Table of Contents
The VRIO Framework is an essential tool in strategic management that helps businesses determine whether their resources can provide a sustained competitive advantage. Developed by Jay B. Barney, VRIO stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization. Let’s explore each component in detail to understand how this framework can propel your business to new heights.
What is the VRIO Framework?
The VRIO Framework is a strategic analysis tool used to evaluate an organization’s resources and capabilities. By examining these elements, businesses can identify the unique strengths that give them a competitive edge in the market. The framework’s goal is to determine whether resources are valuable, rare, difficult to imitate, and well-organized, as these characteristics contribute to sustained competitive advantage.
Key Benefits of Using the VRIO Framework:
- Identify Core Competencies: Pinpoint what sets your business apart from competitors.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Make informed decisions about resource allocation and investment.
- Enhance Competitive Position: Leverage unique resources to outperform competitors.
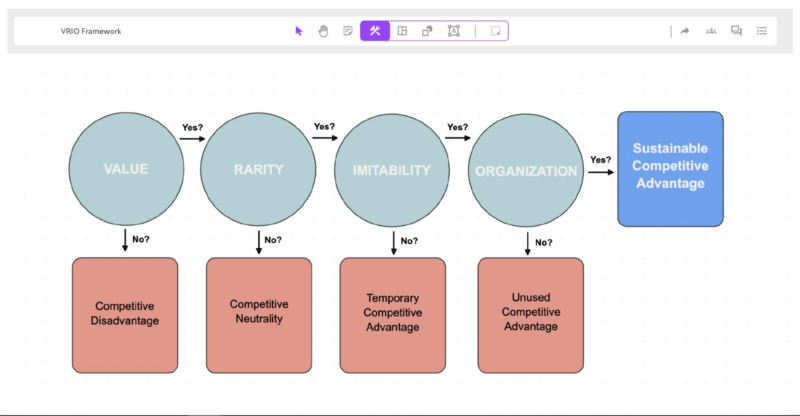
Understanding the Four Components of VRIO
1. Value
The Value aspect of the VRIO framework examines whether a resource or capability enables a firm to exploit opportunities or neutralize threats in the marketplace. A resource is valuable if it can increase customer satisfaction, improve efficiency, or boost profitability.
Key Questions to Ask:
- Does this resource enhance the customer experience or product quality?
- Can it help reduce costs or increase revenue?
- Does it allow the company to seize new opportunities or defend against threats?
Example: Apple’s Brand Reputation
Apple’s brand is a prime example of value. It not only attracts loyal customers but also allows the company to charge premium prices, leading to higher profit margins.
2. Rarity
Rarity assesses whether a resource is scarce or unique within the industry. Resources that are not widely possessed by competitors can provide a temporary competitive advantage, allowing a firm to stand out in the market.
Key Questions to Ask:
- How many competitors have access to this resource?
- Is it something that is not easily found or acquired by others?
Example: Tesla’s Battery Technology
Tesla’s advanced battery technology is rare, providing a significant edge over other automakers in the electric vehicle market.
3. Imitability
Imitability evaluates how easily competitors can replicate a resource. Resources that are challenging to imitate due to cost, complexity, or proprietary technology contribute to a sustained competitive advantage.
Key Questions to Ask:
- How easy is it for competitors to copy this resource?
- Are there barriers, such as patents or trade secrets, that prevent imitation?
Example: Coca-Cola’s Secret Formula
The secret formula of Coca-Cola is a classic example of a resource that is difficult to imitate, maintaining the brand’s dominance in the beverage industry.
4. Organization
The Organization aspect examines whether a company is structured to fully utilize and capture the value of its resources. Even valuable, rare, and inimitable resources require proper alignment with business processes and strategies to realize their full potential.
Key Questions to Ask:
- Is the organization structured to support the resource?
- Do management systems and company culture enhance the use of this resource?
Example: Google’s Innovative Culture
Google’s organizational structure and culture of innovation allow it to capitalize on its technological resources effectively, driving continuous growth and innovation.
Applying the VRIO Framework: Step-by-Step Guide
To leverage the VRIO Framework effectively, follow these steps to analyze and optimize your organization’s resources:
Step 1: Conduct a Resource Audit
Begin by listing all tangible and intangible resources within your organization, including financial assets, intellectual property, brand equity, technological capabilities, and human capital.
Step 2: Evaluate Each Resource with VRIO
Use the VRIO criteria to assess each resource:
- Value: Does it add significant value?
- Rarity: Is it uncommon within the industry?
