Table of Contents
What is Crowdsourcing?
Crowdsourcing is the practice of obtaining ideas, services, or content by soliciting contributions from a large group of people, typically from an online community or open platform. Businesses, organizations, and individuals use crowdsourcing to tap into collective intelligence, creativity, and problem-solving capabilities of diverse groups, allowing them to gather a wealth of insights that might not be available through traditional methods.
The rise of digital platforms has significantly expanded the potential of crowdsourcing, making it possible for companies to engage with participants globally, regardless of location. Whether used for idea generation, product development, market research, or solving complex challenges, crowdsourcing offers a cost-effective and innovative approach to problem-solving.
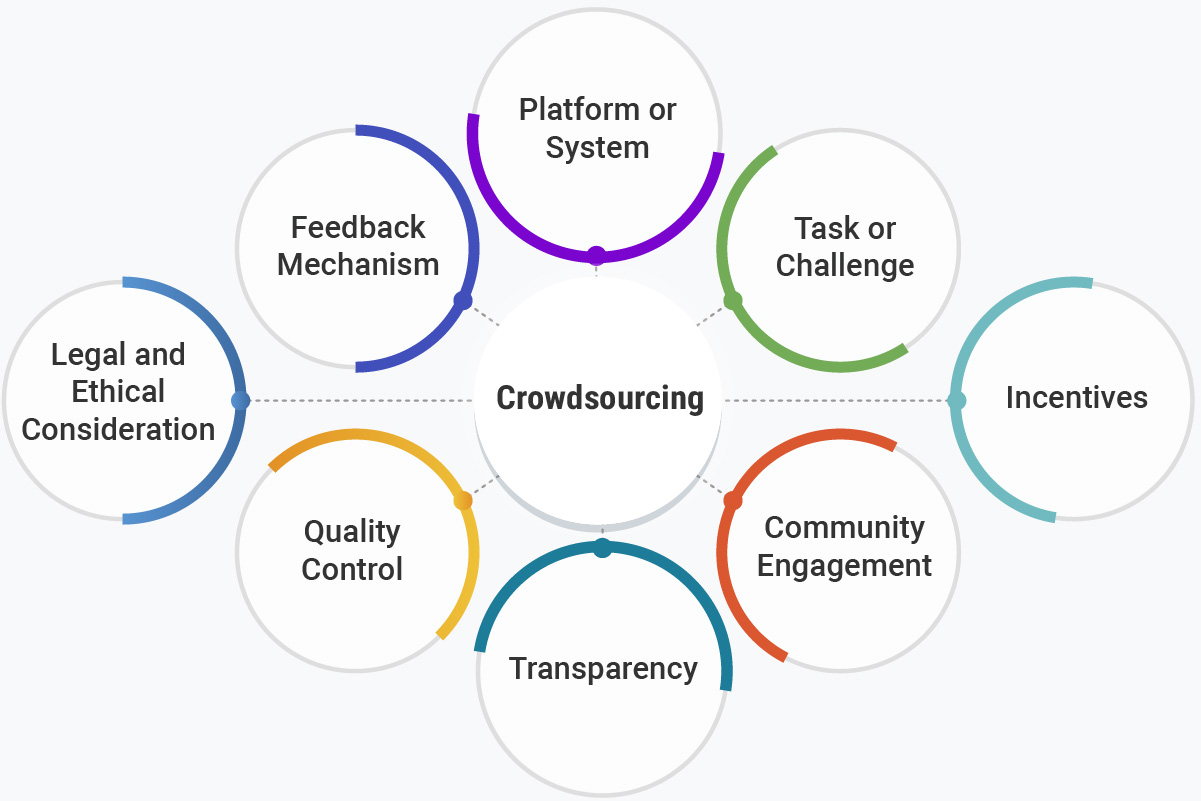
Crowdsourcing key components:
Crowdsourcing involves several key components that collectively contribute to its success and effectiveness. Understanding these components is crucial for organizations looking to implement crowdsourcing strategies.
