Table of Contents
What is Quantitative Research Design?
Quantitative research design is defined as a research method used in various disciplines, including social sciences, psychology, economics, and market research. It aims to collect and analyze numerical data to answer research questions and test hypotheses.
Quantitative research design offers several advantages, including the ability to generalize findings to larger populations, the potential for statistical analysis and hypothesis testing, and the capacity to uncover patterns and relationships among variables. However, it also has limitations, such as the potential for oversimplification of complex phenomena and the reliance on predetermined categories and measurements.
Quantitative research design key elements
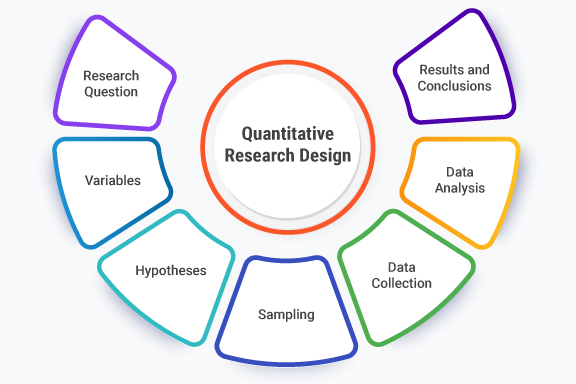
Quantitative research design typically follows a systematic and structured approach. It involves the following key elements:
- Research Question: The researcher formulates a clear and specific question that can be answered through quantitative research. The question should be measurable and objective
- Variables: The researcher identifies and defines the variables relevant to the research question. Variables are attributes or characteristics that can be measured or observed. They can be independent variables (factors that are manipulated or controlled) or dependent variables (outcomes or responses that are measured).
- Hypotheses: The researcher develops one or more hypotheses based on the research question. Hypotheses are verifiable statements that make predictions about the association between variables.
- Sampling: The researcher determines the target population and selects a representative sample from that population. The sample should be large enough to provide statistically significant results and should be chosen using appropriate sampling techniques.
- Data Collection: Quantitative research design relies on the collection of numerical data. This can be done through various methods such as surveys, experiments, quantitative observations, or secondary data analysis. Standardized instruments, such as questionnaires or scales, are often used to ensure consistency and reliability.
- Data Analysis: The collected data is analyzed using statistical methods and techniques. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and describe the data, while inferential statistics are used to draw conclusions and make generalizations about the population based on the sample data.
- Results and Conclusions: The researcher interprets the findings and draws conclusions based on the analysis. The results are typically presented in the form of tables, graphs, and statistical measures, such as means, correlations, or regression coefficients.
Types of Quantitative Research Design
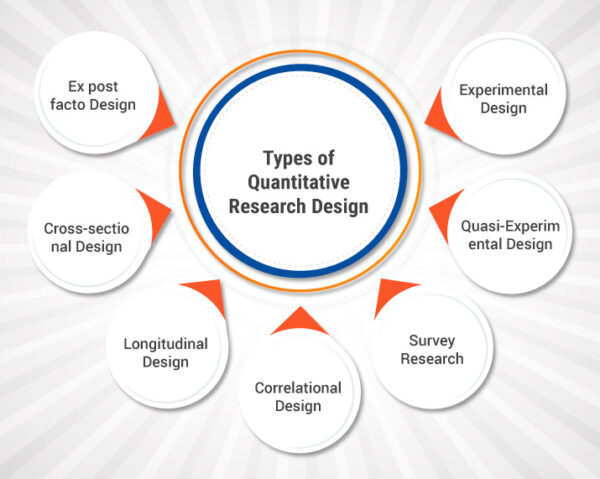
There are several types of quantitative research designs, each suited for different research purposes and questions. Here are some common types of quantitative research designs:
- Experimental Design
Experimental design involves the manipulation of an independent variable to observe its effect on a dependent variable while controlling for other variables. Participants are typically randomly assigned to different groups, such as a control group and one or more experimental groups, to compare the outcomes. This approach enables the establishment of cause-and-effect relationships.
- Quasi-Experimental Design
Quasi-experimental design exhibits similarities to experimental design, yet it lacks the random assignment of participants to groups. The researcher takes advantage of naturally occurring groups or pre-existing conditions to compare the effects of an independent variable on a dependent variable. While it doesn’t establish causality as strongly as experimental design, it can still provide valuable insights.
- Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data through questionnaires or interviews administered to a sample of participants. Surveys allow researchers to gather data on a wide range of variables and can be conducted in various settings, such as online surveys or face-to-face interviews. This design is particularly useful for studying attitudes, opinions, and behaviors within a population. In enterprise environments, survey research is increasingly complemented by crowdsourced idea campaigns that capture both quantitative scoring and qualitative insight.
- Correlational Design
The correlational design investigates the association between two or more variables without engaging in their manipulation. Researchers measure variables and determine the degree and direction of their association using statistical techniques such as correlation analysis. However, correlational research cannot establish causality, only the strength and direction of the relationship.
