What is PESTEL Analysis?
PESTEL analysis is defined as a business impact study that aims to understand the effects of 6 key external factors, which are politics, economics, social, technology, environmental, and legal.
Initially designed in 1967 as a business planning tool, this method was then known as PEST, with environmental and legal factors joining the list as regulations and business environmental factors became larger business influences.
The PESTEL analysis technique is a key tool for a company’s management team during enterprise strategic planning. When correctly done, this analysis technique can help anticipate future challenges and opportunities. This technique is especially helpful when formulating a strategic business plan that methodically takes both internal and external influences on the business into account.
PESTEL Analysis Framework
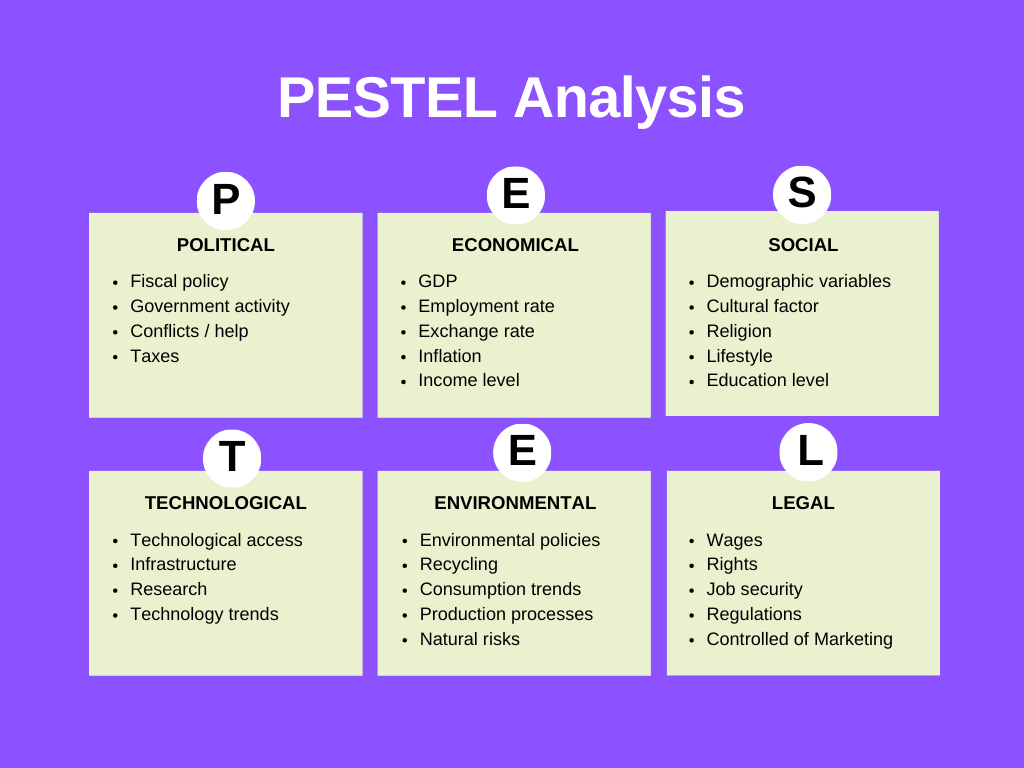
The PESTEL analysis framework is a strategic tool utilized by businesses to assess and respond to external macro-environmental factors influencing their operations. It encompasses six key dimensions:
- Political: Political factors involve governmental policies, regulations, and geopolitical stability impacting business environments. For example, shifts in tax policies or trade agreements can significantly influence market conditions and operational decisions.
- Economic: Economic factors, such as GDP trends, inflation rates, and interest rates, shape consumer behavior and business investment strategies. Industries sensitive to economic fluctuations must adapt pricing and operational strategies accordingly.
- Social: Social factors encompass cultural norms, demographics, and consumer preferences. Understanding societal shifts and behaviors helps businesses tailor their products, services, and marketing strategies to meet diverse customer needs effectively.
- Technological: Technological advancements drive innovation and operational efficiencies across industries. Businesses leveraging emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and automation gain competitive advantages in product development and service delivery.
- Environmental: Environmental factors, including sustainability practices and regulatory requirements, impact operational strategies and consumer perceptions. Adopting eco-friendly practices not only meets regulatory standards but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
- Legal: Legal factors encompass laws and regulations governing business operations, employment practices, and consumer protection. Compliance with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR) and industry-specific regulations is crucial for mitigating legal risks and maintaining trust.
