptions: Focus group research delve into participants’ perceptions, feelings, and experiences related to a specific topic. This provides insight into the underlying reasons behind behaviors and attitudes.
- Non-Verbal Communication: In addition to spoken responses, focus group moderators pay attention to participants’ body language, facial expressions, and other non-verbal cues that can reveal hidden meanings or emotions.
- Multiple Perspectives: Focus group research brings participants together with diverse backgrounds, experiences, and viewpoints. This diversity can lead to a rich exchange of ideas and insights.
- Flexible Structure: While focus group research sessions are guided by a moderator, the discussions themselves can be fluid and dynamic, allowing participants to explore various aspects of the topic.
- Observation and Analysis: Focus group research sessions are typically recorded and transcribed for later analysis. Researchers identify patterns, themes, and recurring ideas in the data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Contextual Understanding: Focus group research is well-suited for exploring the contextual factors that shape participants’ attitudes and behaviors. It provides a deeper understanding of how individuals interact within their social and cultural environments.
- Pilot Testing and Pre-Testing: Focus group research is sometimes used to pilot test or pre-test concepts, materials, or ideas before broader implementation. This helps identify potential issues and refine strategies.
- In-Depth Exploration: Focus group research allows for a deeper exploration of topics that might not be fully captured through quantitative methods alone. They provide context and nuance that can be essential for decision-making.
- Limitations: While focus group research is valuable, it has limitations. Findings are context-specific and may not be easily generalizable to larger populations. Careful consideration is needed when interpreting the results.
Focus group research is a valuable method for gaining insights into participants’ perspectives, attitudes, and experiences. It can help researchers and organizations make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, and gain a deeper understanding of complex topics.
Types of the Focus Group Research
There are several types of focus group research that can be conducted, depending on the specific objectives and research goals. Here are some common types of focus groups:
- Traditional focus groups: These are the most common type of focus group, where participants are physically gathered in a room to discuss the topic at hand. This type of focus group allows for a more personal and interactive discussion but may be limited by geographical constraints and may be costly to conduct.
- Online focus groups: These are conducted online, either through video conferencing or a web-based platform. Online focus groups are more convenient and cost-effective than traditional focus groups and can reach participants from different geographic locations. However, they may be limited by technological issues and may need a more personal touch of face-to-face interaction.
- Dual-moderated focus groups: In this type of focus group research, two moderators facilitate the discussion, with one focusing on the content and the other on the group dynamics. This type of focus group allows for a more in-depth and comprehensive discussion but may be more complex to conduct and analyze.
- Mini-focus groups: These are smaller, more intimate groups of 3-5 participants, and are used when the topic of discussion is sensitive or complex. Mini-focus groups allow for a more personal and detailed discussion, but may not be representative of the larger population.
Learn more: What is Qualitative Observation?
Focus Group Research Method: 6 Key Steps
Conducting focus group research can be an effective way to gather rich, in-depth data that can inform product development, marketing strategies, and other business decisions. Here are some steps to follow when conducting focus group research:
Step 1: Research questions and objectives
Before conducting focus group research, it’s essential to define the research question and objectives. This will help to guide the discussion and ensure that you gather the data you need. Consider what you want to learn from the focus group, and what specific questions you want to ask participants. It’s important to be clear about what you want to achieve and how the data will be used.
Step 2: Recruit participants
Choose participants who fit the criteria you have set for your research. You can recruit participants through social media, online advertising, or by contacting relevant organizations. Make sure you provide clear instructions on the time, location, and duration of the focus group research. It’s essential to ensure that the participants are representative of the target audience and that you have a diverse range of participants who can provide a range of perspectives.
Step 3: Choose a location and prepare the equipment
Choose a location that is comfortable and conducive to discussion. It’s essential to ensure that the room is quiet, private, and has enough space to accommodate all participants. You will also need to ensure that you have all the equipment you need, such as recording devices and notepads. Make sure you test all the equipment beforehand to avoid any technical issues.
