In order to establish a connection with your customers, you need to create empathy with them. Creating empathy plays a vital role in establishing a positive user experience and helps brands achieve their targeted goals. By building an empathetic connection with their customer base, businesses can more effectively meet their needs and build stronger brand loyalty with customers worldwide. Building empathy doesn't always happen naturally, however, and to cultivate it effectively, you can use an empathy map. This article will define an empathy map, talk about how it's a valuable tool in cultivating a professional and empathetic approach for users, and the advantages of implementing one.
Empathy maps are good for creating a creative teamwork environment in offices and help bring the team to collective opinions related to customers and marketing campaigns.
What is An Empathy Map?
Empathy maps, an invaluable tool pioneered by Dave Gray, is defined as a dynamic visualization template, strategically designed to delve into the intricacies of customer behavior and emotions. In essence, these maps not only pinpoint user behaviors but also illuminate pathways for brands to foster more effective communication with their customers. Whether reshaping outreach strategies, refining user experiences, or honing messaging, the primary goal of an empathy map is to envision interactions through the lens of the customer, thereby facilitating improvements from their unique perspective.
This innovative template, a brainchild of Dave Gray, emerges as a powerful catalyst for team unity, allowing them to collectively address the core concerns of customers while documenting their frustrations. The process not only aids in identifying pain points but also guides the creation of consumer-informed solutions.
Employed post-initial customer research, empathy maps play a pivotal role in visualizing user-provided pain points and proposing improvements. This critical step enables designers and marketing teams to leverage data-driven insights, enhancing their strategies. Beyond data analysis, empathy maps play a crucial role in unveiling market gaps and understanding consumer needs, guiding brands toward meaningful improvements.
In essence, by harnessing the collaborative power of empathy maps, brands can navigate the complexities of customer needs, foster transparent communication among team members, and craft solutions that resonate deeply with their target audience.
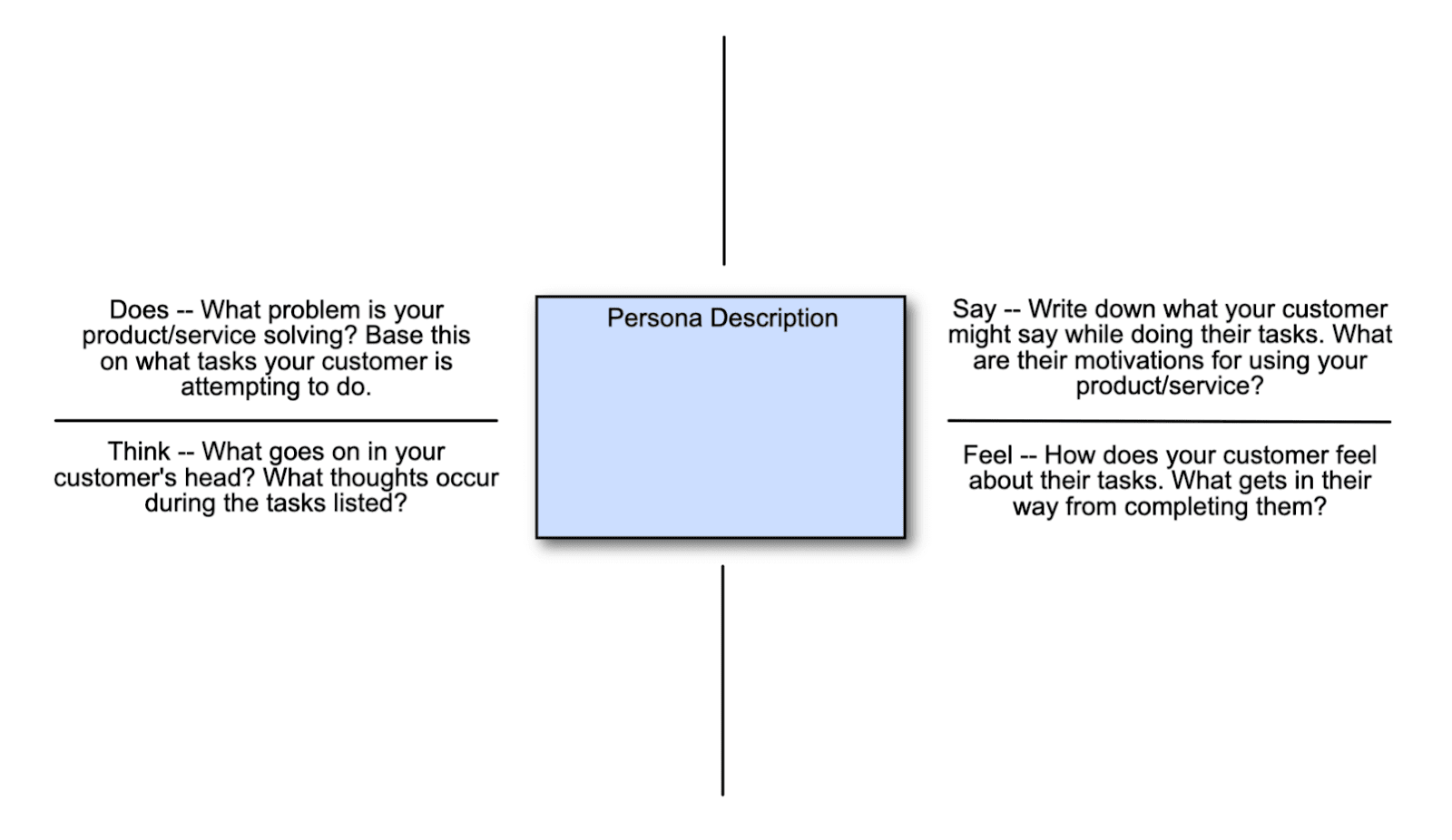
How is an Empathy Map Structured?