- Imitability: Is it difficult for others to replicate?
- Organization: Is your company structured to capitalize on it?
Step 3: Identify and Prioritize Core Competencies
Focus on resources that meet all four VRIO criteria. These are your core competencies and should be prioritized in your strategic planning.
Step 4: Develop Strategic Initiatives
Create initiatives that leverage these core competencies to drive competitive advantage. This may involve product development, market expansion, or process optimization.
Step 5: Monitor and Adapt
Continuously review your resources and market conditions. Adapt your strategy as needed to maintain and enhance your competitive position.
Real-Life Examples of VRIO Framework
The VRIO Framework isn’t just a theoretical tool; it’s actively used by some of the most successful companies worldwide to maintain their competitive edge. Here, we’ll explore real-world examples of how leading brands leverage their resources for sustained success. These examples will not only illustrate the power of the VRIO framework but also provide insights into applying it effectively within your organization.
Example 1: Apple Inc. – Innovation and Brand Power
Apple is a textbook example of the VRIO framework in action. Let’s break down how Apple’s resources align with each VRIO component:
Value
- Technological Innovation: Apple’s continuous innovation in product design and user experience offers significant value to its customers. Products like the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook are seen as industry benchmarks, driving high customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Ecosystem Integration: Apple’s ability to seamlessly integrate hardware, software, and services creates a cohesive user experience that adds tremendous value.
Rarity
- Brand Reputation: Apple’s brand is one of the most valuable and rare in the world, with a level of customer loyalty that is hard to match.
- Proprietary Technology: Apple’s proprietary software, such as iOS and macOS, provides a unique experience that competitors find challenging to replicate.
Imitability
- Design Excellence: Apple’s unique design aesthetic is protected by numerous patents, making it difficult for competitors to imitate without infringing on intellectual property.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Apple’s complex and efficient supply chain processes are built over decades, making them costly and time-consuming to replicate.
Organization
- Organizational Culture: Apple’s culture of innovation encourages employees to think creatively and push boundaries, ensuring that the organization is aligned to capture maximum value from its resources.
- Leadership and Vision: Apple’s strategic vision underpins its organizational success, with leadership consistently prioritizing long-term growth and innovation.
Impact: Apple’s effective use of the VRIO framework has cemented its position as a leader in the technology industry, enabling sustained competitive advantages that drive growth and profitability.
Example 2: Amazon – Mastery in Logistics and Customer Service
Amazon’s success is built on a solid foundation of unique resources and capabilities that exemplify the VRIO framework:
Value
- Customer-Centric Approach: Amazon’s focus on customer satisfaction through low prices, fast delivery, and a wide product selection provides unparalleled value.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations like Amazon Web Services (AWS) add value by offering scalable and reliable cloud computing solutions.
Rarity
- Logistics Network: Amazon’s vast and efficient logistics network, including its Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) service, is rare and difficult for competitors to duplicate.
- Data-Driven Insights: Amazon’s access to vast amounts of customer data allows for personalized recommendations and insights that few competitors can match.
Imitability
- Economies of Scale: Amazon’s size and scale enable cost efficiencies that are hard for smaller competitors to replicate.
- Innovative Culture: The company’s innovative culture, fostered by its leadership, is not easily imitable by companies without similar organizational structures.
Organization
- Agile Operations: Amazon’s organizational structure supports rapid decision-making and adaptability, ensuring the company can quickly respond to market changes.
- Strategic Alignment: The company aligns its vast resources with a clear strategic vision, ensuring that every part of the organization works towards common goals.
Impact: By leveraging the VRIO framework, Amazon has established itself as a dominant force in e-commerce and cloud computing, with competitive advantages that continue to expand its market presence.
Example 3: Netflix – Dominance through Data and Original Content
Netflix has revolutionized the entertainment industry by effectively applying the VRIO framework to its resources:
Value
- Content Library: Netflix’s extensive library of movies and TV shows provides immense value to subscribers, catering to diverse tastes and preferences.
- User Experience: The intuitive and personalized user interface enhances viewing pleasure, driving high levels of user engagement.
Rarity
- Original Programming: Netflix’s investment in original content like “Stranger Things” and “The Crown” sets it apart, offering unique value that competitors struggle to match.
- Subscriber Base: With millions of subscribers worldwide, Netflix has a rare and powerful distribution channel for its content.
Imitability
- Recommendation Algorithm: Netflix’s sophisticated recommendation system is based on complex algorithms and extensive user data, making it challenging for competitors to replicate.