Step 4: Conduct the focus group
Begin by introducing yourself and explaining the purpose of the focus group. Make sure you establish the ground rules, such as respecting each other’s opinions, avoiding interrupting each other, and maintaining confidentiality. Then, ask open-ended questions to encourage participants to share their thoughts and opinions. It’s important to listen actively and avoid leading the discussion. Encourage all participants to participate and ensure that everyone has an opportunity to speak.
Step 5: Analyze the data
After the focus group, transcribe the recording and analyze the data. Look for common themes, patterns, and trends that emerge from the discussion. You can use software tools to help you analyze the data, such as NVivo or Dedoose. Make sure you organize the data into categories and subcategories to make it easier to analyze.
Step 6: Draw conclusions and report the findings
Based on the data you’ve gathered, draw conclusions and report the findings to the relevant stakeholders. These findings can be used to inform product development, marketing strategies, and other business decisions. Make sure you present the data in a clear and concise manner, using charts, graphs, and other visual aids to help illustrate the findings.
Conducting focus group research can be a valuable way to gather insights into the attitudes, beliefs, and experiences of your target audience. By following these steps, you can ensure that you gather high-quality data that can be used to inform business decisions.
Learn more: What is Qualitative Market Research?
Advantages and Limitations of Focus Group Research
Focus group research offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to carefully consider its suitability for a particular research project. Here, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of focus group research, helping you understand its potential benefits and limitations.
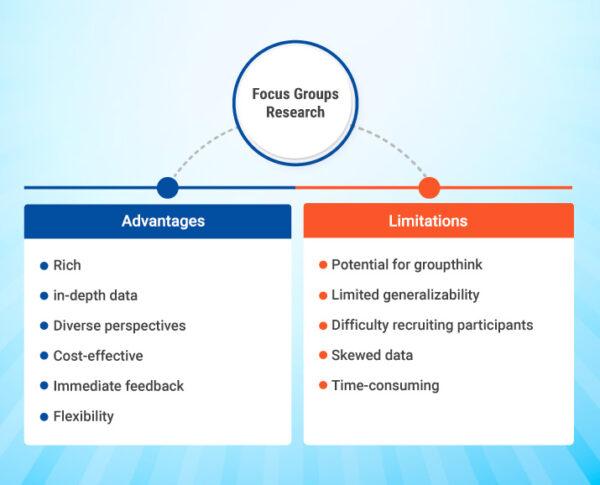
Advantages of focus group research:
- Rich, in-depth data: Focus group research can provide rich, in-depth data that can help businesses gain a deeper understanding of their target audience’s attitudes, beliefs, and experiences.
- Diverse perspectives: Focus groups bring together participants with diverse perspectives, providing businesses with a range of opinions and ideas.
- Cost-effective: Compared to quantitative research or other research methods, focus group research is a cost-effective way of gathering data.
- Immediate feedback: Focus group research provides immediate feedback, allowing businesses to make adjustments and improvements quickly.
- Flexibility: Focus group research can be flexible and adaptable to suit the needs of the research question. For example, it can be used to test new products, evaluate existing products, or gather customer feedback on marketing campaigns.
Limitations of focus group research:
- Potential for groupthink: Groupthink is a phenomenon where individuals conform to the group’s opinions and ideas, leading to a lack of diversity in the data.
- Limited generalizability: The data gathered from a focus group may not be representative of the wider population, making it difficult to generalize the findings.
- Difficulty recruiting participants: Recruiting participants can be challenging, particularly if the research requires a specific demographic or expertise.
- Skewed data: The data gathered from a focus group research can be influenced by the moderator’s bias, the group dynamics, or the participants’ desire to please the moderator.
- Time-consuming: Focus group research can be time-consuming, requiring a significant investment of time and resources.
It is important to consider both the advantages and disadvantages of focus group research when deciding whether it is the right research method for your needs. Careful planning, preparation, and execution can help to mitigate the disadvantages and maximize the advantages of focus group research.