- Crowd: The collective group of individuals contributing to the crowdsourcing initiative. The crowd provides diverse perspectives, skills, and contributions that contribute to problem-solving, idea generation, or project execution.\
- Platform or System: The online or offline infrastructure that facilitates the crowdsourcing process. The platform serves as the medium through which tasks are presented to the crowd, contributions are collected, and collaboration is facilitated. This could be a website, app, or specific software designed for crowdsourcing.\
- Task or Challenge: The specific problem, project, or objective that requires input or contributions from the crowd. Clearly defining the task is essential for successful crowdsourcing. It sets the parameters for what the crowd is expected to achieve and guides the contributions.
- Incentives: Rewards or motivations offered to participants in exchange for their contributions. Incentives can be financial, recognition-based, or tied to the outcome of the crowdsourcing initiative. They encourage active participation and help attract and retain contributors.
- Community Engagement: The level of involvement and interaction within the crowd. Fostering a sense of community encourages active participation and collaboration. Engaging the crowd through forums, discussions, or feedback loops enhances the overall crowdsourcing experience.
- Transparency: Clear communication about the crowdsourcing process, objectives, and outcomes. Transparency builds trust within the crowd and ensures that participants understand the purpose and impact of their contributions. Providing feedback on the results of crowdsourcing efforts enhances transparency.
- Quality Control: Mechanisms to assess and ensure the quality of contributions from the crowd. Implementing checks and balances helps maintain the integrity of the crowdsourced data or outcomes. Quality control measures may include validation processes, peer review, or automated checks.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Adherence to legal and ethical standards governing crowdsourcing activities. Ensuring compliance with privacy laws, intellectual property rights, and ethical guidelines is crucial for the success and sustainability of crowdsourcing initiatives.
- Feedback Mechanism: Systems for providing feedback to participants and incorporating their input. Establishing a feedback loop keeps the crowd informed about the impact of their contributions and encourages continuous improvement. It also enhances the overall experience for participants.
- Scalability: The ability to expand or contract the scope of crowdsourcing initiatives based on demand. Scalability allows organizations to adapt to changing requirements, whether expanding the crowd size for a specific project or scaling down after completion.
Understanding and effectively managing these key components is essential for organizations to leverage the full potential of crowdsourcing, whether for innovation, problem-solving, or engaging a global community in various tasks.
Types of Crowdsourcing
There are several types of crowdsourcing, depending on the goals of the organization:
1. Idea Crowdsourcing
This involves soliciting creative ideas from a large audience to generate innovative solutions. Companies like LEGO and Starbucks have used crowdsourcing platforms to gather product ideas directly from their customers.
2. Crowdsourced Funding
Also known as crowdfunding, platforms like Kickstarter and GoFundMe allow individuals or startups to raise funds from a large number of small contributors. This democratizes the investment process and allows for innovative projects to get financial backing from the public.
3. Crowdsourced Design
In this model, businesses or individuals invite designers from around the world to submit designs for a product or brand. Platforms like 99designs are popular for crowdsourced design contests.
4. Problem-Solving
Some companies crowdsource solutions to specific technical or scientific challenges. For example, NASA and other organizations use platforms like InnoCentive to gather solutions to complex problems from a global pool of experts.
Advantages of Crowdsourcing
- Diverse Perspectives: By engaging a large group of people with different backgrounds, expertise, and experiences, crowdsourcing provides access to a wide range of ideas and viewpoints, enhancing the creative process.
- Cost Efficiency: Crowdsourcing reduces the need for in-house resources or hiring external consultants. Organizations can receive high-quality ideas, designs, or solutions from a global audience at a fraction of the cost.
- Faster Results: With more participants working on a challenge simultaneously, crowdsourcing often leads to faster idea generation and problem-solving than traditional methods.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Crowdsourcing can also improve customer loyalty by giving people a voice in shaping products, services, or decisions. This direct involvement makes customers feel more connected to the brand.
Learn more: What is Crowdsourcing Innovation?