- Global Reach: Establishing a global presence with localized content offerings requires significant resources and expertise, acting as a barrier to imitation.
Organization
- Creative Culture: Netflix fosters a culture that encourages creativity and innovation, essential for producing original content and maintaining its competitive edge.
- Strategic Leadership: The company’s leadership is adept at navigating the fast-changing media landscape, aligning resources with emerging opportunities.
Impact: By harnessing the VRIO framework, Netflix has secured a leading position in the streaming industry, consistently delivering unique and engaging content that attracts and retains subscribers.
Example 4: Toyota – Excellence in Manufacturing and Innovation
Toyota’s approach to manufacturing and innovation illustrates the practical application of the VRIO framework:
Value
- Lean Manufacturing: Toyota’s lean manufacturing processes, including the renowned Toyota Production System (TPS), deliver exceptional value by maximizing efficiency and reducing waste.
- Quality Assurance: The company’s commitment to quality enhances customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Rarity
- Manufacturing Expertise: Toyota’s manufacturing expertise, developed over decades, is rare and difficult for new entrants to acquire.
- Hybrid Technology: As a pioneer in hybrid technology, Toyota holds a unique position in the automotive industry.
Imitability
- Proprietary Processes: Toyota’s proprietary manufacturing processes, protected by trade secrets and patents, are not easily imitable.
- Organizational Learning: The company’s focus on continuous improvement (Kaizen) fosters a learning culture that competitors find challenging to replicate.
Organization
- Global Operations: Toyota’s global operations are strategically aligned to optimize production and distribution across different markets.
- Innovative Culture: The company’s culture of innovation and improvement supports its strategic goals and enhances its competitive position.
Impact: Toyota’s effective use of the VRIO framework has established it as a leader in the automotive industry, with sustainable advantages that continue to drive growth and innovation.
Learn more: How to Use VRIO Framework, the Four Steps
Importance of VRIO Framework
The VRIO framework is important in the field of strategic management and business analysis for several reasons:
- Assessing Competitive Advantage: The VRIO framework provides a structured approach to evaluate a company’s resources and capabilities, helping to identify those that can potentially offer a sustainable competitive advantage. This assessment is crucial for companies seeking to distinguish themselves in a competitive marketplace.
- Resource Allocation: VRIO analysis aids in making informed decisions about resource allocation. By understanding which resources and capabilities are truly valuable and rare, a company can allocate its time, money, and effort more effectively, focusing on areas that will yield the greatest returns.
- Strategic Planning: The framework is a valuable tool in the strategic planning process. It guides companies in formulating and implementing their strategies by helping them identify the strengths they can build upon and the weaknesses they need to address.
- Sustainability of Competitive Advantage: VRIO’s focus on inimitability and organization helps companies determine whether their competitive advantage is sustainable over the long term. This is crucial because a short-lived competitive advantage may not justify significant investments.
- Competitive Positioning: Companies can use the VRIO analysis to better understand their competitive position relative to competitors. It allows them to see where they excel and where they need to improve, facilitating the development of a more effective and targeted competitive strategy.
- Strategic Decision-Making: The framework assists in making informed decisions about mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, and partnerships. It can help companies evaluate whether the resources and capabilities of another entity are valuable and rare, contributing to the decision-making process.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying weaknesses or vulnerabilities in their resources and capabilities, companies can proactively address these areas to reduce strategic risk. In this sense, VRIO can contribute to risk management and contingency planning.
- Communication and Alignment: VRIO analysis provides a common language for discussing and assessing a company’s resources and capabilities. It helps align the understanding of various stakeholders within the organization and can facilitate more effective communication about strategic priorities.
- Innovation and Continuous Improvement: Companies can use the VRIO framework to identify areas where innovation or improvements are needed to enhance their competitive position. It encourages a culture of continuous improvement.
- Adaptation to Environmental Changes: The VRIO framework is not static; it can be reapplied as market conditions and the competitive landscape evolve. This adaptability ensures that a company’s strategy remains relevant and agile in response to changes in the business environment.
The VRIO framework is a valuable tool for organizations in evaluating their resources and capabilities, making strategic decisions, and ultimately achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. It promotes a systematic and analytical approach to strategic management, which is essential in today’s dynamic and competitive business world.
VRIO Analysis
VRIO Analysis emerges as a pivotal methodology for companies keen on assessing their competitive prowess. Originating from the visionary mind of Jay Barney, VRIO Analysis scrutinizes a company’s resources and capabilities through a lens defined by four critical criteria: Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, and Organized.