PESTEL Analysis Examples and Factors
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic tool used by businesses and organizations to assess and analyze the external macro-environmental factors that can impact their operations and decision-making. Here’s an example of a PESTEL analysis for a fictional company in the renewable energy industry:
1. Political Factors:
- Government policies and regulations promoting renewable energy sources.
- Tax incentives for renewable energy projects.
- International political stability affecting trade and investments.
- Energy security policies.
2. Economic Factors:
- Economic stability and growth in the company’s target markets.
- Exchange rates and their impact on imported components.
- Funding and financing options for renewable energy projects.
- Consumer disposable income and its influence on demand for renewable energy.
3. Social Factors:
- Growing awareness and concern for environmental sustainability.
- Changing consumer preferences towards clean and green energy sources.
- Demographic trends that may affect energy consumption patterns.
- Public perception of renewable energy technologies.
4. Technological Factors:
- Rapid advancements in renewable energy technologies.
- Research and development opportunities in the sector.
- Potential for cost-effective energy storage solutions.
- Integration of smart grids and IoT in the energy sector.
5. Environmental Factors:
- Influence of climate change on the generation and utilization of energy.
- Environmental regulations and emissions standards.
- Availability of renewable energy resources (e.g., sunlight and wind).
- The company’s carbon footprint and sustainability initiatives.
6. Legal Factors:
- Environmental protection laws and regulations.
- Intellectual property protection for innovative technologies.
- Trade restrictions and tariffs affect the renewable energy supply chain.
- Health and safety regulations for employees.
By analyzing these factors, the company can better understand the opportunities and threats in its external environment. This analysis can inform strategic decision-making, risk management, and the development of a competitive advantage in the renewable energy industry. It’s important to note that the significance of these factors may vary depending on the industry, location, and specific circumstances of the company being analyzed.
Key Benefits of Applying PESTEL Analysis
Let’s dive into the enterprise benefits brought about by conclusions drawn using PESTEL analysis:
- Better threat anticipation and management
An enterprise that has planned for all the key 6 external factors highlighted in PESTEL, is in a position where they have a wider and more in-depth understanding of any threats emerging out of external factors. This helps businesses make plans for contingencies, to avoid the threat or to deal with it in the most prudent way possible.
- Increased chances for business continuity during disasters
Business disasters can be natural, political, geopolitical, or economic. Companies who are actively aware of these shifting landscapes have more capacity to absorb these challenges and ensure business continuity and perhaps even growth during such periods. A recent example would be the sudden rise in Federal Reserve interest rates to tackle inflation in 2022 where many companies who had taken business loans based on floating interest rates (especially to stay afloat during COVID lockdowns) now found themselves paying 3-4 times in interest amount within just a year. This rate hike however was much discussed and anticipated and businesses that repaid or maintained sufficient cash margins accounting for anticipated rate hikes, have a much better chance of ensuring the financial stability of the firm.
- Competitive tech-stack
PESTEL analysis included technology as a key factor that keeps the management team aware of the level of maturity of the company’s tech stack vis-a-vis competition and what is available in the market. Consider this against a CTO trying to convince the board of tech investment without the right macro context.
A company’s management team may be composed of more experienced but demographically older members. A PESTEL analysis enables the management to keep themselves tech-savvy and aware of the latest technology and its benefits to enterprise growth. These tech investments may span across the organization chart such as improving human resource management efficiency, better employee surveying for feedback, better quality customer data collection, better enterprise data management, planning product and service improvements/ innovations, etc.
- New opportunities identification
External factors are not just threats and compliance, they can and often are filled with business opportunities to be explored. A change in the landscape can be an opportunity for the entity who is already prepared to take advantage. For example, while GDPR regulations led to a reduced volume of business inquiries from websites, they also improved the quality of these leads who were now more sales-ready. This was because visitors who gave their consent to be contacted by sales or cookie tracking for better product recommendations or receive newsletters on the product etc, were clearly more ready to make a purchase. Companies who invested more, not less, on the website quality and better quality online resources post-GDPR, were able to leverage improved lead quality and therefore better sales opportunities in the European market.
- Focused strategic planning
A company’s strategic plan is the overarching business operations and growth plans that drive every other objective. PESTEL analysis is a primary tool for an enterprise’s management team seeking to create a realistic, achievable, and competitive strategic plan that takes into account all external factors. While several other methods also take into account external opportunities and threats, it is only PESTEL that clearly breaks down for the management team the 6 factors that allow for a broad, yet in-depth analysis of external business influences.
