Table of Contents
What is Idea Management?
Idea management is defined as the process of capturing, organizing, evaluating, and implementing ideas within an organization. It involves creating a structured system to gather ideas from employees, customers, or other stakeholders, and then systematically reviewing and selecting the most promising ideas for further development or implementation.
The goal of idea management is to ignite innovation, improve problem-solving, and drive continuous improvement within an organization. By actively soliciting and managing ideas, companies can tap into the collective intelligence of their employees and stakeholders, leveraging diverse perspectives and knowledge to generate creative solutions and drive growth.
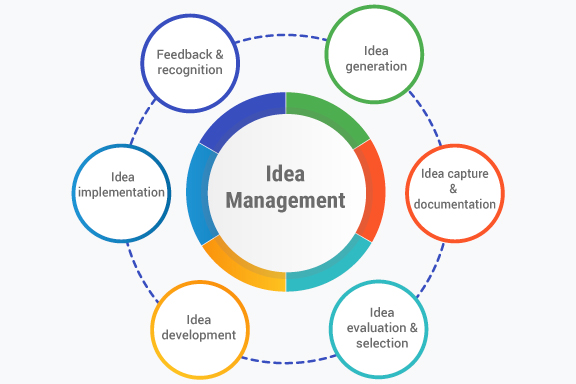
Key components of idea management typically include:
- Idea generation: Encouraging individuals to generate and submit their ideas through various channels, such as suggestion boxes, digital platforms, brainstorming sessions, or innovation challenges.
- Idea capture and documentation: Collecting and recording ideas in a centralized system or platform, ensuring that no valuable ideas are lost or overlooked.
- Idea development: Refining and developing selected ideas further, potentially involving cross-functional collaboration, prototyping, and testing to validate concepts and determine their viability.
- Idea evaluation and selection: Assessing the feasibility, potential impact, and alignment with strategic objectives of each idea. This evaluation may involve expert reviews, feasibility studies, market research, or other evaluation methods.
- Idea implementation: Once an idea has been thoroughly developed and validated, it moves into the implementation phase. This may involve allocating resources, creating action plans, and monitoring progress to bring the idea to fruition.
- Feedback and recognition: Providing feedback to idea contributors, acknowledging their contributions, and recognizing their efforts to encourage ongoing participation and engagement in the idea management process.
Importance of Idea Management for Organizations

By embracing idea management, organizations can stay ahead of the curve, adapt to changing market conditions, and foster a culture of innovation and growth. Idea management holds great importance for organizations due to several key reasons:
- Fostering innovation: Idea management provides a structured framework for nurturing and harnessing innovation within an organization. It encourages employees and stakeholders to share their ideas, which can lead to breakthrough innovations, process improvements, new products or services, and other creative solutions.
- Employee engagement and empowerment: By involving employees in the idea management process, organizations demonstrate that their opinions and contributions are valued. This boosts employee morale, engagement, and satisfaction, as they feel empowered to contribute to the organization’s growth and success.
- Competitive advantage: Ideation through effective idea management can give organizations a competitive edge in the market. By continuously exploring new ideas and implementing innovative solutions, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors, adapt to changing market dynamics, and seize opportunities for growth.
- Problem-solving and continuous improvement: Idea management allows organizations to tap into the collective intelligence of their workforce. By gathering diverse perspectives and insights, organizations can address challenges more effectively, solve complex problems, and drive continuous innovation across various areas of the business.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing: Idea management promotes collaboration and cross-functional communication within an organization. It encourages individuals from different teams, departments, or even external stakeholders to contribute and collaborate on ideas, fostering a culture of knowledge sharing and synergy.
- Risk mitigation: Effective idea management includes a rigorous evaluation and selection process for ideas. By carefully assessing ideas for feasibility, potential risks, and alignment with strategic goals, organizations can identify and address potential pitfalls or challenges early on, minimizing risks associated with implementing unviable ideas.
- Customer-centricity: Idea management can involve gathering ideas and feedback from customers directly. By involving customers in the innovation process, organizations gain valuable insights into customer needs, preferences, and pain points. This customer-centric approach enables organizations to develop products and services that better meet customer expectations and drive customer loyalty.
- Organizational learning: Idea management encourages a culture of innovation for learning and experimentation. It creates an environment where failures are seen as learning opportunities and encourages individuals to share their insights and lessons learned from both successful and unsuccessful ideas. This promotes an environment where learning and improvement are ongoing priorities for the organization.
Learn more: What is Innovation Management?
Idea Management Process: 8 Key Steps
By following these 8 steps, organizations can establish a systematic approach to idea management, promoting innovation, collaboration, and organizational growth.
Step 1. Idea Generation
Encourage individuals to generate and submit their ideas. This can be done through various channels such as suggestion boxes, digital platforms, brainstorming sessions, innovation challenges, or dedicated ideation sessions. The goal is to gather a wide range of ideas from different sources.