1. Identify Resources and Capabilities
Start by identifying the key resources and capabilities of the company. Resources can include physical assets, intellectual property, financial capital, skilled employees, and more. Capabilities refer to the company’s ability to use these resources effectively, such as its unique processes, skills, and knowledge.
2. Assess Value (V)
Determine whether each resource or capability is valuable by asking: Does it enable the company to exploit opportunities or defend against threats in the external environment? Does it contribute to the company’s ability to generate higher profits or achieve strategic objectives?
3. Assess Rarity (R)
Evaluate the rarity of each resource or capability by asking: Is it uncommon or rare among competitors? If a resource is common and easily accessible to competitors, it may not provide a competitive advantage.
4. Assess Inimitability (I)
Consider whether the resources and capabilities are inimitable. In other words, are they difficult for competitors to duplicate or imitate? This can result from proprietary technology, unique skills, complex processes, or strong brand identity.
5. Assess Organization (O)
Analyze whether the resources and capabilities are effectively organized and integrated into the company’s strategy and operations. The organization’s structure, culture, and processes should support and leverage these resources.
6. Evaluate the VRIO Criteria (VRIO)
For each resource or capability, combine the assessments of value, rarity, inimitability, and organization to determine whether it meets the VRIO criteria. Resources or capabilities can fall into one of the following categories:
- VRIO: Resources or capabilities that are Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, and Organized represent a sustainable competitive advantage.
- VR: Resources that are Valuable and Rare but not Inimitable or Organized may offer a temporary competitive advantage.
- VRO: Resources that are Valuable, Rare, and Organized but not Inimitable can provide a competitive advantage but may not be sustainable over the long term.
- VRN: Resources that are Valuable but not Rare may not offer a competitive advantage as competitors can easily acquire them.
7. Strategic Implications
Based on the VRIO analysis, assess the strategic implications for the company. Identify which resources and capabilities represent the core of the company’s strategy and should be leveraged to maintain or gain a competitive advantage. Conversely, recognize areas that need improvement or protection.
8. Action Plans
Develop action plans to further enhance the value, rarity, and inimitability of resources or capabilities that have potential but are not fully meeting the VRIO criteria. This may involve investing in innovation, intellectual property protection, or organizational changes.
The VRIO framework analysis is an iterative process and should be revisited as market conditions change, and as the company evolves. It helps organizations make more informed decisions about their strategic priorities and resource allocation, ultimately contributing to long-term success in a competitive environment.
Integrating VRIO with Other Strategic Tools
The VRIO Framework can be used alongside other strategic tools to provide a comprehensive analysis of your business environment:
- SWOT Analysis: Combine VRIO with SWOT to identify internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats.
- PESTLE Analysis: Understand how external factors such as political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental influences interact with your internal resources.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Analyze industry competition and assess how your resources can help you navigate competitive pressures.
VRIO Analysis vs. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is an advanced strategic planning tool that assists businesses in identifying areas where they are up to the mark and where they may improve, both externally and internally.
There are plenty of similarities between the SWOT Analysis and the VRIO Framework. However, while both SWOT and VRIO can be used in the early phases of strategic planning, they are distinct methods that provide different results.
Here are some of the key differences between both methods:
SWOT Analysis
- External elements such as threats and opportunities and Internal factors such as weakness and strengths are examined.
- Based on your situation, the SWOT analysis can help assess prospects.
- The SWOT table offers a quick summary of the company’s situation.
- A SWOT analysis is only applicable to one stage of your company strategy. For increasingly complex issues, more study is necessary.
VRIO Analysis
- VRIO analysis is carried out individually for each resource. In comparison, SWOT carries out the analysis of the entire business.
- Concentrates on resources that you possess rather than broad strengths, resulting in highly concrete solutions.
- Emphasizes the qualities that generate a competitive edge and the factors that might make or break a company.
- VRIO analysis requires a detailed grasp of your distinct value and competitive environment.
Learn more: The SWOT Analysis Framework: Limitations and Benefits
Endnote
The distinguishing features and benefits you discover through VRIO will help you select how to engage the market and guide strategic decisions that will define your firm’s future. A strategic plan will coordinate the procedures, resources, and structures required to develop these resources and convert them into long-term competitive advantages.
The VRIO framework is an excellent strategic planning tool for any business. As with other strategic planning tools, collaboration is vital when doing a VRIO analysis. If you want to learn more about using an online whiteboard with your team, check out IdeaScale Whiteboard.
Most Recent Posts
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.