- Longitudinal Design
Longitudinal design involves collecting data from the same individuals or groups over an extended period. This design allows researchers to study changes and patterns over time, providing insights into the stability and development of variables. Longitudinal studies can be conducted retrospectively (looking back) or prospectively (following participants into the future).
- Cross-sectional Design
Cross-sectional design collects data from a specific population at a single point in time. Researchers examine different variables simultaneously and analyze the relationships among them. This design is often used to gather data quickly and assess the prevalence of certain characteristics or behaviors within a population.
- Ex post facto Design
Ex post facto design involves studying the effects of an independent variable that is beyond the researcher’s control. The researcher selects participants based on their exposure to the independent variable, collecting data retrospectively. This design is useful when random assignment or manipulation of variables is not feasible or ethical.
Learn more: What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative Research Design Methods
Quantitative research design methods refer to the specific techniques and approaches used to collect and analyze numerical data in quantitative research. Below are several commonly utilized quantitative research methods:
- Surveys: Surveys involve administering questionnaires or structured interviews to gather data from a sample of participants. Surveys can be implemented through different channels, such as conducting them in person, over the phone, via mail, or utilizing online platforms. Researchers use various question types, such as multiple-choice, Likert scales, or rating scales, to collect quantitative data on attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and demographics.
- Experiments: Experiments involve manipulating one or more independent variables and measuring their effects on dependent variables. To compare outcomes, participants are assigned randomly to various groups, including control and experimental groups. Experimental designs allow researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships by controlling for confounding factors.
- Observational Studies: Observational studies involve systematically observing and recording behavior, events, or phenomena in natural settings. Researchers can use structured or unstructured quantitative observation methods, depending on the research objectives. Quantitative data can be collected by counting the frequency of specific behaviors or by using coding systems to categorize and analyze observed data.
- Archival Research: Archival research involves analyzing existing data collected for purposes other than the current study. Researchers may use historical documents, government records, public databases, or organizational records to extract data through quantitative research. Archival research allows for large-scale data analysis and can provide insights into long-term trends and patterns.
- Secondary Data Analysis: Similar to archival research, secondary data analysis involves using existing datasets that were collected by other researchers or organizations. Researchers analyze the data to answer new research questions or test different hypotheses. Secondary data sources can include government surveys, social surveys, or market research data.
- Content Analysis: Content analysis is a method used to analyze textual or visual data to identify patterns, themes, or relationships. Researchers code and categorize the content of documents, interviews, articles, or media sources. The coded data is then quantified and statistically analyzed to draw conclusions. Content analysis can be both qualitative and quantitative, depending on the approach used.
- Psychometric Testing: Psychometric testing involves the development and administration of tests or scales to measure psychological constructs, such as intelligence, personality traits, or attitudes. Researchers use statistical techniques to analyze the test data, such as factor analysis, reliability analysis, or item response theory.
Learn more: What is Quantitative Observation?
Quantitative Research Design Process: 10 Key Steps
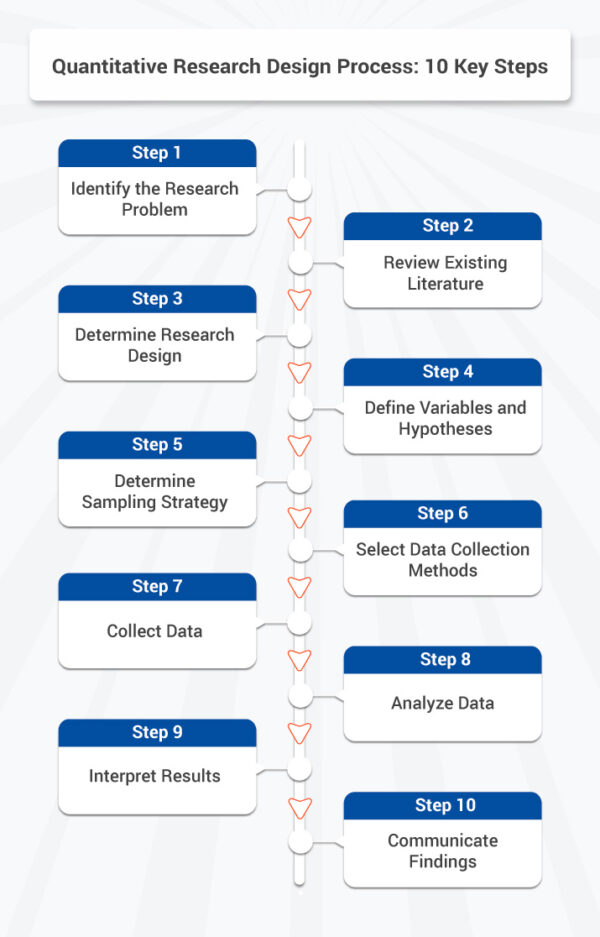
The quantitative research design process typically involves several key steps to ensure a systematic and rigorous approach to data collection and analysis. While the specific steps may vary depending on the research context, here are the key stages commonly involved in quantitative research design:
1. Identify the Research Problem
Clearly define the research problem or objective. Determine the research question(s) and objectives that you want to address through your quantitative research study. Ensure that your research question is specific, measurable, and aligned with your research goals.
