Table of Contents
What is Continuous Innovation?
Continuous innovation is defined as the ongoing process of introducing new ideas, methods, products, or services within an organization or industry to maintain a competitive edge and drive growth. It is the practice of consistently seeking and implementing improvements, advancements, and changes to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Unlike traditional and discontinuous innovation, which often involves major breakthroughs or disruptive changes, continuous innovation focuses on making incremental improvements and adaptations over time. It emphasizes a proactive approach to innovation, where organizations continually identify opportunities for enhancement and react swiftly to market shifts and customer needs.
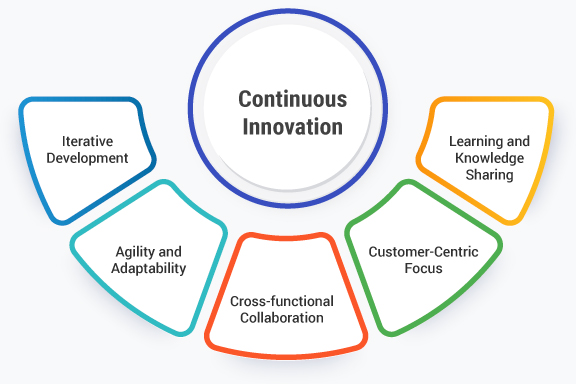
Continuous innovation involves several key elements:
- Iterative Development: It follows an iterative approach where new ideas or concepts are tested, refined, and implemented in multiple cycles. Feedback from customers, users, or employees is gathered and integrated into the development process, leading to continuous refinement and optimization.
- Agility and Adaptability: Continuous innovation requires organizations to be flexible and adaptable to changes in the market, technology, or customer preferences. It involves a willingness to experiment, take risks, and embrace change to stay responsive and relevant.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: It encourages collaboration across different teams, departments, or even external stakeholders to foster a culture of innovation. Bringing together diverse perspectives and expertise can lead to creative solutions and accelerate the innovation process.
- Customer-Centric Focus: Continuous innovation places a strong emphasis on understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points. By collecting and analyzing customer feedback and data, organizations can develop and refine products or services that better meet customer expectations.
- Learning and Knowledge Sharing: It involves a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing within the organization. Employees are encouraged to share ideas, insights, and best practices, creating an environment that supports innovation and fosters personal and professional growth.
Continuous innovation is particularly relevant in dynamic industries where technological innovation and changing consumer demands drive rapid transformations. By embracing continuous innovation, organizations can improve their products, streamline processes, enhance customer experiences, and ultimately gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Benefits and Challenges of Continuous Innovation
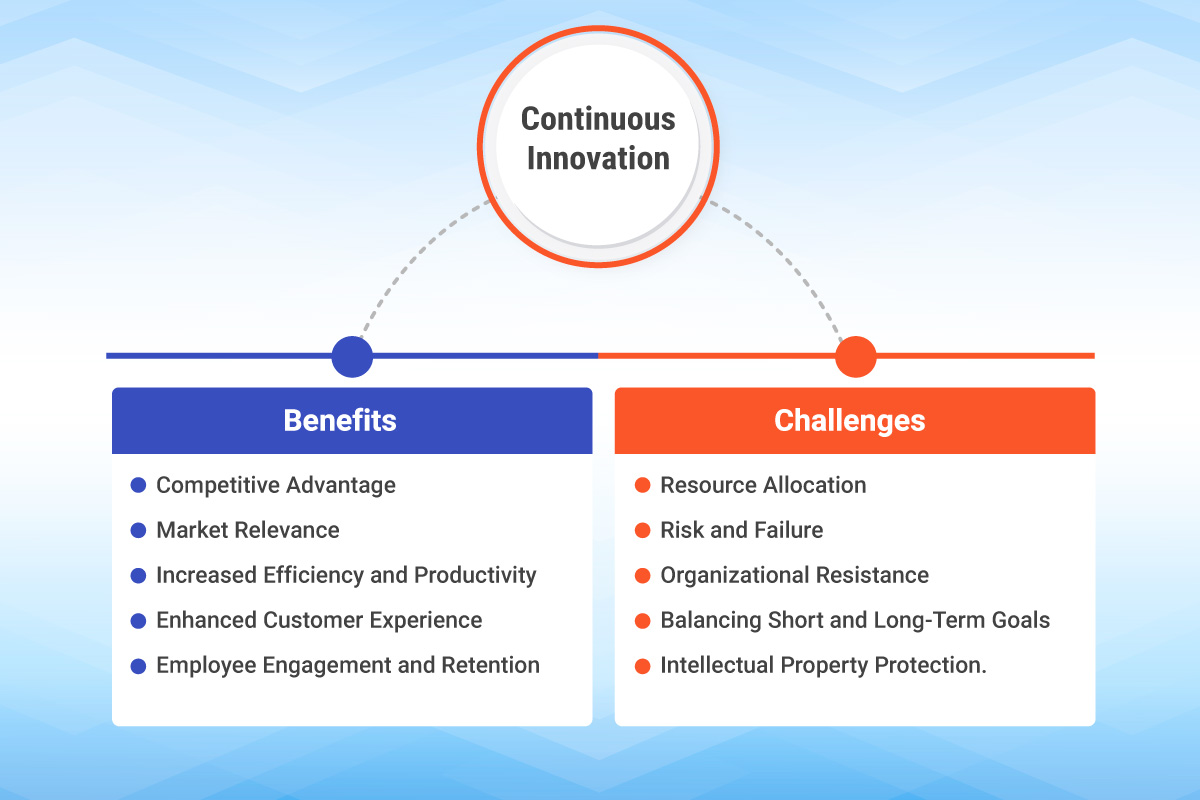
Benefits of Continuous Innovation:
- Competitive Advantage: Continuous innovation allows organizations to stay ahead of the competition by regularly introducing new and improved products, services, or processes. It enables them to differentiate themselves in the market and meet evolving customer needs, giving them a competitive edge.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Continuously innovating allows organizations to better understand their customers and deliver enhanced experiences. By actively seeking customer feedback and integrating it into product innovation, companies can create solutions that address customer pain points and deliver added value.
- Market Relevance: By continuously innovating, organizations can adapt to changing market dynamics, emerging trends, and customer preferences. This helps them to remain relevant and avoid becoming obsolete in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Continuous innovation often involves process innovation and the adoption of new technologies, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. By streamlining operations and eliminating bottlenecks, organizations can optimize resource utilization and achieve better outcomes.
- Employee Engagement and Retention: A culture of innovation fosters employee engagement and encourages them to contribute ideas, take ownership, and embrace new challenges. This can lead to higher job satisfaction, improved retention rates, and a more innovative and motivated workforce.
Challenges of Continuous Innovation:
- Resource Allocation: Continuous innovation requires investments in research, development, and experimentation. Allocating sufficient resources, both financial and human, can be a challenge, especially for smaller organizations with limited budgets or competing priorities.
- Risk and Failure: Innovation inherently involves risk, and not all ideas or initiatives will succeed. Continuous innovation requires organizations to embrace failure as a learning opportunity and be willing to take calculated risks. However, managing risk and minimizing potential negative impacts can be a challenge.
- Organizational Resistance: Some organizations may face resistance to change and innovation from employees or stakeholders who are comfortable with the status quo. Overcoming resistance and fostering a culture that values and encourages innovation may require effective change management strategies and leadership support.
- Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Continuous innovation often involves a balance between short-term and long-term goals. While organizations need to focus on immediate market needs and quick wins, they must also allocate resources for long-term research and development to ensure sustainable innovation.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Continuous innovation can lead to the creation of valuable intellectual property. Protecting intellectual property rights and preventing unauthorized use or infringement can be a complex and ongoing challenge, requiring legal safeguards and strategies.
Learn more: What is Disruptive Innovation?