Focus Group Research Examples
These focus group research questions are just examples and can be tailored to fit the specific research needs of a business or organization. The key is to ask open-ended questions that allow participants to express their thoughts and opinions freely, while also ensuring that the questions are specific enough to provide actionable insights. Here are some examples of focus group research questions.
Example 1. Product development questions:
- What features are most important to you when considering a new smartphone?
- What do you think of the packaging design for this new snack food?
- What would make you more likely to try a new fitness app?
Example 2. Marketing campaigns questions:
- What are your thoughts on the messaging in this ad campaign?
- What type of imagery would you associate with this type of clothing brand?
- How do you feel about the tone of voice in this social media campaign?
Example 3. Customer experience questions:
- What are your expectations when visiting a coffee shop?
- What do you think of the menu offerings at this restaurant?
- What are the most important factors to consider when choosing a hotel to stay in?
Example 4. Brand perception questions:
- How would you describe your perception of this brand?
- What do you think of the logo for this new startup?
- What emotions come to mind when you think of this clothing brand?
Example 5. User experience questions:
- How easy was it to navigate through this app?
- What do you think of the overall design of this website?
- How intuitive is this new software program to use?
Learn more: What is Customer Feedback?
Top 15 Focus Group Research Best Practices
When conducting focus group research, it is important to follow best practices to ensure the validity and reliability of the data collected. Below are several essential best practices to consider:
1. Define objectives: Clearly define the research objectives and the specific information you hope to gather from the focus group. This will serve as a valuable resource to steer the entire research process in the right direction.
2. Recruit participants: Carefully select participants who are representative of your target audience or specific demographics. Use appropriate screening criteria to ensure participants meet the desired characteristics.
3. Group size: Aim for a group size of 6-10 participants. This number allows for meaningful interaction and discussion without becoming overwhelming or too diluted.
4. Moderator selection: Choose an experienced moderator who can facilitate the discussion effectively. The moderator should be skilled in keeping the conversation focused, encouraging participation, and managing any potential conflicts.
5. Discussion guide: Prepare a well-structured discussion guide that outlines the key topics and questions to be addressed during the focus group research. This will help ensure consistency across groups and provide a framework for the moderator.
6. Establish rapport: Begin the session by establishing rapport with the participants. Create a comfortable and non-threatening environment where participants feel encouraged to share their opinions and experiences.
7. Encourage participation: Actively encourage participation from all participants. Ensure that everyone has an opportunity to contribute and that no individual dominates the conversation.
8. Active listening: The moderator should actively listen to participants’ responses, follow up on interesting points, and probe deeper when necessary. This helps to elicit richer insights and encourages participants to elaborate on their thoughts.
9. Avoid leading questions: Ask open-ended questions that allow participants to express their thoughts freely. Avoid leading questions that may influence or bias responses.
10. Use multiple moderators or observers: Consider having multiple moderators or observers present during the focus group research to capture a variety of perspectives and ensure comprehensive data collection.
11. Document and record: Take detailed notes during the session or consider recording the discussion with the participants’ consent. This will help in analyzing the data accurately and capturing nuances that may be missed during live observation.
12. Maintain confidentiality: Assure participants that their responses will be kept confidential. This helps create a safe space for open and honest discussion.
13. Analyze and interpret: Thoroughly analyze the collected data, looking for common themes, patterns, and insights. Use a systematic approach to identify key findings and draw meaningful conclusions.
14. Triangulation: Consider using multiple research methods (such as quantitative and qualitative research methods), and sources of data to validate and cross-reference the findings from the focus group research. This can help enhance the credibility of the research.
15. Report findings: Present the findings in a clear and concise manner, highlighting the key insights and recommendations. Provide an accurate and comprehensive report that can be easily understood by stakeholders.
Learn more: What is Customer Experience (CX) Research?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.