Learn more: What is a MoSCoW Analysis?
PESTEL Analysis in Strategic Management
A PESTEL analysis is a valuable tool in the field of strategic management. It is used to assess and analyze the macro-environmental factors that can affect an organization’s strategic decisions and long-term planning. Strategic management involves setting the direction and goals of an organization, and the PESTEL analysis helps in understanding the external factors that can impact this process. Here’s how a PESTEL analysis is relevant in the context of strategic management:
- Identifying Opportunities and Threats: By examining Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors, organizations can identify both opportunities and threats in their external environment. This information is critical for crafting strategies that leverage opportunities and mitigate threats.
- Scenario Planning: PESTEL analysis aids in scenario planning, where organizations can consider various future scenarios based on different combinations of these external factors. By doing so, they can develop strategies that are robust and adaptable to various potential futures.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Understanding the external environment through a PESTEL analysis is essential for making informed strategic decisions. It helps in shaping business strategies that align with the current and future landscape.
- Risk Management: Organizations can use PESTEL analysis to assess risks associated with changes in the external environment. For example, changes in government regulations, economic downturns, or technological disruptions can pose risks to the organization, and a PESTEL analysis can help identify and manage these risks.
- Innovation and Adaptation: The Technological and Environmental factors in a PESTEL analysis can guide innovation and adaptation efforts. It can help organizations stay ahead of technological advancements and align their strategies with environmental sustainability.
- Global Expansion: For organizations considering international expansion, a PESTEL analysis is crucial for understanding the unique factors and challenges in each target market. It helps in tailoring strategies to fit specific international environments.
- Regulatory Compliance: The Legal factors in the analysis help in identifying legal requirements and compliance issues that can affect the organization’s strategies. This is particularly relevant in industries with high regulatory oversight, such as healthcare or finance.
- Stakeholder Communication: Understanding the Social and Environmental factors can aid in effective communication with stakeholders. It enables organizations to demonstrate their commitment to societal and environmental concerns, which can be a key part of their strategic positioning.
PESTEL analysis is a fundamental component of strategic management. It provides a comprehensive view of the external environment, allowing organizations to make informed decisions, plan for the future, and adapt to changes in their operating environment. It helps in crafting strategies that are not only relevant but also resilient in a dynamic and complex world.
Top 5 Best Practices for PESTEL Analysis
1. Get the latest data
Every contributing factor in PESTEL analysis requires the management team to have access to facts and figures. For example, for economic factors, one needs inflation data, central bank interest rate charts, GDP trends, etc. Often a small change in this core data collection can lead to significant changes in perception and reality.
For example, if the inflation rate threshold is 2% for the US Federal Reserve, and it changes to 3% in two or three consecutive quarters, it may trigger the Fed to hike rates to bring inflation down. However, if the company only had access to 1-year-old data, then this event would not have been factored into the enterprise plan.
It is therefore critical to ensure that the latest released data across all PESTEL factors are accessed and taken into account for planning and analysis stages.
2. Prioritize facts over forecasts
Since PESTEL is used for future enterprise strategic planning, by default there is some level of forecasting involved. However, the key is to ensure that facts are not stretched to fit a desirable narrative, especially when evaluating political and economic factors which are quite dynamic and hard to predict by nature.
3. Get a second opinion
Whether the management team has hired a consultant, or external agency or is conducting the analysis internally, it is always a best practice to get a second opinion before framing final conclusions from the report. This is because, while PESTEL relies on data, many factors have qualitative aspects that can always use a second perspective.
4. Incorporate results in all levels enterprise of enterprise planning
The conclusions of the PESTEL analysis are usually directed toward strategic planning, and management needs to ensure that the conclusions are trickled down to all levels of company planning. For instance, decisions stemming from online legal and compliance requirements need to be streamed down to the execution teams where marketing, web development, and legal teams collaborate for accurate implementation.
5. Use visual software for presentation
Visual tools such as FrescoPad have built-in templates to brainstorm and visually present PESTEL analysis results. The technique of PESTEL analysis itself is a collaborative effort across department leaders in the management team spread across geographic locations and requires in-depth qualitative and quantitative discussions. This software helps to make the analysis process interactive and makes it easier to save and share conclusions in a visual format.
Learn more: What is SWOT Analysis Framework?