Step 2. Idea Capture and Documentation
Collect and document the ideas in a centralized system or platform to ensure they are not lost or overlooked. This could involve creating an idea management software tool or utilizing a digital platform specifically designed for idea capture and tracking. Each idea should be recorded along with relevant details such as the idea originator, date, description, and any supporting documents or visuals.
Step 3. Idea Evaluation and Selection
Evaluate the feasibility, potential impact, and alignment with strategic objectives for each idea. This step involves a thorough review of the ideas by subject matter experts, cross-functional teams, or designated evaluators. The evaluation criteria may include factors such as market potential, resource requirements, technical feasibility, alignment with company values, and the ability to solve a specific problem or meet a customer’s need. Based on the evaluation, ideas are shortlisted or prioritized for further development.
Step 4. Idea Development
Once a selection of promising ideas has been made, they move into the development phase. This involves refining and expanding on the selected ideas. It may include conducting market research, feasibility studies, prototyping, or creating business cases. Cross-functional collaboration is often necessary during this stage to leverage expertise from different areas of the organization and ensure the comprehensive development of the ideas.
Step 5. Idea Implementation
After the ideas have been thoroughly developed and validated, they are ready for implementation. This step involves creating action plans, allocating necessary resources, and defining timelines for execution. Depending on the nature of the idea, implementation could involve product innovation, process improvements, marketing campaigns, organizational changes, or other initiatives. Clear ownership and accountability are essential to ensure successful execution.
Step 6. Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuously monitor and evaluate the progress and impact of the implemented ideas. This helps determine whether the ideas are achieving the desired outcomes and whether any adjustments or modifications are needed. It is important to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) or success metrics upfront to measure the effectiveness and track the results of the implemented ideas.
Step 7. Feedback and Recognition
Provide feedback to idea contributors or customer feedback on the status and progress of their ideas. It is crucial to acknowledge and recognize the efforts of individuals who contributed valuable ideas. This recognition can be in the form of incentives, rewards, or public acknowledgments, fostering a culture of appreciation and motivating further participation in the idea management process.
Step 8. Iteration and Continuous Improvement
Idea management is an iterative process. It involves continuously generating, evaluating, and implementing new ideas while learning from previous experiences. Gather insights from implemented ideas, lessons learned, and feedback received, and use this knowledge to refine and improve the idea management process itself.
Learn more: What is Product Ideation?
Top 10 Idea Management Best Practices in 2023

By implementing the following 10 best practices, organizations can create a conducive environment for idea generation, collaboration, and innovation, leading to improved outcomes and sustained growth.
1. Foster a Culture of Innovation: Cultivate a culture of innovation that values and encourages innovation throughout the organization. This includes promoting open communication, risk-taking, and a mindset that embraces new ideas and experimentation.
2. Provide Clear Goals and Objectives: Clearly communicate the organization’s strategic goals and objectives to align the idea management process with the overall vision. This helps individuals understand the focus areas and encourages them to generate ideas that contribute to the organization’s strategic priorities.
3. Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration: Promote collaboration and diversity of perspectives by involving employees from different departments and levels in the idea management process. This enables a broader range of expertise and insights to be considered during idea evaluation and development.
4. Embrace Technology: Leverage technology tools and platforms specifically designed for idea management. These tools streamline the ideation, evaluation, and implementation processes, making it easier for employees to contribute and collaborate on ideas. Look for platforms that offer features like idea submission, evaluation workflows, collaboration spaces, and reporting capabilities.
5. Prompt and Regular Communication: Keep participants informed about the status of their ideas and provide regular updates on the progress of the idea management process. Promptly acknowledge idea submissions and communicate any decisions, whether it is selected for further development or reasons for rejection. Transparent communication enhances engagement and maintains the momentum of the idea management process.
6. Training and Support: Offer training and resources to employees to help them develop their ideation and evaluation skills. Provide guidance on how to articulate and document ideas effectively. This helps individuals contribute more effectively to the idea management process and improves the quality of ideas submitted.
7. Create Multiple Idea Channels: Establish various channels for idea submission to cater to different preferences and work styles. This could include digital platforms, suggestion boxes, dedicated ideation sessions, or regular innovation challenges. By providing multiple channels, organizations can capture ideas from diverse sources and increase participation.
8. Recognize and Reward Contributions: Recognize and reward employees who contribute valuable ideas. This can be done through monetary rewards, incentives, certificates, or public recognition. Celebrating and highlighting successful ideas and their contributors motivates others to actively participate and increases engagement in the idea management process.
9. Measure and Evaluate Impact: Establish metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of implemented ideas. Regularly evaluate the outcomes and results to assess the effectiveness of the idea management process. Use this data to improve and refine the process continuously.
10. Learn from Failures: Encourage a mindset that views failures as learning opportunities. Embrace a culture that is open to discussing and learning from unsuccessful ideas, allowing for adjustments and improvements in future iterations of the idea management process.
Learn more: What is Business Innovation?
Frequently Asked Questions
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.