Fundamentally, empathy maps are divided into four main quadrants and have a customer-centric approach. These quadrants focus on some of the primary ways a user or consumer gives any response. These four quadrants are:
- Speaks
- Thinks or Perceives
- Feels
- Does
These four quadrants highlight how users feel about their experience using a product and how they communicate their joy/frustration differently. For example, their frustration from a pain point may not be verbalized, but it will change their future actions. This dichotomy will be reflected in the empathy map, and your team can use it to better their experience. We have precisely given an overview of how these four quadrants function in an empathy map for better understanding.
- Says or Speaks: This section is all about what a user says about your product; it can include any queries and remarks that users have about the product. It can consist of interviews, reviews, feedback, and statements. This feedback can be received both from the user directly or from their peers.
- Thinks or Perceive: The thinks & perceives quadrant is all about how users perceive your brand. This section focuses on things users don't speak about often, but it involves how they think about an experience. It can be hard to uncover how users think about a given experience, so in this step, teams often use qualitative analysis to understand what users are thinking.
- Feels: This section is also based on non-tangible factors of a user's experience and focuses mainly on how they feel. It considers how they naturally feel towards your product and how their feelings change given certain stimuli or steps in the journey. This section is all about the customer's emotional state and how that affects their perception of your brand.
- Does: This section is dedicated to the physical actions that users perform while using your product/service. What specific steps do they take and how are these actions informed by their feelings towards your brand?
This section is more quantifiable because you can easily tell what actions users are taking. The vital point is tracking these actions back to the mindset behind the decisions.
Learn more: 8 Crucial Empathy Map Benefits for Your Team
Why Use an Empathy Map?
Empathy maps are a great tool for understanding consumer needs and their demands for a given product. They help extract relevant data in a more organized way to help deliver the best solution for the customers. From this, you can extrapolate what needs to be done to increase customer engagement and satisfaction.
When finding these solutions, empathy maps are a great way to enhance communication within a team and build a well-informed solution inside and out. Integrating collaboration into these exercises is a great way to build team alignment and create customer-centric goals.
Empathy maps also help give the team members organized and transparent tasks so that they can fully contribute to the project's development.
Empathy Map Examples
Empathy maps stand as powerful tools in the realm of design thinking and user-centered design, offering a visual journey into a user's thoughts, feelings, actions, and experiences. Elevate your understanding of this essential concept with our comprehensive empathy map examples.
An empathy map comprises several key components, each providing unique insights:
- User Persona: Begin by identifying your target audience. Meet Sarah, a 28-year-old graphic designer. This detailed persona sets the stage for a deeper understanding.
- Says: Delve into the user's expressions. Uncover statements like "I hope for greater intuitiveness in this design software" and gain valuable insights into user expectations.
- Thinks: Explore the user's inner thoughts and concerns, such as optimism about software updates and worries about potential issues affecting deadlines.
- Feels: Understand the emotional landscape, from frustration to determination, providing a nuanced view of the user's experience.
- Does: Examine the user's likely actions, from investing extra time in learning new tools to seeking collaboration and regularly updating software.
- Sees: Analyze the user's environment, encompassing colleagues using various design software, online tutorials, and exposure to industry trends.
- Hears: Understand external influences by exploring what the user hears, be it complaints about design software limitations or positive reviews on social media.
- Pain Points: Summarize challenges, from struggles with complex software to concerns about collaboration and deadlines.
- Gains: Envision the user's goals, including a desire for user-friendly design tools, efficient collaboration, and professional recognition.
Why Our Examples Matter
By crafting empathy maps like the one outlined above, design and product teams gain profound insights into user needs and motivations. This deeper understanding translates into the development of products and services that authentically resonate with target audiences.
Explore the nuances of empathy maps with our illustrative examples, and empower your teams to create solutions that truly connect with users.