Top 10 Examples of Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing has become a versatile strategy employed across various industries to harness collective intelligence and creativity. Here are some notable examples of crowdsourcing in action:
1. Wikipedia (Online encyclopedia)
Wikipedia relies on a vast community of volunteers to create, edit, and update its content collaboratively. Contributors from around the world add and refine articles on diverse topics, making Wikipedia a comprehensive and continually evolving knowledge resource.
2. Open Source Software Development (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
Open-source projects like Linux, Mozilla Firefox, and Apache Hadoop involve a global community of developers contributing to the development and improvement of software. The collaborative effort results in high-quality, free-to-use software products.
3. Crowdfunding Platforms (Kickstarter, Indiegogo, GoFundMe)
Crowdfunding platforms allow individuals or businesses to present their projects to the public, and people from around the world can contribute funds to bring these ideas to life. Projects range from innovative tech gadgets to artistic endeavors.
4. Google Maps (Mapping and navigation service)
Google Maps incorporates user-generated content for improving mapping data. Users can contribute by adding reviews, photos, and information about businesses and locations, enhancing the accuracy and richness of map data.
5. Threadless (Online design community)
Threadless allows artists to submit their T-shirt designs, and the community votes on their favorites. Winning designs are then produced and sold through the platform, providing a platform for artists and ensuring that popular designs reach the market.
6. Innocentive (Online innovation platform)
Innocentive connects organizations facing complex challenges with a global network of problem solvers. Solvers compete to provide solutions, and the organization rewards the best solution with a cash prize.
7. Foldit (Online puzzle game)
Foldit challenges players to solve complex scientific problems related to protein folding. The game leverages the gaming community’s problem-solving skills to contribute to real-world scientific research.
8. Zooniverse (Citizen science platform)
Zooniverse enables volunteers to participate in scientific research projects by analyzing large sets of data. Projects cover various fields, including astronomy, biology, and climate science.
9. LEGO Ideas (LEGO’s crowdsourcing platform)
LEGO Ideas enables enthusiasts to submit their unique LEGO set designs. The community votes on the designs, and if a project receives enough support, LEGO may produce and sell the set, with the original designer receiving royalties.
10. Amazon Mechanical Turk (Online marketplace)
Amazon Mechanical Turk connects businesses with a global workforce to perform tasks that computers can’t easily do. Individuals, known as “Turkers,” complete small tasks, contributing to data processing, content moderation, and other microtasks.
These examples showcase the diverse applications of crowdsourcing, highlighting its effectiveness in solving problems, fostering innovation, and engaging communities on a global scale.
10 Benefits of Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing offers a plethora of benefits across diverse industries, contributing to innovation, problem-solving, and efficiency. Here are some key advantages of incorporating crowdsourcing into business strategies:
- Diverse Perspectives: Enhanced Creativity: By tapping into a broad and diverse crowd, businesses gain access to a wide range of perspectives, ideas, and creative solutions that may not be present within their internal teams.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced Overheads: Crowdsourcing allows organizations to allocate tasks or projects to a distributed workforce, eliminating the need for hiring specialized individuals or maintaining large in-house teams. This may lead to substantial reductions in expenses.
- Accelerated Innovation: Rapid Idea Generation for Competitive Edge: The collaborative nature of crowdsourcing accelerates the innovation process, fostering rapid idea generation. With a diverse pool of contributors, businesses can generate creative solutions swiftly, ensuring they stay ahead in competitive markets.
- Enhanced Problem Solving: Collective Intelligence: Crowdsourcing leverages the collective intelligence of the crowd, enabling more effective problem-solving. Complex challenges can be addressed by drawing on the diverse skills and knowledge of a broad audience.
- Increased Flexibility: Adaptability: Crowdsourcing allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on project needs. This flexibility is especially valuable for organizations facing fluctuating workloads or those seeking specialized skills for specific tasks.
- Global Reach: Access to Global Talent: With the power of the internet, crowdsourcing provides access to a global talent pool. Organizations can engage contributors from different countries and cultural backgrounds, bringing in a variety of skills and perspectives.