Continuous Innovation Process: 7 Key Steps
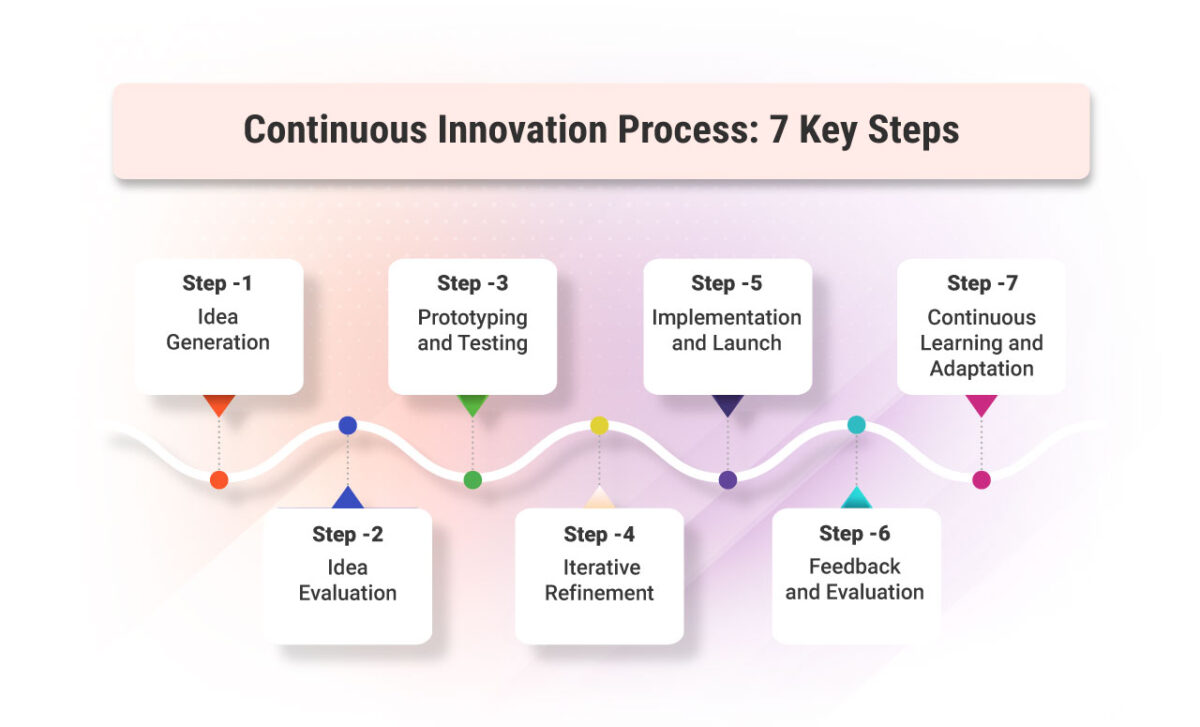
The continuous innovation process involves several key steps that organizations can follow to foster a culture of innovation and drive ongoing improvements. Here are the key steps in the continuous innovation process:
1. Idea Generation: The first step is to generate a pool of ideas. This can be done through various methods such as brainstorming sessions, suggestion boxes, innovation contests, market research, insights from employees and stakeholders, or customer feedback. The goal is to gather a diverse range of ideas that have the potential to address challenges, improve products or processes, or meet customer needs.
2. Idea Evaluation: Once a collection of ideas is generated, the next step is to evaluate their feasibility and potential impact. Ideas can be evaluated based on various criteria, such as alignment with strategic objectives, market demand, technical feasibility, resource requirements, and potential risks. This evaluation helps prioritize and select the most promising ideas to move forward.
3. Prototyping and Testing: Selected ideas are then developed into prototypes or minimum viable products (MVPs). Prototyping allows organizations to quickly create tangible representations of ideas to gather feedback and assess their viability. Testing involves putting prototypes in the hands of users or conducting experiments to gather data, validate assumptions, and identify areas for improvement.
4. Iterative Refinement: Based on the feedback and data gathered from testing, the next step is to refine and improve the prototype or MVP. This iterative refinement process involves making incremental changes, addressing identified issues, and enhancing features or functionality. Feedback from users, customers, and stakeholders is continuously incorporated into the development process.
5. Implementation and Launch: Once the prototype or MVP has been refined, it is ready for implementation. This step involves scaling up the innovation and integrating it into the organization’s operations or product/service offerings. Careful planning, coordination, and execution are essential to ensure a smooth transition from development to implementation.
6. Feedback and Evaluation: After the innovation is implemented, organizations gather customer feedback and evaluate its performance. This includes monitoring key metrics, assessing customer satisfaction, and analyzing the impact on business goals. Feedback and evaluation provide insights into the success of the innovation and identify opportunities for further improvements or adjustments.
7. Continuous Learning and Adaptation: The final step is to foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. Organizations should encourage knowledge sharing, capture lessons learned, and apply the insights gained from the innovation process to future initiatives. This creates a feedback loop that feeds back into the ideation stage and drives ongoing innovation and improvement.
6 Key Examples of Continous Innovation
There are numerous examples of continuous innovation across various industries. Here are some key examples:
- Apple Inc.: Apple is known for its continuous innovation in the technology sector. The company regularly introduces new versions of its products, such as the iPhone, iPad, and Mac computers, with incremental innovation in design, features, and performance. Apple also innovates in software and services, regularly releasing updates and new features to enhance user experience and stay ahead in the market.
- Amazon: Amazon is a prime example of continuous innovation in the e-commerce industry. The company continually introduces new services, such as Amazon Prime, which offers fast shipping and exclusive content, and expands into new areas like cloud computing with Amazon Web Services (AWS). Amazon constantly seeks ways to enhance its customer experience, logistics, and delivery systems to maintain its market leadership.