Empathy Map in Design Thinking
There are five stages of design thinking where empathy maps can play: empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing. When creating an empathy map, you will first start your process from the empathizing stage and include all your research into it. This phase is mainly where an empathy map can be impactful.
After your research is complete, you can move further towards compiling and organizing your data. The data can be from interviews, reviews, responses, feedback, or surveys. Then attach each of them to a different section or quadrant that we mentioned earlier. Through this process, you can effectively visualize how empathy is created with your users and boost your team's ability to effectively utilize design thinking.
Empathy Map Advantages
There are multiple advantages associated with empathy maps and their daily use in improving user experience. These basic empathy map advantages help improve usability and customer research.
1. Better Targeted Audience: The popularity of empathy maps is based on their effectiveness in providing insight to the targeted audience. You will quickly target your consumers, their demands and needs from your brand, and what you have to do to make your brand stand out. This provides both information on your consumers and narrows the focus on your ideal target audience.
2. Cost Affective: Who does not want a cost-effective solution to reaching multiple consumers and having accurate data about them?. Often large businesses struggle to keep up with their expenses, and empathy maps are a great way to start utilizing your decision and research skills without spending tons of money. This map can be implemented easily online and is a collaborative platform for multiple people to use at once.
3. Customization Options: You will want to include multiple customization options once you understand what your customers desire from your brand. Empathy maps are a great way to enhance your product and add customization options after organizing your user feedback.
4. Builds an Understanding of User Behaviour: The first goal of the empathy map is to see what users are experiencing and break down their behaviors towards a particular brand. With empathy maps, you will be able to detect the current conditions of market and consumer behavior.
You will be able to know what your users are experiencing, their thoughts, and feelings, and it will give you an ideal canvas to create your following marketing strategies.
5. Profile Analysis: Profile analysis is a crucial step for many companies when it comes to extracting data for research or launching a new product. With empathy maps, you won't have to do all the hard work of collecting different samples of user data and concluding it to fit into your assumptions.
Empathy maps help you understand the minor details of the profile analysis and give you an elaborate view of what your consumers are going through.
6. Risk Averse: With empathy maps, you can easily spot your risks and come up with suitable management strategies to counter those risks early. This strategy can also evolve through multiple different target consumers to ensure that your customer is satisfied regardless of their profile.
Building an Empathy Map
When understanding how empathy maps are important, it's critical to know how they are built. Learning this step-by-step process highlights the goals of an empathy map and is helpful when using one with your team.
Here is our brief and easy explanation of how you can build one,
1. Establish Focus & Goals
Establishing focus and goals is the first step to building your empathy map. You first need to identify the purpose or intent of creating an empathy map. If you don't have any purpose or goal, your empathy map will not have any effect on your product, and it will not be an effective exercise for your team.
Secondly, you need to have a focused approach. Without a focused approach, you will miss a lot of parts of an empathy map and will end up with skewed results. Try to identify the user in your map and then proceed. Understand the users' needs their experiences and the stages they went through in order to develop a fully informed solution.
2. Examine User Experience
This is your second step to building an empathy map. In this step, you will have to analyze and examine your consumer's experiences and how they react to different tasks or different stages of the interaction. In this section, you need to put yourself in your consumer's shoes and examine their experience in a certain situation and what they felt at a certain point.
You have to analyze what your customer is seeing, observing, or analyzing and do the same thing to get a similar effect. This will include everything g that is happening around them, including people, the environment, and places. Furthermore, the section focuses on all the different experiences a consumer can have. Each stage will conjure a different experience, and these all have to be taken into mind.
3. Understand the Mind
In this step, you have to analyze what a consumer is thinking when interacting with your brand or product. Focus on ways to explore what is in their mind and try to extract information that can help you improve your connection to them.
It will take time for you to understand other people's decisions, thoughts, perceptions, and feelings. Use the data to state a tentative decision about the consumers and use their feelings to back up these decisions.
In the final stages, you also have to see what the consumers are gaining and their pain points. It can be simplified into what the users achieved during the interaction with the product and what were the points or stages where they were frustrated. In this way, you will understand your opportunities and hurdles in achieving your goals.
4. Summarize
The final step entails summarizing the data and its careful placement in the relevant quadrants. You can now share your thoughts with your team and can collect their opinions on certain stages regarding the empathy map.
In this stage, you will have to give our team enough space to understand the whole user experience and how you curated the researched data. Try to take your team on a collaborative approach and have their decisions evaluated carefully for you to implement them in further stages of your product.
Learn more: Experience Map Applications
Conclusion
Empathy maps are a great tool to know what your brand needs in terms of creating better user engagement and having a user-centric approach. You will be able to make a quick and sound decision after utilizing empathy maps and will have accurate researched data on your targeted audience.
Next time you want to reach out to your consumers, try using an empathy map on IdeaScale Whiteboard for better and more accurate results.
Most Recent Posts
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.