- User Engagement: Community Building: Crowdsourcing fosters a sense of community and engagement. Participants often feel a connection to the projects they contribute to, leading to increased enthusiasm and dedication to the success of the initiative.
- Efficiency and Speed: Faster Execution: By distributing tasks among a large number of contributors, organizations can complete projects more quickly. This is particularly advantageous for time-sensitive initiatives or projects with tight deadlines.
- Market Validation: Testing Ideas: Crowdsourcing provides a platform for testing ideas, products, or services with a diverse audience. Feedback from the crowd can serve as valuable market validation, helping businesses refine their offerings.
- Inclusivity: Open to Everyone: Crowdsourcing promotes inclusivity by allowing anyone with relevant skills or insights to contribute. This democratic approach ensures that talent and ideas are not limited to a specific group or geographical location.
Incorporating crowdsourcing into business strategies requires careful planning and management, but the potential benefits make it a valuable tool for organizations looking to innovate, solve problems, and engage a global community.
Crowdsourcing Best Practices: How It Works
Implementing crowdsourcing successfully requires careful planning and adherence to best practices. Here are some key crowdsourcing best practices to guide organizations in leveraging the collective intelligence of the crowd effectively:
- Clearly Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals and objectives of the crowdsourcing initiative. Define the problem to be solved or the task at hand to provide a clear direction for participants.
- Understand Your Audience: Identify and understand the target audience or crowd. Tailor your crowdsourcing approach to engage participants who possess the relevant skills and knowledge for the task.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Clearly communicate the task or challenge to participants. Provide detailed instructions, guidelines, and any necessary background information to ensure a common understanding.
- Establish Incentives: Offer meaningful incentives to motivate and reward participants for their contributions. Incentives can include financial rewards, recognition, or exclusive access to the outcomes of the crowdsourcing initiative.
- Foster Community Engagement: Create and nurture a sense of community among participants. Facilitate communication channels such as forums, discussion boards, or social media groups to encourage collaboration and idea-sharing.
- Implement Quality Control Measures: Implement mechanisms to assess and ensure the quality of contributions. This may include validation processes, peer review, or automated checks to maintain the integrity of the collected data or outcomes.
- Promote Transparency: Maintain transparency throughout the crowdsourcing process. Clearly communicate the purpose, progress, and impact of the initiative to build trust among participants.
- Provide Feedback: Establish a feedback mechanism to keep participants informed about the results of their contributions. Acknowledge and celebrate the efforts of the crowd, and provide constructive feedback for continuous improvement.
- Ensure Legal and Ethical Compliance: Adhere to legal and ethical standards governing crowdsourcing activities. Ensure that participants’ rights are respected, and address any privacy or intellectual property concerns.
- Facilitate Scalability: Design crowdsourcing initiatives with scalability in mind. Ensure that the infrastructure and processes can adapt to changing demands, whether scaling up for larger projects or scaling down after completion.
- Use Technology Wisely: Leverage technology and appropriate platforms to facilitate the crowdsourcing process. User-friendly interfaces, mobile accessibility, and intuitive tools can enhance the participant experience.
- Iterate and Learn: Treat crowdsourcing as an iterative process. Learn from each initiative, gather insights, and apply lessons learned to improve future crowdsourcing efforts.
- Encourage Diversity and Inclusion: Strive for diversity in the crowd to bring a variety of perspectives and ideas. Ensure inclusivity by removing barriers that may limit participation based on factors such as language or accessibility.
- Align with Organizational Culture: Ensure that crowdsourcing initiatives align with the overall culture and values of the organization. This alignment fosters a positive relationship between the organization and the crowd.
- Monitor and Measure Impact: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of crowdsourcing initiatives. Regularly monitor and evaluate the outcomes against these metrics to assess success and identify areas for improvement.
By following these best practices, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of their crowdsourcing initiatives, fostering innovation, solving complex problems, and engaging with a global community in a meaningful way.
Learn more: What is Idea Crowdsourcing?
Most Recent Posts
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.