- Toyota: Toyota has been a pioneer in continuous innovation in the automotive industry. The company’s Toyota Production System (TPS) revolutionized manufacturing with concepts like Just-in-Time and Kaizen (continuous improvement). Toyota regularly introduces new models and enhances existing ones, incorporating technology innovation to meet changing customer demands and improve performance and fuel efficiency.
- Google: Google is renowned for its continuous innovation in the field of internet services and technology. The company constantly introduces new features and updates to its search engine, as well as to its suite of products and services, including Google Maps, Google Docs, and Google Assistant. Google also invests in research and development to explore emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and self-driving cars.
- Procter & Gamble (P&G): P&G is a consumer goods company that exemplifies continuous innovation in its product portfolio. The company continually improves and innovates its brands, introducing new formulations, packaging, and features. P&G also embraces open innovation by collaborating with external partners and leveraging consumer insights to develop innovative products and stay competitive in the market.
- Tesla: Tesla has transformed the automotive industry with its continuous innovation in electric vehicles (EVs). The company consistently improves its EV models by extending battery range, enhancing charging infrastructure, and introducing new features through over-the-air software updates. Tesla also pushes the boundaries of autonomous driving technology, striving to make self-driving cars a reality.
Learn more: What is Business Model Innovation?
Top 10 Best Practices of Continous Innovation Management

Managing continuous innovation effectively requires a set of best practices to foster a culture of innovation, support ongoing improvements, and drive successful outcomes. Here are some key best practices for continuous innovation management:
1. Establish a Clear Innovation Strategy
Develop a clear and well-defined innovation strategy aligned with your organization’s overall goals and objectives. This strategy should outline the areas of focus, target markets, desired outcomes, and resource allocation for innovation initiatives.
2. Foster a Culture of Innovation
Create an encouraging and supportive organizational culture of innovation. This involves promoting openness, creativity, and a willingness to take risks. Encourage employees to generate and share ideas, recognize and reward innovative efforts, and provide opportunities for learning and experimentation.
3. Encourage Cross-functional Collaboration
Encourage the dismantling of silos and cultivate a collaborative environment that promotes cross-departmental and inter-team cooperation. Encourage diverse perspectives and expertise to come together and collaborate on innovation projects. Cross-functional teams can bring different skills and insights to the table, leading to more innovative solutions.
4. Empower and Support Employees
Provide employees with the resources, tools, and autonomy to pursue innovative ideas. Encourage a bottom-up approach, where employees at all levels are empowered to contribute their ideas and take ownership of innovation initiatives. Support them with training, mentorship, and an environment that encourages risk-taking and learning from failures.
5. Implement Effective Idea Management Systems
Establish systems and processes to capture, evaluate, and prioritize ideas effectively. This can include innovation portals, suggestion boxes, or dedicated platforms for idea submission and evaluation. Ensure there is a transparent and well-defined process for evaluating ideas, providing feedback, and moving forward with the most promising ones.
6. Embrace Rapid Prototyping and Iterative Development
Foster a culture of rapid prototyping and iterative development. Encourage the development of minimum viable products (MVPs) or prototypes to quickly test and gather customer feedback. Emphasize the importance of iteration and continuous improvement based on user feedback, market insights, and data-driven decision-making.
7. Foster External Collaboration and Open Innovation
Look beyond internal resources and collaborate with external partners, such as customers, suppliers, research institutions, or startups. Embrace open innovation by seeking external inputs, ideas, and collaborations to complement internal capabilities and expand the innovation ecosystem.
8. Emphasize Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Encourage a learning mindset within the organization. Establish mechanisms for capturing and sharing knowledge, insights, and lessons learned from innovation initiatives. Regularly review and evaluate the performance and impact of innovation projects to identify areas for improvement and apply those learnings to future initiatives.
9. Establish Key Metrics and Evaluation Criteria
Define key metrics and evaluation criteria to measure the success and impact of innovation initiatives. This can include metrics related to revenue growth, market share, customer satisfaction, or employee engagement. Regularly monitor and evaluate these metrics to track progress, make informed decisions, and ensure continuous improvement.
10. Leadership Support and Commitment
Strong leadership support is crucial for continuous innovation. Leaders should communicate the importance of innovation, actively participate in the innovation process, allocate resources, and provide guidance and support. Leadership commitment helps create a culture where innovation thrives and becomes embedded in the organization’s DNA.
Learn more: What is Process Innovation?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.