2. Review Existing Literature
Conduct a comprehensive review of existing literature and research on the topic. This helps you understand the current state of knowledge, identify gaps in the literature, and inform your research design. It also helps in selecting appropriate variables and developing hypotheses.
3. Determine Research Design
Based on your research question and objectives, determine the appropriate research design. Decide whether an experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, or another design would best suit your research goals. Consider factors such as feasibility, ethical considerations, and resources available.
4. Define Variables and Hypotheses
Identify the variables that are pertinent to your research question. Clearly define each variable and its operational definitions (how they will be measured or observed). Develop hypotheses that state the expected relationships between variables based on existing theories or prior research.
5. Determine Sampling Strategy
Define the target population for your study and determine the sampling strategy. Decide on the sample size and the sampling method (e.g., random sampling, stratified sampling, convenience sampling). Ensure that your sample is representative of the population you want to generalize your findings to.
6. Select Data Collection Methods
Choose the appropriate data collection methods to gather data through quantitative research. This can include surveys, experiments, observations, or secondary data analysis. Develop or select validated instruments (e.g., questionnaires, scales) for data collection. Perform a pilot test on the instruments to ensure their reliability and validity.
7. Collect Data
Implement your data collection plan. Administer surveys, conduct experiments, observe participants, or extract data from existing sources. Ensure proper data management and organization to maintain accuracy and integrity. Consider ethical considerations and obtain necessary permissions or approvals.
8. Analyze Data
Perform data analysis using appropriate statistical techniques. Depending on your research design and data characteristics, apply descriptive statistics (e.g., means, frequencies) and inferential statistics (e.g., t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis) to analyze relationships, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions. Use statistical software for efficient and accurate analysis.
9. Interpret Results
Interpret the findings of your data analysis. Examine statistical outputs, identify significant relationships or patterns, and relate them to your research question and hypotheses. Consider the limitations of your study and address any unexpected or contradictory results.
10. Communicate Findings
Prepare a research report or manuscript that summarizes your research process, findings, and conclusions. Present your results in a clear and understandable manner using appropriate visualizations (e.g., tables, graphs). Consider disseminating your findings through academic publications, conferences, or other appropriate channels.
Top 11 Best Practices for Quantitative Research Design
To ensure the quality and validity of your quantitative research design, here are some best practices to consider:
1. Define Research Objectives Clearly: Initiate the process by providing a clear definition of your research objectives and formulating precise research questions. This clarity will guide your study design and data collection process.
2. Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review: Thoroughly review existing literature and research on your topic to understand the current state of knowledge. This helps you identify research gaps, refine your research question, and avoid duplication of efforts.
3. Use Validated Measures: When selecting or developing measurement instruments, ensure that they have established validity and reliability. Use validated scales, questionnaires, or tests that have been previously tested and proven to measure the constructs of interest accurately.
4. Pilot Testing: Before implementing your data collection, conduct pilot testing to evaluate the effectiveness of your research instruments and procedures. Pilot testing helps identify any issues or shortcomings and allows for adjustments before the main data collection.
5. Ensure Sample Representativeness: Pay attention to sample selection to ensure it is representative of the target population. Use appropriate sampling techniques and consider factors such as sample size, demographics, and relevant characteristics to enhance generalizability.
6. Minimize Nonresponse Bias: Address potential nonresponse bias by employing strategies to maximize response rates, such as providing clear instructions, using follow-up reminders, and ensuring confidentiality. Analyze nonresponse patterns to assess potential bias and consider appropriate weighting techniques if needed.
7. Maintain Data Quality: Implement robust data management practices to ensure data quality and integrity. Conduct data cleaning, perform checks for outliers and missing values, and document any data transformations or manipulations. Document your data collection procedures thoroughly to facilitate replication and transparency.
8. Employ Appropriate Statistical Analysis: Choose statistical techniques that align with your research design and data characteristics. Use appropriate descriptive and inferential statistics to analyze relationships, test hypotheses, and draw valid conclusions. Ensure proper interpretation and reporting of statistical results.
9. Address Potential Confounding Factors: Identify potential confounding variables that may influence the relationship between your independent and dependent variables. Consider controlling for these factors through study design or statistical techniques to isolate the effects of the variables of interest.
10. Consider Ethical Considerations: Adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain necessary approvals or permissions before conducting your research. Protect participants’ rights, ensure informed consent, maintain confidentiality, and handle data responsibly.
11. Document and Report: Document your research design, data collection, and analysis procedures thoroughly. This helps ensure the transparency and reproducibility of your study. Prepare a comprehensive research report or manuscript that clearly presents your methodology, findings, limitations, and implications.
Real-world application:
See how organizations apply quantitative idea scoring and evaluation models in real programs in these innovation and crowdsourcing case studies.
Read the case study: City of Atlanta – Saving Millions of Dollars Annually
Learn more: What is Quantitative Research?
Most Recent Blogs
Explore the latest innovation insights and trends with our recent blog posts.